Abstract
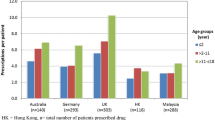
Background Prescribing medicines in an unlicensed and off-label manner for children is a widespread practice around the world. Objectives To determine the extent and predictors of off-label respiratory drug prescriptions for children in the outpatient clinics of a hospital in Malaysia. Setting Outpatient clinics at the Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre, a tertiary teaching hospital in Malaysia. Methods The pharmacy-based computer system and medical records of the patients were utilized to collect data from 220 pediatric patients who were prescribed at least one respiratory drug from July 2011 to December 2011. Main outcome measure Characteristics of the off-label respiratory drug prescriptions were measured. Results A total of 134 children (60.9 %) received at least one respiratory drug prescribed in an off-label manner. The most common reasons for the off-label prescribing of drugs were off-label use by indication (31.5 %), followed by higher than the recommended dose (24.9 %) and lower than the recommended frequency (17.1 %). Diphenhydramine was the most common respiratory drug prescribed off-label. The number of medications prescribed was the only significant predictor of off-label prescription of respiratory drugs. Pediatric patients receiving 4–6 medications were 7.8 times more likely to receive at least one off-label respiratory drug compared to pediatric patients that received 1–3 medications (OR 7.8, 95 % CI 1.74–37.44). Conclusion There was substantial prescribing of respiratory drugs for children in an off-label manner at the outpatient clinics at the Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre. This highlights the need for more research to be carried out on respiratory drugs in the pediatric population.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Turner S, Nunn A, Choonara I. Unlicensed drug use in children in the UK. Paediatr Perinat Drug Ther. 1997;1:52–5.
Drug Control Authority. Terms of Reference. National Pharmaceutical Control Bureau: Ministry of Health Malaysia. 1984.
National Pharmaceutical Control Bureau, (NPCB) Ministry of Health Malaysia. [cited 1 Nov 2012]; Available from http://portal.bpfk.gov.my/index.cfm?&menuid=47.
Mason J, Pirmohamed M, Nunn T. Off-label and unlicensed medicine use and adverse drug reactions in children: a narrative review of the literature. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2012;68:21–8.
Rocchi F, Paolucci P, Ceci A, Rossi P. The European paediatric legislation: benefits and perspectives. Ital J Pediatr. 2010;36:56.
European Commission. EU pharmaceutical legislation 2006. [cited 20 Oct 2014]; Available from http://ec.europa.eu/health/files/eudralex/vol-1/reg_2006_1901/reg_2006_1901_en.pdf.
Kemper EM, Merkus M, Wierenga PC, Van Rijn PC, Van der Werff D, Lie-A-Huen L, Offringa M. Towards evidence-based pharmacotherapy in children. Paediatr Anaesth. 2011;21:183–9.
Silva D, Ansotegui I, Morais-Almeida M. Off-label prescribing for allergic diseases in children. World Allergy Organ J. 2014;7:4.
Baiardi P, Ceci A, Felisi M, Cantarutti L, Girotto S, Sturkenboom M, Baraldi E. In-label and off-label use of respiratory drugs in the Italian paediatric population. Acta Paediatr. 2010;99:544–9.
Smyth AR, Barbato A, Beydon N, Bisgaard H, de Boeck K, Brand P, et al. Respiratory medicines for children: current evidence, unlicensed use and research priorities. Eur Respir J. 2010;35:247–65.
‘t Jong GW, Eland IA, Sturkenboom MC, van den Anker JN, Strickerf BH. Unlicensed and off-label prescription of respiratory drugs to children. Eur Respir J. 2004;23:310–3.
Drug Formulary, 5th ed. Pharmacy Department, Pusat Perubatan Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia; 2010.
Master Index of Medical Specialties (MIMS) Malaysia. [cited 12 Nov 2012]; Available from http://www.mims.com.
ICH Expert Working Group. International Conference on Harmonization of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use: ICH Harmonized Tripartite Guidelines, Clinical Investigation of Medicinal Products in the Pediatric Population (E11). 2000. [cited 20 Oct 2014]; Available from http://www.ich.org.
Chalumeau M, Tréluyer JM, Salanave B, Assathiany R, Chéron G, Crocheton N, et al. Off label and unlicensed drug use among French office based paediatricians. Arch Dis Child. 2000;83:502–5.
Conroy S, Choonara I, Impicciatore P, Mohn A, Arnell H, Rane A, et al. Survey of unlicensed and off-label drug use in paediatric wards in European countries. BMJ. 2000;320:79–82.
Santos DB, Clavenna A, Bonati M, Coelho HLL. Off-label and unlicensed drug utilization in hospitalized children in Fortazela, Brazil. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2008;64:1111–8.
Horen B, Montastruc JL, Lapeyre-Mestre M. Adverse drug reactions and off-label drug use in paediatric outpatients. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2002;54:665–70.
Impicciatore P, Mohn A, Chiarelli F, Pandolfini C, Bonati M. Adverse drug reactions to off-label drugs on a paediatric ward: an Italian prospective pilot study. Paediatr Perinat Drug Ther. 2002;5:19–24.
Turner S, Nunn AJ, Fielding K, Choonara I. Adverse drug reactions to unlicensed and off-label drugs on paediatric wards: a prospective study. Acta Paediatr. 1999;88:965–8.
Bazzano AT, Mangione-Smith R, Schonlau M, Suttorp MJ, Brook RH. Off-label prescribing to children in the United States outpatient setting. Acad Pediatr. 2009;9:81–8.
Giacoia G, Birenbaum D, Sachs H, Mattison D. The newborn drug development initiative. Pediatrics. 2006;117:S1–8.
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to the pharmacy staff at the UKMMC for access to the pharmacy’s computerized dispensing database. The authors would also like to thank the hospital medical records staff for their help in retrieving the medical records.
Funding
No funding was received for this research study.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohamad, N.F., Mhd Ali, A. & Mohamed Shah, N. Respiratory drugs prescribed off-label among children in the outpatient clinics of a hospital in Malaysia. Int J Clin Pharm 37, 127–132 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11096-014-0049-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11096-014-0049-0