Abstract
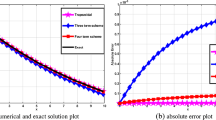
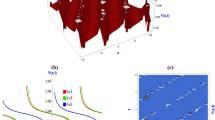
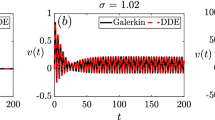
In this research we apply an analytic approach to solve the well-known Lorenz system in the non-chaotic regime. The proposed approach is based on modal expansion by infinite series. The analytical-numerical results show that for real initial conditions and under the non-convective regime the modal expansion series reproduce correctly the dynamical behavior of the solution of the Lorenz system. The validity and reliability of the proposed analytical approach with few terms is tested by its application to the convective and non-convective regime with various parameter values. The main advantage is that the obtained solution is global and is presented in analytical form.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasbandy, S., Shivanian, E.: Exact analytical solution of a nonlinear equation arising in heat transfer. Phys. Lett. A 374(4), 567–574 (2010)
Acedo, L., González-Parra, G., Arenas, A.: An exact global solution for the classical SIRS epidemic model. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 11(3), 1819–1825 (2010)
Acedo, L., González-Parra, G., Arenas, A.: Modal series solution for a epidemic model. Phys A 389, 1151–1157 (2010)
Al-sawalha, M.M., Noorani, M.: Adaptive reduced-order anti-synchronization of chaotic systems with fully unknown parameters. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 15(10), 3022–3034 (2010)
Alomari, A., Noorani, M., Nazar, R., Li, C.: Homotopy analysis method for solving fractional Lorenz system. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 15(7), 1864–1872 (2010)
Arenas, A.J., González-Parra, G., Jódar, L., Villanueva, R.J.: Piecewise finite series solution of nonlinear initial value differential problem. Appl. Math. Comput. 212(1), 209–215 (2009)
Birger, B.: Application of the Lorenz equations for studying thermal convection in the lithosphere. Izvestiya Phys. Solid Earth 47, 541–554 (2011)
van Buuren, S., Hetzler, H., Hinterkausen, M., Seemann, W.: Novel approach to solve the dynamical porous journal bearing problem. Tribol. Int. 46(1), 30–40 (2012)
Chowdhury, M., Hashim, I., Momani, S.: The multistage homotopy-perturbation method: A powerful scheme for handling the Lorenz system. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 40(4), 1929–1937 (2009)
Costin, O.: Topological construction of transseries and introduction to generalized Borel summability. AMS CONM SERIES 373, 137 (2005)
González-Parra, G., Arenas, A., Jódar, L.: Piecewise finite series solutions of seasonal diseases models using multistage Adomian method. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 14, 3967–3977 (2009)
Hashim, I., Noorani, M., Ahmad, R., Bakar, S., Ismail, E., Zakaria, A.: Accuracy of the Adomian decomposition method applied to the Lorenz system. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 28(5), 1149–1158 (2006)
Hongli, A.: Numerical pulsrodons of the -dimensional rotating shallow water system. Phys. Lett. A 375(19), 1921–1925 (2011)
Liao, S.: Beyond Perturbation. Introduction to the Homotopy Analysis Method. Chapman and Hall/CRC (2004)
Lorenz, E.: Deterministic nonperiodic flow1. J. Atmosph. Sci. 20, 130 (1963)
Lu, X., Lu, T., Viljanen, M.: A new analytical method to simulate heat transfer process in buildings. Appl. Therm. Eng. 26(16), 1901–1909 (2006)
Allan, M.F.: Construction of analytic solution to chaotic dynamical systems using the homotopy analysis method. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 39(4), 1744–1752 (2009)
Mahmud, M., Hashim, I.: Effects of a magnetic field on chaotic convection in fluid layer heated from below. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 38(4), 481–486 (2011)
Sparrow, C.: The Lorenz equations: Bifurcations, Chaos,and strange attractors. Springer-Verlag (1982)
Tignol, J.P.: Galois theory of algebraic equations. World Scientific, Singapore (2001)
Zorrilla, S.E., Rubiolo, A.C.: Modelling average concentrations of salt and salt substitute in partial or total volumes of semihard cylindrical cheeses. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 33(6), 501–508 (1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
González-Parra, G., Acedo, L. & Arenas, A.J. A novel approach to obtain analytical-numerical solutions of nonlinear Lorenz system. Numer Algor 67, 93–107 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-013-9776-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-013-9776-x