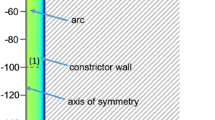
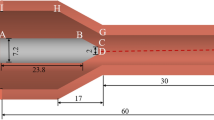
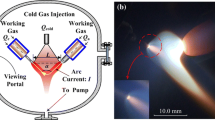
Abstract
Accurate numerical modeling is prerequisite of predicting plasma behavior and understanding the complex physical and chemical processes in a plasma system. The evolution of nonequilibrium modeling of arcjet to its current state of development is traced, and some uncertainties in the way of further progress are discussed. It is demonstrated that the accuracy of two-temperature plasma transport coefficients can be improved by adopting more reasonable interatomic potentials. A comparison of the chemical kinetic rate coefficients for the same kinetic process shows some discrepancies, which further indicates that there exist some uncertainties on the inelastic cross sections obtained from experimental measurement or theoretic calculation. Application and extension of three-level atomic model of argon in nonequilibrium modeling are briefly reviewed, and the criteria required in the choice of chemical kinetic processes are discussed. The elementary processes involved in high velocity plasma flow can be investigated by collisional radiative model (CR model). The method of applying CR model on the analysis of nonequilibrium plasma processes in arcjet is presented as an example in some detail.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martinez-Sanchez M, Miller SA (1996) Arcjet modeling: status and prospects. J Propuls Power 12(6):1035–1043
Megli TW, Krier H, Burton RL, Mertogul A (1996) Two-temperature plasma modeling of nitrogen/hydrogen arcjets. J Propuls Power 12(6):1062–1069
Miller SA, Martinez-Sanchez M (1996) Two-fluid nonequilibrium simulation of hydrogen arcjet thrusters. J Propuls Power 12(1):112–119
Trelles JP, Pfender E, Heberlein JVR (2007) Modelling of the arc reattachment process in plasma torches. J Phys D Appl Phys 40(18):5635–5648
Benilov M (2008) Understanding and modelling plasma–electrode interaction in high-pressure arc discharges: a review. J Phys D Appl Phys 41(14):144001
Heberlein J, Mentel J, Pfender E (2010) The anode region of electric arcs: a survey. J Phys D Appl Phys 43(2):023001
Rat V, Murphy AB, Aubreton J, Elchinger MF, Fauchais P (2008) Treatment of non-equilibrium phenomena in thermal plasma flows. J Phys D Appl Phys 41(18):183001
Butler GW, Kull AE, King DQ (1994) Single fluid simulations of low power hydrogen arcjets. 30th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, Indianapolis, IN
Wang HX, Chen X, Pan WX, Murphy AB, Geng JY, Jia SX (2010) Modelling study to compare the flow and heat transfer characteristics of low-power hydrogen, nitrogen and argon arc-heated thrusters. Plasma Sci Technol 12(6):692–701
Wang HX, Geng JY, Chen X, Pan WX, Murphy AB (2010) Modeling study on the flow, heat transfer and energy conversion characteristics of low-power arc-heated hydrogen/nitrogen thrusters. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 30(6):707–731
Biberman L, Vorob’ev VS, Yakubov I (1979) Low-temperature plasmas with nonequilibrium ionization. Phys Usp 22(6):411–432
Devoto RS (1967) Simplified expressions for the transport properties of ionized monatomic gases. Phys Fluids 10(10):2105–2112
Rat V, André P, Aubreton J, Elchinger MF, Fauchais P, Lefort A (2001) Transport properties in a two-temperature plasma: theory and application. Phys Rev E 64(2):026409
Zhang XN, Li HP, Murphy AB, Xia WD (2013) A numerical model of non-equilibrium thermal plasmas. I. Transport properties. Phys Plasmas 20(3):033508
Hirschfelder JO, Curtiss CF, Bird RB (1954) Molecular theory of gases and liquids. Wiley, New York
O’Hara H, Smith FJ (1970) The efficient calculation of the transport properties of a dilute gas to a prescribed accuracy. J Comput Phys 5(2):328–344
Smith FJ, Munn RJ (1964) Automatic calculation of the transport collision integrals with tables for the Morse potential. J Chem Phys 41(11):3560–3568
Barker JA, Fock W, Smith F (1964) Calculation of gas transport properties and the interaction of argon atoms. Phys Fluids 7(6):897–903
Murphy AB, Arundell CJ (1994) Transport coefficients of argon, nitrogen, oxygen, argon–nitrogen, and argon–oxygen plasmas. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 14(4):451–490
Aziz RA, Slaman MJ (1990) The repulsive wall of the Ar–Ar interatomic potential reexamined. J Chem Phys 92(2):1030–1035
Aziz RA, Slaman MJ (1986) The argon and krypton interatomic potentials revisited. Mol Phys 58(4):679–697
Aziz RA, Slaman MJ (1986) On the Xe–Xe potential energy curve and related properties. Mol Phys 57(4):825–840
Hepburn J, Scoles G, Penco R (1975) A simple but reliable method for the prediction of intermolecular potentials. Chem Phys Lett 36(4):451–456
Maitland GC, Rigby M, Smith EB (1981) Intermolecular forces: their origin and determination. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Tang KT, Norbeck JM, Certain PR (1976) Upper and lower bounds of two- and three-body dipole, quadrupole, and octupole van der Waals coefficients for hydrogen, noble gas, and alkali atom interactions. J Chem Phys 64(7):3063–3074
Aziz RA, Chen H (1977) An accurate intermolecular potential for argon. J Chem Phys 67(12):5719–5726
Kestin J, Knierim K, Mason EA, Najafi B, Ro ST, Waldman M (1984) Equilibrium and transport properties of the noble gases and their mixtures at low density. J Phys Chem Ref Data 13(1):229–303
Nain VPS, Aziz RA, Jain PC, Saxena SC (1976) Interatomic potentials and transport properties for neon, argon, and krypton. J Chem Phys 65(8):3242–3249
Dawe RA, Smith EB (1970) Viscosities of the inert gases at high temperatures. J Chem Phys 52(2):693–703
Maitland GC, Smith EB (1972) Critical reassessment of viscosities of 11 common gases. J Chem Eng Data 17(2):150–156
Saxena VK, Saxena SC (1969) Thermal conductivity of krypton and xenon in the temperature range 350–1500 K. J Chem Phys 51(8):3361–3368
Murphy AB (2000) Transport coefficients of hydrogen and argon–hydrogen plasmas. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 20(3):279–297
Murphy AB, Tam E (2014) Thermodynamic properties and transport coefficients of arc lamp plasmas: argon, krypton and xenon. J Phys D Appl Phys 47(29):295202
Devoto RS (1965) The transport properties of a partially ionized monatomic gas. In Department of Aeronauctics and Astronautics. Stanford University: Ann Arbor, Michigan
Aubreton J, Bonnefoi C, Mexmain J (1986) Calcul de propriétés thermodynamiques et des coefficients de transport dans un plasma Ar–O2 en non-équilibre thermodynamique et à la pression atmosphérique. Revue de Physique Appliquée 21(6):365–376
Rat V, André P, Aubreton J, Elchinger MF, Fauchais P, Lefort A (2002) Two-temperature transport coefficients in argon–hydrogen plasmas–I: elastic processes and collision integrals. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 22(4):453–474
Rat V, André P, Aubreton J, Elchinger MF, Fauchais P, Lefort A (2002) Two-temperature transport coefficients in argon–hydrogen plasmas–II: inelastic processes and influence of composition. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 22(4):475–493
Colombo V, Ghedini E, Sanibondi P (2009) Two-temperature thermodynamic and transport properties of argon–hydrogen and nitrogen–hydrogen plasmas. J Phys D Appl Phys 42(5):055213
Wang HX, Sun WP, Sun SR, Murphy AB, Ju YG (2014) Two-temperature chemical-nonequilibrium modelling of a high-velocity argon plasma flow in a low-power arcjet thruster. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 34(3):559–577
Zhu XM, Pu YK (2010) A simple collisional–radiative model for low-temperature argon discharges with pressure ranging from 1 Pa to atmospheric pressure: kinetics of Paschen 1 s and 2p levels. J Phys D Appl Phys 43(1):015204
Baeva M, Bösel A, Ehlbeck J, Loffhagen D (2012) Modeling of microwave-induced plasma in argon at atmospheric pressure. Phys Rev E 85(5):056404
Gudmundsson JT, Thorsteinsson EG (2007) Oxygen discharges diluted with argon: dissociation processes. Plasma Sour Sci Technol 16:399–412
Shon JW, Kushner MJ (1994) Excitation mechanisms and gain modeling of the high-pressure atomic Ar laser in He/Ar mixtures. J Appl Phys 75(4):1883–1890
Khakoo MA et al (2004) Electron impact excitation of the argon 3p5 4 s configuration: differential cross-sections and cross-section ratios. J Phys B: At Mol Opt Phys 37(1):247
Tachibana K (1986) Excitation of the levels of argon by low-energy electrons. Phys Rev A 34(2):1007–1015
De Heer FJ, Jansen RHJ, Van der Kaay W (1979) Total cross sections for electron scattering by Ne, Ar, Kr and Xe. J Phys B: At Mol Phys 12(6):979
Vriens L, Smeets AHM (1980) Cross-section and rate formulas for electron-impact ionization, excitation, deexcitation, and total depopulation of excited atoms. Phys Rev A 22(3):940–951
Kieffer CG, Dunn GH (1966) Electron impact ionization cross-section data for atoms, atomic ions, and diatomic molecules: I. Experimental data. Rev Modern Phys 38(1):1–35
Braun CG, Kunc JA (1987) Collisional-radiative coefficients from a three-level atomic model in nonequilibrium argon plasmas. Phys Fluids 30(2):499–509
Braun CG, Kunc JA (1988) An analytical solution of a collisional-radiative model for nonequilibrium argon plasmas. Phys Fluids 31(3):671–681
Chang CH, Ramshaw JD (1994) Numerical simulation of nonequilibrium effects in an argon plasma jet. Phys Plasmas 1(11):3698–3708
Baeva M, Uhrlandt D (2013) Plasma chemistry in the free-burning Ar arc. J Phys D Appl Phys 46(32):325202
Baeva M, Kozakov R, Gorchakov S, Uhrlandt D (2012) Two-temperature chemically non-equilibrium modelling of transferred arcs. Plasma Sour Sci Technol 21(5):055027
Wei FZ, Wang HX, Murphy AB, Sun WP, Liu Y (2013) Numerical modelling of the nonequilibrium expansion process of argon plasma flow through a nozzle. J Phys D Appl Phys 46(50):505205
Van Sijde BD, Van der Mullen JJAM, Schram DC (1984) Collisional radiative models in plasmas. Beiträge aus der Plasmaphysik 24(5):447–473
Bultel A, Annaloro J (2013) Elaboration of collisional–radiative models for flows related to planetary entries into the Earth and Mars atmospheres. Plasma Sour Sci Technol 22(2):025008
Bultel A, van Ootegem B, Bourdon A, Vervisch P (2002) Influence of Ar2 + in an argon collisional-radiative model. Phys Rev E 65(4):046406
Vlcek J (1989) A collisional-radiative model applicable to argon discharges over a wide range of conditions. I: formulation and basic data. J Phys D Appl Phys 22:623–631
Bogaerts A, Gijbels R, Vlcek J (1998) Collisional-radiative model for an argon glow discharge. J Appl Phys 84(1):121–136
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11275021, 11072020, 50836007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, HX., Sun, SR. & Sun, WP. Status and Prospects on Nonequilibrium Modeling of High Velocity Plasma Flow in an Arcjet Thruster. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 35, 543–564 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-015-9610-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-015-9610-4