Abstract
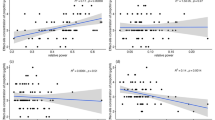
Inhalation anesthetics facilitate surgical procedures in millions of children each year. However, animal studies demonstrate that exposure to the inhalation anesthetic isoflurane may cause neuronal cell death in developing brains. The long-term cytotoxic effects of sevoflurane, the most popular pediatric anesthetic, have not been compared with isoflurane. Thus, this study was designed to compare the effects of equipotent doses of these two anesthetics on neonatal long-term neurotoxicity. Postnatal 7-day-old (P7) C57/BL male mice were exposed to 1.5% isoflurane or 2.2% sevoflurane 2 h a day for 3 days. Non-anesthetized mice served as controls. The effects of anesthesia on learning and memory were assessed using the Morris Water Maze (MWM) at Postnatal days 30 (P30) and P60 respectively. The hippocampal content of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunits (NMDA), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and synaptophysin (Syn) were determined by Western Blot. Neuron structure and apoptosis were assessed via Nissl and TUNEL staining, respectively. The isoflurane group exhibited cognitive impairment at P30. Repeated inhalation of isoflurane or sevoflurane caused different degrees of apoptosis and damaged hippocampal neurons in neonatal mice, particularly isoflurane. In neonatal mice, repeated exposure to isoflurane, but not sevoflurane, caused spatial cognitive impairments in juvenile mice. Our findings suggest that isoflurane induces significantly greater neurodegeneration than an equipotent minimum alveolar concentration of sevoflurane.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wilder RT, Flick RP, Sprung J, Katusic SK, Barbaresi WJ, Mickelson C, Gleich SJ, Schroeder DR, Weaver AL, Warner DO (2009) Early exposure to anesthesia and learning disabilities in a population-based birth cohort. Anesthesiology 110:796–804
Kalkman CJ, Peelen L, Moons KG, Veenhuizen M, Bruens M, Sinnema G, de Jong TP (2009) Behavior and development in children and age at the time of first anesthetic exposure. Anesthesiology 110:805–812
Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Hartman RE, Izumi Y, Benshoff ND, Dikranian K, Zorumski CF, Olney JW, Wozniak DF (2003) Early exposure to common anesthetic agents causes widespread neurodegeneration in the developing rat brain and persistent learning deficits. J Neurosci 23:876–882
Ikonomidou C, Bosch F, Miksa M, Bittigau P, Vockler J, Dikranian K, Tenkova TI, Stefovska V, Turski L, Olney JW (1999) Blockade of NMDA receptors and apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing brain. Science 283:70–74
Olney JW, Young C, Wozniak DF, Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Ikonomidou C (2004) Do pediatric drugs cause developing neurons to commit suicide? Trends Pharmacol Sci 25:135–139
Yang H, Liang G, Hawkins BJ, Madesh M, Pierwola A, Wei HF (2008) Inhalational anesthetics induce cell damage by disruption of intracellular calcium homeostasis with different potencies. Anesthesiology 109:243–250
Wei H, Kang B, Wei W, Liang G, Meng QC, Li Y, Eckenhoff RG (2005) Isoflurane and sevoflurane affect cell survival and BCL-2/BAX ratio differently. Brain Res 1037:139–147
Cascio M, Xing Y, Gong D, Popovich J, Eger EI 2nd, Sen S, Peltz G, Sonner JM (2007) Mouse chromosome 7 harbors a quantitative trait locus for isoflurane minimum alveolar concentration. Anesth Analg 105:381–385
Lee HT, Chen SW, Doetschman TC, Deng C, D’Agati VD, Kim M (2008) Sevoflurane protects against renal ischemia and reperfusion injury in mice via the transforming growth factor-ß1 pathway. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 295:F128–F136
Puig NR, Ferrero P, Bay ML, Hidalgo G, Valenti J, Amerio N, Elena G (2002) Effects of sevoflurane general anesthesia. Immunological studies in mice. Int Immunopharmacol 2:95–104
Satomoto M, Satoh Y, Terui K, Miyao H, Takishima K, Ito M, Imaki J (2009) Neonatal exposure to sevoflurane induces abnormal social behaviors and deficits in fear conditioning in mice. Anesthesiology 110:628–637
Kalkman CJ, Peelen L, Moons KQ, Veenhuizen M, Bruens M, Sinnema G, de Jong TP (2009) Behavior and development in and age at the time of first anesthetic exposure. Anesthesiology 110:805–812
Mellon RD, Simone AF, Rappaport BA (2007) Use of anesthetic agents in neonates and young children. Anesth Analg 104:509–520
Loepke AW, McCann JC, Kurth CD, McAuliffe JJ (2006) The physiologic effects of isoflurane anesthesia in neonatal mice. Anesth Analg 102:75–80
Stratmann G, May LD, Sall JW, Alvi RS, Bell JS, Ormerod BK, Rau V, Hilton JF, Dai R, Lee MT, Visrodia KH, Ku B, Zusmer EJ, Guggenheim J, Firouzian A (2009) Effect of hypercarbia and isoflurane on brain cell death and neurocognitive dysfunction in 7-day-old rats. Anesthesiology 110:849–861
Peng S, Zhang Y, Sun DP, Zhang DX, Fang Q, Li GJ (2011) The effect of sevoflurane anesthesia on cognitive function and the expression of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 in CA1 region of hippocampus in old rats. Mol Biol Rep 38:1195–1199
Shih J, May LD, Gonzalez HE, Lee EW, Alvi RS, Sall JW, Rau V, Bickler PE, Lalchandani GR, Yusupova M, Woodward E, Kang H, Wilk AJ, Carlston CM, Mendoza MV, Guggenheim JN, Schaefer M, Rowe AM, Stratmann G (2012) Delayed environmental enrichment reverses sevoflurane-induced memory impairment in rats. Anesthesiology 116:586–602
Callaway JK, Jones NC, Royse AG, Royse CF (2012) Sevoflurane anesthesia does not impair acquisition learning or memory in the Morris water maze in young adult and aged rats. Anesthesiology 117:1091–1101
Feng X, Liu JJ, Zhou X, Song FH, Yang XY, Chen XS, Huang WQ, Zhou LH, Ye JH (2012) Single sevoflurane exposure decreases neuronal nitric oxide synthase levels in the hippocampus of developing rats. Br J Anaesth 109:225–233
Franks NP (2008) General anaesthesia: from molecular targets to neuronal pathways of sleep and arousal. Nat Rev Neurosci 9(5):370–386
Ikonomidou C, Bosch F, Miksa M, Bittigau P, Vöckler J, Dikranian K, Tenkova TI, Stefovska V, Turski L, Olney JW (1999) Blockade of NMDA receptors and apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing brain. Science 283:70–74
Herschkowitz N, Kagan J, Zilles K (1997) Neurobiological bases of behavioral development in the first year. Neuropediatrics 28:296–306
Paoletti P, Neyton J (2007) NMDA receptor subunits: function and pharmacology. CurrOpinPharmacol 7:39–47
Barth AL, Malenka RC (2001) NMDAR EPSC kinetics do not regulate the critical period for LTP at thalamocortical synapses. Nat Neurosci 4:235–236
Yoshimura Y, Ohmura T, Komatsu Y (2003) Two forms of synaptic plasticity with distinct depend enceonage, experience, and NMDA receptor subtype in rat visual cortex. J Neurosci 23:6557–6566
Nase G, Weishaupt J, Stem P, Singer W, Monyer H (1999) Genetic and epigenetic regulation of NMDA receptor expression in the rat visual cortex. Eur J Neurosci 11:4320–4326
Quinlan EM, Olstein DH, Bear MF (1999) Bidirectional, experience-dependent regulation of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunit composition in the rat visual cortex during postnatal development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:12876–12880
Carmignoto G, Vicini S (1992) Activity-dependent decrease in NMDA receptor responses during development of the visual cortex. Science 258:1007–1011
Tang YP, Shimizu E, Dube GR, Rampon C, Kerchner GA, Zhuo M, Liu G, Tsien JZ (1999) Genetic enhancement of learning and memory in mice. Nature 401:63–69
Lee YS, Silv AJ (2009) The molecular and cellular biology of enhanced cognition. Nat Rev Neurosci 10:126–140
White TL, Youngentob SL (2004) The effect of NMDA-NR2B receptor subunit over-expression on olfactory memory task performance in the mouse. Brain Res 1021:1–7
Clayton DA, Mesches MH, Alvarez E, Bickford PC, Browning MD (2002) A hippocampal NR2B deficit can mimic age-related changes in long-term potentiation and spatial learning in the Fischer 344 rat. Neuroscience 22:3628–3637
Liu J, Wang P, Zhang X, Zhang W, Gu G (2014) Effects of different concentration and duration time of isoflurane on acute and long-term neurocognitve function of young adult C57BL/6 mouse. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7(9):5828–5836
Liu J, Zhang X, Zhang W, Gu G, Wang P (2015) Effects of sevoflurane on young male adult C57BL/6 mice spatial cognition. Plos One 10(8):e0134217
McAllister AK, Katz LC, Lo DC (1999) Neurotrophins and synaptic plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci 22:295–318
Poo MM (2001) Neurotrophins as synaptic modulators. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:24–32
Lindholm D, Castrén E, Berzaghi M, Blöchl A, Thoenen H (1994) Activity-dependent and hormonal regulation of neurotrophin mRNA levels in the brain: implications for neuronal plasticity. J Neurobiol 25:1362–1372
Lindvall O, Kokaia Z, Bengzon J, Elmér E, Kokaia M (1994) Neurotrophins and brain insults. Trends Neurosci 17:490–496
Schinder AF, Poo MM (2000) The neurotrophin hypothesis for synaptic plasticity. Trends Neurosci 23:639–645
Thoenen H (2000) Neurotrophins and activity-dependent plasticity. Prog Brain Res 128:183–191
Carter AR, Chen CF, Schwartz PM, Segal RA (2002) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor modulates cerebellar plasticity and synaptic ultrastructure. J Neurosci 22:1316–1327
Katoh-Semba R, Takeuchi IK, Semba R, Kato K (1997) Distribution of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rats and its changes with development in the brain. J Neurochem 69:34–42
Croll SD, Ip NY, Lindsay RM, Wiegand SJ (1998) Expression of BDNF and trkB as a function of age and cognitive performance. Brain Res 812:200–208
Connor B, Dragunow M (1998) The role of neuronal growth factors in neurodegenerative disorders of the human brain. Brain Res Rev 27:1–39
Murer MG, Yan Q, Raisman-Vozari R (2001) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the control human brain, and in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 63:71–124
Hayashi M, Yamashita A, Shimizu K (1997) Somatostatin and brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA expression in the primate brain: decreased levels of mRNAs during aging. Brain Res 749:283–289
Korte M, Carroll P, Wolf E, Brem G, Thoenen H, Bonhoeffer T (1995) Hippocampal long-term potentiation is impaired in mice lacking brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:8856–8860
Korte M, Staiger V, Griesbeck O, Thoenen H, Bonhoeffer T (1996) The involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in hippocampal long-term potentiation revealed by gene targeting experiments. J Physiol (Lond) 90:157–164
Ma YL, Wang HL, Wu HC, Wei CL, Lee EHY (1998) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor antisense oligonucleotide impairs memory re-tention and inhibits long-term potentiation in rats. Neuroscience 82:957–967
Kovalchuk Y, Hanse E, Kafitz KW, Konnerth A (2002) Postsynaptic induction of BDNF-mediated long-term potentiation. Science 295:1729–1734
Yu Z, You S, Xu M, Lin H, Di M, Lian Q (2013) Effect of acute exposure to sevoflurane and isoflurane on learning, memory and brain derived neurotrophic factor expression in hippocampus of juvenile SD rats. Chin J Pharmacol Toxicol 27(2):132–137
Lunardi N, Ori C, Erisir A et al (2010) General anesthesia causes long-lasting disturbances in the ultrastructural properties of developing synapses in young rats. Neurotox Res 17:179–188
Nikizad H, Yon JH, Carter LB, Jevtovic-Todorovic V (2007) Early exposure to general anesthesia causes significant neuronal deletion in the developing rat brain. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1122:69–82. doi:10.1196/annals.1403.005
Zheng H, Dong Y, Xu Z, Crosby G, Culley DJ, Zhang Y, Xie Z (2013) Sevoflurane anesthesia in pregnant mice induces neurotoxicity in fetal and offspring mice. Anesthesiology 118(3):516–526
Suehara T, Morishita J, Ueki M, Ueno M, Maekawa N, Mizobuchi S (2016) Effects of sevoflurane exposure during late pregnancy on brain development of offspring mice. Paediatr Anaesth 26(1):52–59. doi:10.1111/pan.12785
Tessier-Lavigne M, Goodman CS (1996) The molecular biology of axon guidance. Science 274:1123–1133
Ikonomidou C, Bittigau P, Ishimaru MJ, Wozniak DF, Koch C, Genz K, Price MT, Stefovska V, Hörster F, Tenkova T, Dikranian K, Olney JW (2000) Ethanol-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration and fetal alcohol syndrome. Science 287:1056–1060
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the fundings: National Natural Science Foundation of China (81600934); Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai, China (16ZR1432200); Science Lead Supporting project of Shanghai, China (16411967700) awarded to Jianhui Liu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Jianhui Liu and Yanhong Zhao are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Zhao, Y., Yang, J. et al. Neonatal Repeated Exposure to Isoflurane not Sevoflurane in Mice Reversibly Impaired Spatial Cognition at Juvenile-Age. Neurochem Res 42, 595–605 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2114-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2114-7