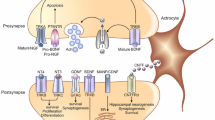
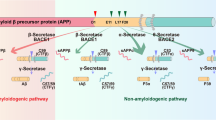
Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common type of neurodegenerative dementia that affects the elderly population. Nerve growth factor (NGF) contributes to the survival, regeneration and death of neurons during aging and in neurodegenerative diseases. Recently, research has shown that NGF is related to the pathology, mechanisms and symptoms of AD. Therefore, there is a need to summarize the new advancements in NGF research and its potential therapeutic implications in AD. In this review, we will focus on NGF distribution, production, and function; the interaction of Aβ and NGF; and the effect of different therapy methods on AD. In summary, we hope to describe the experimental and clinical data demonstrating the important roles of NGF for AD treatment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang YJ, Valadares D, Sun Y, Wang X, Zhong JH, Liu XH, Majd S, Chen L, Gao CY, Chen S, Lim Y, Pollard A, Salegio EA, Gai WP, Yang M, Zhou XF (2010) Effects of ProNGF on neuronal viability, neurite growth and amyloid-β metabolism. Neurotox Res 17:257–267
Ayton S, Lei P, Bush AI (2015) Biometals and their therapeutic implications in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurotherapeutics 12:109–120
Lad SP, Neet KE, Mufson EJ (2003) Nerve growth factor: structure, function and therapeutic implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord 2:315–334
Cohen S, Levi-Montalcini R, Hamburger V (1954) A nerve growth-stimulating factor isolated from sarcom as 37 and 180. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 40:1014–1018
Levi-Montalcini R, Hamburger V (1951) Selective growth stimulating effects of mouse sarcoma on the sensory and sympathetic nervous system of the chick embryo. J Exp Zool 116:321–361
Fahnestock M, Yu G, Coughlin MD (2004) ProNGF: a neurotrophic or an apoptotic molecule? Prog Brain Res 146:101–110
Hempstead BL (2009) Commentary: regulating ProNGF action: multiple targets for therapeutic intervention. Neurotox Res 16:255–260
Lee R, Kermani P, Teng KK, Hempstead BL (2001) Regulation of cell survival by secreted proneurotrophins. Science 294:1945–1948
Cuello AC, Bruno MA, Allard S, Leon W, Iulita MF (2010) Cholinergic involvement in Alzheimer’s disease. A link with NGF maturation and degradation. J Mol Neurosci 40:230–235
Iulita MF, Cuello AC (2014) Nerve growth factor metabolic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease and Down syndrome. Trends Pharmacol Sci 35:338–348
Nykjaer A, Lee R, Teng KK, Jansen P, Madsen P, Nielsen MS, Jacobsen C, Kliemannel M, Schwarz E, Willnow TE, Hempstead BL, Petersen CM (2004) Sortilin is essential for ProNGF-induced neuronal cell death. Nature 427:843–848
Capsoni S, Giannotta S, Cattaneo A (2002) β-Amyloid plaques in a model for sporadic Alzheimer’s disease based on transgenic anti-nerve growth factor antibodies. Mol Cell Neurosci 21:15–28
Yuen EC, Howe CL, Li Y, Holtzman DM, Mobley WC (1996) Nerve growth factor and the neurotrophic factor hypothesis. Brain Dev 18:362–368
Allen SJ, Watson JJ, Shoemark DK, Barua NU, Patel NK (2013) GDNF, NGF and BDNF as therapeutic options for neurodegeneration. Pharmacol Ther 138:155–175
Cirulli F, Alleva E, Antonelli A, Aloe L (2000) NGF expression in the developing rat brain: effects of maternal separation. Dev Brain Res 123:129–134
Woodhall E, West AK, Chuah MI (2001) Cultured olfactory ensheathing cells express nerve growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, glia cell line-derived neurotrophic factor and their receptors. Mol Brain Res 88:203–213
Lu B, Yokoyama M, Dreyfus CF, Black I (1991) NGF gene expression in actively growing brain glia. J Neurosci 11:318–326
Heese K, Fiebich BL, Bauer J, Otten U (1997) Nerve growth factor (NGF) expression in rat microglia is induced by adenosine A 2a-receptors. Neurosci Lett 231:83–86
Zafra F, Lindholm D, Castren E, Hartikka J, Thoenen H (1992) Regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor mRNA in primary cultures of hippocampal neurons and astrocytes. J Neurosci 12:4793–4799
Du Y, Dreyfus CF (2002) Oligodendrocytes as providers of growth factors. J Neurosci Res 68:647–654
Byravan S, Foster LM, Phan T, Verity AN, Campagnoni AT (1994) Murine oligodendroglial cells express nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:8812–8816
Freund V, Pons F, Joly V, Mathieu E, Martinet N, Frossard N (2002) Upregulation of nerve growth factor expression by human airway smooth muscle cells in inflammatory conditions. Eur Respir J 20:458–463
Heumann R, Lindholm D, Bandtlow C, Meyer M, Radeke MJ, Misko TP, Shooter E, Thoenen H (1987) Differential regulation of mRNA encoding nerve growth factor and its receptor in rat sciatic nerve during development, degeneration, and regeneration: role of macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:8735–8739
Taniuchi M, Clark HB, Schweitzer JB, Johnson E (1988) Expression of nerve growth factor receptors by Schwann cells of axotomized peripheral nerves: ultrastructural location, suppression by axonal contact, and binding properties. J Neurosci 8:664–681
Kawamoto K, Aoki J, Tanaka A, Itakura A, Hosono H, Arai H, Kiso Y, Matsuda H (2002) Nerve growth factor activates mast cells through the collaborative interaction with lysophosphatidylserine expressed on the membrane surface of activated platelets. J Immunol 168:6412–6419
Aloe L, Rocco ML (2015) NGF and therapeutic prospective: what have we learned from the NGF transgenic models? Ann Ist Super Sanita 51:5–10
Patapoutian A, Reichardt LF (2001) Trk receptors: mediators of neurotrophin action. Curr Opin Neurobiol 11:272–280
Fukuda Y, Fukui T, Hikichi C, Ishikawa T, Murate K, Adachi T, Imai H, Fukuhara K, Ueda A, Kaplan AP (2015) Neurotropin promotes NGF signaling through interaction of GM1 ganglioside with Trk neurotrophin receptor in PC12 cells. Brain Res 1596:13–21
Gu G, Zhang W, Li M, Ni J, Wang P (2015) Transplantation of NSC-derived cholinergic neuron-like cells improves cognitive function in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Neuroscience 291:81–92
Ruberti F, Capsoni S, Comparini A, Di Daniel E, Franzot J, Gonfloni S, Rossi G, Berardi N, Cattaneo A (2000) Phenotypic knockout of nerve growth factor in adult transgenic mice reveals severe deficits in basal forebrain cholinergic neurons, cell death in the spleen, and skeletal muscle dystrophy. J Neurosci 20:2589–2601
Zhang YW, Chen Y, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Liao FF, Xu H (2013) APP regulates NGF receptor trafficking and NGF-mediated neuronal differentiation and survival. PLoS One 8:e80571
Arevalo MÁ, Roldan PM, Chacón PJ, Rodríguez-Tebar A (2009) Amyloid β serves as an NGF-like neurotrophic factor or acts as a NGF antagonist depending on its concentration. J Neurochem 111:1425–1433
Xu C-J, Wang J-L, Jin W-L (2015) The neural stem cell microenvironment: focusing on axon guidance molecules and myelin-associated factors. J Mol Neurosci 56:887–897. doi:10.1007/s12031-015-0538-1
Wang Y-J, Wang X, Lu J-J, Li Q-X, Gao C-Y, Liu X-H, Sun Y, Yang M, Lim Y, Evin G (2011) p75NTR regulates Aβ deposition by increasing Aβ production but inhibiting Aβ aggregation with its extracellular domain. J Neurosci 31:2292–2304
Zhang Y-W, Chen Y, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Liao F-F, Xu H (2013) APP regulates NGF receptor trafficking and NGF-mediated neuronal differentiation and survival. PLoS One 8:e80571. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0080571
Cuello A, Ferretti M, Iulita M (2012) Preplaque (‘preclinical’) Aβ-induced inflammation and nerve growth factor deregulation in transgenic models of Alzheimer’s disease-like amyloid pathology. Neurodegener Dis 10:104–107. doi:10.1159/000333339
Bruno MA, Leon WC, Fragoso G, Mushynski WE, Almazan G, Cuello AC (2009) Amyloid β-induced nerve growth factor dysmetabolism in Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 68:857–869
Wakabayashi M, Matsuzaki K (2007) Formation of amyloids by Aβ-(1–42) on NGF-differentiated PC12 cells: roles of gangliosides and cholesterol. J Mol Biol 371:924–933
Matrone C, Ciotti MT, Mercanti D, Marolda R, Calissano P (2008) NGF and BDNF signaling control amyloidogenic route and Aβ production in hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:13139–13144
Marei HE, Farag A, Althani A, Afifi N, Abd-Elmaksoud A, Lashen S, Rezk S, Pallini R, Casalbore P, Cenciarelli C (2015) Human olfactory bulb neural stem cells expressing hNGF restore cognitive deficit in Alzheimer’s disease rat model. J Cell Physiol 230:116–130
Yang C, Liu Y, Ni X, Li N, Zhang B, Fang X (2014) Enhancement of the nonamyloidogenic pathway by exogenous NGF in an Alzheimer transgenic mouse model. Neuropeptides 48:233–238
Xu CJ, Xu L, Huang LD, Li Y, Yu PP, Hang Q, Xu XM, Lu PH (2011) Combined NgR vaccination and neural stem cell transplantation promote functional recovery after spinal cord injury in adult rats. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 37:135–155
Borlongan CV (2012) Recent preclinical evidence advancing cell therapy for Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Neurol 237:142–146
Heese K, Low JW, Inoue N (2006) Nerve growth factor, neural stem cells and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosignals 15:1–12
Yu J, Zhang X, Liu C, Meng Y, Han J (2006) Effect of acupuncture treatment on vascular dementia. Neurol Res 28:97–103
Chen J-H, Liang J, Wang G-B, Han J-S, Cui C-L (2005) Repeated 2 Hz peripheral electrical stimulations suppress morphine-induced CPP and improve spatial memory ability in rats. Exp Neurol 194:550–556
Lee M, Shin BC, Ernst E (2009) Acupuncture for Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review. Int J Clin Pract 63:874–879
Guo H-D, Tian J-X, Zhu J, Li L, Sun K, Shao S-J, Cui G-H (2015) Electroacupuncture suppressed neuronal apoptosis and improved cognitive impairment in the AD model rats possibly via downregulation of notch signaling pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2015:393569. doi:10.1155/2015/393569
Whitehouse PJ, Price DL, Struble RG, Clark AW, Coyle JT, Delon MR (1982) Alzheimer’s disease and senile dementia: loss of neurons in the basal forebrain. Science 215:1237–1239
Lehéricy S, Hirsch ÉC, Cervera-Piérot P, Hersh LB, Bakchine S, Piette F, Duyckaerts C, Hauw JJ, Javoy-Agid F, Agid Y (1993) Heterogeneity and selectivity of the degeneration of cholinergic neurons in the basal forebrain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J Comp Neurol 330:15–31
Hou X-Q, Zhang L, Yang C, Rong C-P, He W-Q, Zhang C-X, Li S, Su R-Y, Chang X, Qin J-H (2015) Alleviating effects of Bushen–Yizhi formula on ibotenic acid-induced cholinergic impairments in rat. Rejuvenation Res 18:111–127
Wang R, Yan H (2006) Progress in studies of huperzine A, a natural cholinesterase inhibitor from Chinese herbal medicine. Acta Pharmacol Sin 27:1–26
Moon M, Kim HG, Choi JG, Oh H, Lee PK, Ha SK, Kim SY, Park Y, Huh Y, Oh MS (2014) 6-Shogaol, an active constituent of ginger, attenuates neuroinflammation and cognitive deficits in animal models of dementia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 449:8–13
Gao J, Inagaki Y, Li X, Kokudo N, Tang W (2013) Research progress on natural products from traditional Chinese medicine in treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Drug Discov Ther 7:46–57
Geula C, Mesulam M-M (1995) Cholinesterases and the pathology of Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 9:23–28
Weinstock M, Kirschbaum-Slager N, Lazarovici P, Bejar C, Youdim MB, Shoham S (2001) Neuroprotective effects of novel cholinesterase inhibitors derived from rasagiline as potential anti-Alzheimer drugs. Ann N Y Acad Sci 939:148–161
Liston DR, Nielsen JA, Villalobos A, Chapin D, Jones SB, Hubbard ST, Shalaby IA, Ramirez A, Nason D, White WF (2004) Pharmacology of selective acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: implications for use in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Pharmacol 486:9–17
Capsoni S, Giannotta S, Stebel M, Garcia AA, De Rosa R, Villetti G, Imbimbo BP, Pietra C, Cattaneo A (2004) Ganstigmine and donepezil improve neurodegeneration in AD11 antinerve growth factor transgenic mice. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Dement 19:153–160
Aboukhatwa M, Dosanjh L, Luo Y (2010) Antidepressants are a rational complementary therapy for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurodegener 5:10. doi:10.1186/1750-1326-5-10
Russo-Neustadt A, Beard RC, Cotman CW (1999) Exercise, antidepressant medications, and enhanced brain derived neurotrophic factor expression. Neuropsychopharmacology 21:679–682
Lang UE, Hellweg R, Kalus P, Bajbouj M, Lenzen KP, Sander T, Kunz D, Gallinat J (2005) Association of a functional BDNF polymorphism and anxiety-related personality traits. Psychopharmacology 180:95–99
Akkad DA, Kruse N, Arning L, Gold R, Epplen JT (2008) Genomic NGFB variation and multiple sclerosis in a case control study. BMC Med Genet 9:107
Nagata T, Shinagawa S, Nukariya K, Nakayama R, Nakayama K, Yamada H (2011) Association between nerve growth factor gene polymorphism and executive dysfunction in Japanese patients with early-stage Alzheimer’s disease and amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 32:379–386
Di Maria E, Giorgio E, Uliana V, Bonvicini C, Faravelli F, Cammarata S, Novello MC, Galimberti D, Scarpini E, Zanetti O (2012) Possible influence of a non-synonymous polymorphism located in the NGF precursor on susceptibility to late-onset Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. J Alzheimers Dis 29:699
Alberts MJ, Pericak-Vance MA, Royal V, Bebout J, Gaskell P, Thomas J, Hung WY, Clark C, Earl N, Roses AD (1991) Genetic linkage analysis of nerve growth factor (β) in familial Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 30:216–219
Qosa H, Mohamed LA, Batarseh YS, Alqahtani S, Ibrahim B, LeVine H, Keller JN, Kaddoumi A (2015) Extra-virgin olive oil attenuates amyloid-β and tau pathologies in the brains of TgSwDI mice. J Nutr Biochem 26:1479–1490. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.07.022
Yu J, Gattoni-Celli M, Zhu H, Bhat NR, Sambamurti K, Gattoni-Celli S, Kindy MS (2011) Vitamin D3-enriched diet correlates with a decrease of amyloid plaques in the brain of AβPP transgenic mice. J Alzheimers Dis 25:295–307. doi:10.3233/JAD-2011-101986
Lee J, Duan W, Long JM, Ingram DK, Mattson MP (2000) Dietary restriction increases the number of newly generated neural cells, and induces BDNF expression, in the dentate gyrus of rats. J Mol Neurosci 15:99–108
Duan W, Lee J, Guo Z, Mattson MP (2001) Dietary restriction stimulates BDNF production in the brain and thereby protects neurons against excitotoxic injury. J Mol Neurosci 16:1–12
Yao J, Chen S, Mao Z, Cadenas E, Brinton RD (2011) 2-Deoxy-d-glucose treatment induces ketogenesis, sustains mitochondrial function, and reduces pathology in female mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 6:e21788
Um H-S, Kang E-B, Koo J-H, Kim H-T, Kim E-J, Yang C-H, An G-Y, Cho I-H, Cho J-Y (2011) Treadmill exercise represses neuronal cell death in an aged transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Res 69:161–173
Berardi N, Braschi C, Capsoni S, Cattaneo A, Maffei L (2007) Environmental enrichment delays the onset of memory deficits and reduces neuropathological hallmarks in a mouse model of Alzheimer-like neurodegeneration. J Alzheimers Dis 11:359–370
Zhang Z, Liu X, Schroeder JP, Chan C-B, Song M, Yu SP, Weinshenker D, Ye K (2014) 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone prevents synaptic loss and memory deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychopharmacology 39:638–650
Maliartchouk S, Feng Y, Ivanisevic L, Debeir T, Cuello AC, Burgess K, Saragovi HU (2000) A designed peptidomimetic agonistic ligand of TrkA nerve growth factor receptors. Mol Pharmacol 57:385–391
Scarpi D, Cirelli D, Matrone C, Castronovo G, Rosini P, Occhiato E, Romano F, Bartali L, Clemente A, Bottegoni G (2012) Low molecular weight, non-peptidic agonists of TrkA receptor with NGF-mimetic activity. Cell Death Dis 3:e339
Massa SM, Xie Y, Longo FM (2003) Alzheimer’s therapeutics. J Mol Neurosci 20:323–326
Tuszynski MH, Thal L, Pay M, Salmon DP, Bakay R, Patel P, Blesch A, Vahlsing HL, Ho G, Tong G (2005) A phase 1 clinical trial of nerve growth factor gene therapy for Alzheimer disease. Nat Med 11:551–555
Wahlberg LU, Lind G, Almqvist PM, Kusk P, Tornøe J, Juliusson B, Söderman M, Selldén E, Seiger Å, Eriksdotter-Jönhagen M (2012) Targeted delivery of nerve growth factor via encapsulated cell biodelivery in Alzheimer disease: a technology platform for restorative neurosurgery: clinical article. J Neurosurg 117:340–347
Rafii MS, Baumann TL, Bakay RA, Ostrove JM, Siffert J, Fleisher AS, Herzog CD, Barba D, Pay M, Salmon DP (2014) A phase 1 study of stereotactic gene delivery of AAV2-NGF for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 10:571–581
Friden PM, Walus LR, Watson P, Kozarich J, Backman C, Bergman H, Hoffer B, Bloom F, Granholm A (1993) Blood–brain barrier penetration and in vivo activity of an NGF conjugate. Science 259:373–377
Kastin AJ, Pan W, Maness LM, Banks WA (1999) Peptides crossing the blood–brain barrier: some unusual observations. Brain Res 848:96–100
Acknowledgments
This project is supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LY13H090007) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31171033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we did not receive financial support or maintain relationships that may have posed a conflict of interest.
Additional information
Chao-jin Xu and Jun-Ling Wang have contributed equally to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, CJ., Wang, JL. & Jin, WL. The Emerging Therapeutic Role of NGF in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochem Res 41, 1211–1218 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1829-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1829-9