Abstract
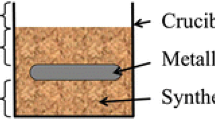
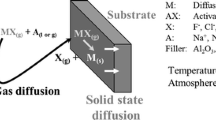
Corrosion under deposit is one of the main mechanisms responsible of degradation and failure observed on heat exchangers in waste-to-energy plants. In this study, two heat exchanger materials, a low alloy steel (16Mo3) and a nickel-based alloy (Inconel 625) were isothermally exposed in air to two different synthetic ashes with low and high chloride contents at temperatures between 450 and 650 °C in a muffle furnace. After the test, thickness and mass losses were evaluated on two separate samples and metallographic cross sections of the specimens were characterized with a SEM/EDS analyzer. Results were in good agreement and have shown that the corrosion rates of both materials increase with chloride content especially for the ferritic steel. Additionally, it has been observed that corrosion rates increase above the temperature of solidus of salt mixtures, and thus, with the apparition of molten phase.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Kawahara, Corrosion Science 44, 2002 (223).
D. Bramhoff, H. J. Grabke and H. P. Schmidt, Effects of Hydrogen Chloride and of Nitrogen in the Oxidation of Fe-20Cr, (Springer, Netherlands, 1989), p. 335.
H. J. Grabke, Materials at High Temperatures 11, 1993 (23).
H. J. Grabke, E. Reese and M. Spiegel, Corrosion Science 37, (7), 1995 (1023).
M. Spiegel and H. J. Grabke, Materials and Corrosion (Germany) 47, (4), 1996 (179–189).
N. Otsuka, Corrosion Science 44, (2), 2002 (265–283).
K. Weulersse, G. Moulin, P. Billard and G. Pierotti, Materials Science Forum 461, 2004 (973).
A. Ruh and M. Spiegel, Materials and Corrosion 57, (3), 2006 (237–243).
P. Viklund, High temperature corrosion during waste incineration. Characterization, causes and prevention of chlorine-induced corrosion, Licentiate Thesis (Kungliga Tekniska Högskolan, Stockholm, 2011).
J. Reichelt, G. Pfrang-Stotz, B. Bergfeldt, H. Seifert and P. Knapp, Waste Management 33, (1), 2013 (43–51).
M. Takemura, M. J. McNallan, Environmental effects on molten chloride accelerated corrosion in waste incineration systems corrosion/95, Paper, (568), 1995.
T. Ishitsuka and K. Nose, Corrosion Science 44, (2), 2002 (247–263).
R. A. Rapp, K. S. Goto. The hot corrosion of metals by molten salts. In Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on Molten Salts (Vol. 81, No. 10, p. 159). Physical Electrochemistry Division, Electrochemical Society (1981).
P. Steinmetz and C. Rapin, Materials Science Forum 251, 1997 (505–518).
K. Persson, M. Broström, J. Carlsson, A. Nordin and R. Backman, Fuel Processing Technology 88, (11), 2007 (1178–1182).
A. Phongphiphat, C. Ryu, Y. B. Yang, K. N. Finney, A. Leyland, V. N. Sharifi and J. Swithenbank, Corrosion Science 52, (12), 2010 (3861–3874).
P. Viklund, A. Hjörnhede, P. Henderson, A. Stålenheim and R. Pettersson, Fuel Processing Technology 105, 2013 (106–112).
B. A. Baker, G. D. Smith, L. E. Shoemaker, Performance of Commercial Alloys in Simulated Waste Incineration Environments. CORROSION/2001, Paper, (183), 2001.
H. J. Grabke, M. Spiegel and A. Zahs, Materials Research 7, (1), 2004 (89–95).
Y. Kawahara, M. Kira, M. Ike, Effect of Gas Temperature and Its Fluctuation on the High Temperature Corrosion of WTE Boiler Materials. CORROSION 2001, 2001.
F. Lebel, C. Rapin, J. F. Mareche, R. Podor, X. Chaucherie, P. Y. Guernion and J. M. Brossard, Materials Science Forum 595, 2008 (271–280).
J. M. Brossard, I. Diop, X. Chaucherie, F. Nicol, C. Rapin and M. Vilasi, Materials and Corrosion 62, (6), 2011 (543–548).
J. Lehmusto, P. Yrjas, B. J. Skrifvars and M. Hupa, Fuel Processing Technology 104, 2012 (253–264).
J. Pettersson, N. Folkeson, L. G. Johansson and J. E. Svensson, Oxidation of Metals 76, (1–2), 2011 (93–109).
D. Bankiewicz, P. Yrjas, D. Lindberg and M. Hupa, Corrosion Science 66, 2013 (225–232).
T. Jonsson, N. Folkeson, J. E. Svensson, L. G. Johansson and M. Halvarsson, Corrosion Science 53, (6), 2011 (2233–2246).
T. Varis, D. Bankiewicz, P. Yrjas, M. Oksa, T. Suhonen, S. Tuurna, K. Ruusuvuori and S. Holmström, Surface and Coatings Technology 265, 2015 (235–243).
A. Ruh and M. Spiegel, Corrosion Science 48, (3), 2006 (679–695).
Y. S. Li, M. Spiegel and S. Shimada, Materials Chemistry and Physics 93, (1), 2005 (217–223).
J. Lehmusto, B. J. Skrifvars, P. Yrjas and M. Hupa, Corrosion Science 53, (10), 2011 (3315–3323).
S. Enestam, D. Bankiewicz, J. Tuiremo, K. Mäkelä and M. Hupa, Fuel 104, 2013 (294–306).
Y. Kawahara, Materials and Corrosion 57, (1), 2006 (60–72).
G. D. Smith, D. J. Tillack, S. J. Patel and E. A. Loria, Superalloys 718, 625, 706 and Various Derivatives, (The Minerals Metals & Materials Society, Warrendale, 2001), p. 35.
S. Andersson, E. W. Blomqvist, L. Bäfver, F. Jones, K. Davidsson, J. Froitzheim, M. Karlsson, E. Larsson and J. Liske, Waste Management 34, (1), 2014 (67–78).
W. W. Luo, Z. D. Liu, Y. T. Wang and R. J. Yang, Procedia Engineering 36, 2012 (212–216).
C. W. Bale, P. Chartrand, S. A. Degterov, G. Eriksson, K. Hack, R. B. Mahfoud, J. Melancon, A. D. Pelton and S. Petersen, Calphad 26, (2), 2002 (189–228).
ISO/DIS 17248, AFNOR, (2014)
J. J. Rowe, G. W. Morey, C. S. Zen. The quinary reciprocal salt system Na, K, Mg, Ca/Cl, SO4—a review of the literature with new data, Geological Survey Professional Paper (US) 741, 1–37, 1972
J. M. Sangster, A. D. Pelton, Critical Coupled Evaluation of Phase Diagrams and Thermodynamic Properties of Binary and Ternary Alkali Salt Systems, Special Report to the Phase Equilibria Program, Part B: Evaluations for 54 common-ion binary systems involving (Li, Na, K) and (F, Cl, OH, NO3, CO3, SO4), American Ceramic Society, Westerville, Ohio, 4–231, 1987
J. Mochinaga, H. Ohtani and K. Igarashi, Denki Kagaku Oyobi Kogyo Butsuri Kagaku 49, 1981 (19).
J. J. Rowe, G. W. Morey and I. D. Hansen, Journal of Inorganic and Nuclear Chemistry 27, (1), 1965 (53–58).
H. Mueller, Beilage-band 30, 1910 (36).
A. G. Bergman and M. S. Golubeva, Doklady Akademiia Nauk SSR 89, 1953 (471–473).
M. Spiegel, Materials and Corrosion 51, (5), 2000 (303–312).
A. Roine, HSC Chemistry Version 4.1. (Outokumpu Research Organization, Pori, 1999).
R. A. Rapp, Corrosion Science 44, (2), 2002 (209–221).
F. Soutrel, Comportement de metaux purs (Fe, Ni, Cr ET Al) et de leurs alliages dans des conditions simulant celles rencontrees en incinerateur d’O. M. (Doctoral dissertation), 1998.
R. A. Rapp and N. Otsuka, ECS Transactions 16, (49), 2009 (271–282).
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by the French National Research Agency with Project ANR SCAPAC 11-RMNP-0016 in partnership with, AIR LIQUIDE, SEDIS and CIRIMAT/ENSIACET. The authors thank S. Mathieu of the service of microscopy and microanalyses (SCMEM) of the Faculty of Science and Techniques of Nancy (France) for carrying out SEM analyses and L. Aranda of Institut Jean Lamour, Nancy (France) for carrying out TMA and DTA analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schaal, E., David, N., Panteix, P.J. et al. Effect of Chloride Content in Ash in Oxidation Kinetics of Ni-Based and Fe-Based Alloys. Oxid Met 84, 307–327 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-015-9556-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-015-9556-1