Abstract
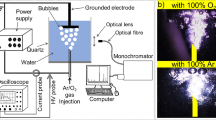
In this study, an experimental investigation of the removal of NO from an atmospheric air stream has been carried out with a non-thermal plasma dielectric barrier discharge reactor filled with different catalytic materials. TiO\(_2\), CuO–MnO\(_2\)–TiO\(_2\), CuO–MnO\(_2\)–Al\(_2\)O\(_3\) catalysts were used to study the synergy between the plasma and the catalysts. The NO\(_\mathrm{{x}}\) removal efficiency and by-products formation were studied as a function of energy density, pulse rise time and width using a plasma catalytic configuration. It was observed that the shorter pulses are more efficient for NO\(_\mathrm{{x}}\) removal but at the expense of higher by-products formation such as N\(_2\)O and O\(_3\). A comparison has been made between an in-plasma catalytic configuration and a post-plasma catalytic configuration. Among all the three catalysts that were studied, CuO–MnO\(_2\)–TiO\(_2\) catalyst showed the best performance with respect to the removal efficiency as well as the by-products formation in both the in-plasma and the post-plasma catalytic configuration. In general, the post-plasma configuration showed better results with respect to low by-products formation.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
European environment agency. http://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/indicators/transport-emissions-of-air-pollutants-8/transport-emissions-of-air-pollutants-9. Accessed 12 April 2014
European automobile manufacturers association. http://www.acea.be/industry-topics/tag/category/euro-standards. Accessed 12 April 2014
Hammer T, Kappes T, Baldauf M (2004) Plasma catalytic hybrid processes: gas discharge initiation and plasma activation of catalytic processes. Catal Today 89(1):5–14
Oda T, Kato T, Takahashi T, Shimizu K (1997) Nitric oxide decomposition in air by using non-thermal plasma processing-with additives and catalyst. J Electrostat 42(1):151–157
Chang JS (2001) Recent development of plasma pollution control technology: a critical review. Sci Technol Adv Mater 2(3):571–576
Penetrante B, Hsiao M, Merritt B, Vogtlin G, Wan C (1997) Plasma-assisted heterogeneous catalysis for \(\text{NO}_{{\rm x}}\) reduction in lean-burn engine exhaust. technical report, DTIC Document
Penetrante BM, Brusasco RM, Merritt BT, Vogtlin GE (1999) Environmental applications of low-temperature plasmas. Pure Appl Chem 71(10):1829–1835
Sun M, Ravi V (2010) Role of oxygen in the plasma catalytic removal of \(\text{NO}_{{\rm x}}\). VIVECHAN IJR 1(2):1–9
Beckers FJCM, Hoeben WFLM, Pemen aJM, van Heesch EJM (2013) Low-level \(\text{NO}_{{\rm x}}\) removal in ambient air by pulsed corona technology. J Phys D Appl Phys 46:295201
Neyts E, Bogaerts A (2014) Understanding plasma catalysis through modelling and simulation a review. J Phys D Appl Phys 47(22):224010
Yamamoto T, Okubo M, Hayakawa K, Kitaura K (2001) Towards ideal \(\text{NO}_{{\rm x}}\) control technology using a plasma-chemical hybrid process. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 37(5):1492–1498
Conrads H, Schmidt M (2000) Plasma generation and plasma sources. Plasma Sour Sci Technol 9(4):441–454
Tendero C, Tixier C, Tristant P, Desmaison J, Leprince P (2006) Atmospheric pressure plasmas: a review. Spectrochim Acta Part B Atomic Spectrosc 61(1):2–30
Samukawa S, Hori M, Rauf S, Tachibana K, Bruggeman P, Kroesen G, Whitehead JC, Murphy AB, Gutsol AF, Starikovskaia S, Kortshagen U, Boeuf J-P, Sommerer TJ, Kushner MJ, Czarnetzki U, Mason N (2012) The 2012 plasma roadmap. J Phys D Appl Phys 45(25):253001
Whitehead JC (2010) Plasma catalysis: a solution for environmental problems. Pure Appl Chem 82(6):1329–1336
Chen HL, Lee HM, Chen SH, Chang MB, Yu SJ, Li SN (2009) Removal of volatile organic compounds by single-stage and two-stage plasma catalysis systems: a review of the performance enhancement mechanisms, current status, and suitable applications. Environ Sci Technol 43(7):2216–2227
Jolibois J, Takashima K, Mizuno A (2012) Application of a non-thermal surface plasma discharge in wet condition for gas exhaust treatment: \(\text{NO}_{{\rm x}}\) removal. J Electrostat 70:300–308
Yamamoto T, Member S, Yang C-L, Beltran MR, Kravets Z (2000) Plasma-assisted chemical process for \(\text{NO}_{{\rm x}}\) control. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 36(3):923–927
Miessner H, Francke K-P, Rudolph R (2002) Plasma-enhanced HC-SCR of \(\text{NO}_{{\rm x}}\) in the presence of excess oxygen. Appl Catal B Environ 36:53–62
McAdams R, Beech P, Shawcross JT (2008) Low temperature plasma assisted catalytic reduction of \(\text{NO}_{{\rm x}}\) in simulated marine diesel exhaust. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 28:159–171
Tran D, Aardahl C, Rappe K, Park P, Boyer C (2004) Reduction of \(\text{NO}_{{\rm x}}\) by plasma-facilitated catalysis over In-doped \(\gamma\)-alumina. Appl Catal B Environ 48:155–164
Kim HH, Takashima K, Katsura S, Mizuno A (2001) Low-temperature \(\text{NO}_{{\rm x}}\) reduction processes using combined systems of pulsed corona discharge and catalysts. J Phys D Appl Phys 34(4):604
Bröer S, Hammer T (2000) Selective catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides by combining a non-thermal plasma and a \(\text{V}_2\text{O}_5\)-\(\text{WO}_3/\text{TiO}_2\) catalyst. Appl Catal B Environ 28(2):101–111
Oda T, Kato T, Takahashi T, Shimizu K (1998) Nitric oxide decomposition in air by using nonthermal plasma processing with additives and catalyst. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 34(2):268–272
Puchkarev V, Gundersen M (1997) Energy efficient plasma processing of gaseous emission using a short pulse discharge. Appl Phys Lett 71(23):3364–3366
Gentile AC, Kushner MJ (1995) Reaction chemistry and optimization of plasma remediation of \(\text{N}_{{\rm x}}\text{O}_{{\rm y}}\) from gas streams. J Appl Phys 78(3):2074–2085
Oda T (2003) Non-thermal plasma processing for environmental proection: decomposition of dilute VOCs in air. J Electrostat 57(3–4):293–311
Li J, Ke R, Li W, Hao J (2008) Mechanism of selective catalytic reduction of NO over \(\text{Ag}/\text{Al}_2\text{O}_3\) with the aid of non-thermal plasma. Catal Today 139:49–58
Nasonova A, Pham HC, Kim D-J, Kim K-S (2010) NO and \(\text{SO}_2\) removal in non-thermal plasma reactor packed with glass beads-\(\text{TiO}_2\) thin film coated by PCVD process. Chem Eng J 156:557–561
Oda T, Kato T, Takahashi T, Shimizu K (1997) Nitric oxide decomposition in air by using non-thermal plasma processing-with additives and catalyst. J Electrostat 42:151–157
Jõgi I, Erme K, Haljaste A, Laan M (2013) Oxidation of nitrogen oxide in hybrid plasma-catalytic reactors based on DBD and \(\text{Fe}_2\text{O}_3\). Eur Phys J Appl Phys 61(02):24305
Futamura S, Zhang A, Einaga H, Kabashima H (2002) Involvement of catalyst materials in nonthermal plasma chemical processing of hazardous air pollutants. Catal Today 72(3):259–265
Fan X, Zhu T, Wang M, Li X (2009) Removal of low-concentration btx in air using a combined plasma catalysis system. Chemosphere 75(10):1301–1306
Chang C-L, Lin T-S (2005) Elimination of carbon monoxide in the gas streams by dielectric barrier discharge systems with mn catalyst. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 25(4):387–401
Jarrige J, Vervisch P (2009) Plasma-enhanced catalysis of propane and isopropyl alcohol at ambient temperature on a \(\text{MnO}_2\)-based catalyst. Appl Catal B Environ 90(1):74–82
Van Durme J, Dewulf J, Sysmans W, Leys C, Van Langenhove H (2007) Efficient toluene abatement in indoor air by a plasma catalytic hybrid system. Appl Catal B Environ 74(1–2):161–169
Subrahmanyam C (2009) Catalytic non-thermal plasma reactor for total oxidation of volatile organic compounds. Indian J Chem 48(August):1062–1068
Morales MR, Barbero BP, Cadús LE (2008) Evaluation and characterization of mn–cu mixed oxide catalysts for ethanol total oxidation: influence of copper content. Fuel 87(7):1177–1186
Morales MR, Barbero BP, Lopez T, Moreno A, Cadús LE (2009) Evaluation and characterization of mn–cu mixed oxide catalysts supported on TiO2 and ZrO2 for ethanol total oxidation. Fuel 88(11):2122–2129
Vitello P, Penetrante B, Bardsley J (1994) Simulation of negative-streamer dynamics in nitrogen. Phys Rev E 49(6):5574
PekárekP S, UsamaP K (2011) Ozone generation by surface dielectric barrier discharge with \(\text{TiO}_2\) photocatalyst. In: 30th ICPIG. pp 10–13
Blin-Simiand N, Tardiveau P, Risacher A, Jorand F, Pasquiers S (2005) Removal of 2-heptanone by dielectric barrier discharges—the effect of a catalyst support. Plasma Process Polym 2(3):256–262
Ogata A, Saito K, Kim H-H, Sugasawa M, Aritani H, Einaga H (2010) Performance of an ozone decomposition catalyst in hybrid plasma reactors for volatile organic compound removal. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 30(1):33–42
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chirumamilla, V.R., Hoeben, W.F.L.M., Beckers, F.J.C.M. et al. Experimental Investigation on the Effect of a Microsecond Pulse and a Nanosecond Pulse on NO Removal Using a Pulsed DBD with Catalytic Materials. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 36, 487–510 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-015-9670-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-015-9670-5