Abstract
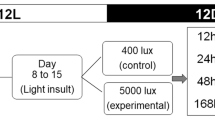
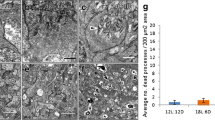
Aquaporins (AQPs) are integral membrane proteins which maintain cellular water and ion homeostasis. Alterations in AQP expression have been reported in rod-dominated rodent retinas exposed to light. In rodents and also in birds, light of moderate intensities (700–2000 lux) damages the retina, though detailed changes were not examined in birds. The aim of our study was to see if light affects cone dominated retinas, which would be reflected in expression levels of AQPs. We examined AQP1 and AQP4 expressions in chick retina exposed to 2000 lux under 12 h light:12 h dark (12L:12D; normal photoperiod), 18L:6D (prolonged photoperiod) and 24L:0D (constant light). Additionally, morphological changes, apoptosis (by TUNEL) and levels of glutamate and GFAP (a marker of injury) in the retina were examined to correlate these with AQP expressions. Constant light caused damage in outer and inner nuclear layer (ONL, INL) and ganglion cell layer (GCL). Also, there were associated increases in GFAP and glutamate levels in retinal extracts. In normal photoperiod, AQP1 was expressed in GCL, outer part of INL and photoreceptor inner segments of. AQP4 was additionally expressed in nerve fiber layer. Immunohistochemistry and Western blotting revealed over all decreased AQP1 and AQP4 expression in constant light condition compared to those in other two groups. The elevated GFAP and glutamate levels might be involved in the reduction of AQPs in constant light group. Such decreases in AQP expressions are perhaps linked with retinal cell damage seen in constant light condition, while their relatively enhanced expression in two other conditions may help in maintaining a normal retinal architecture, indicating their neuroprotective potential.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agre P, Bonhivers M, Borgnia MJ (1998) The aquaporins, blueprints for cellular plumbing systems. J Biol Chem 273:14659–14662
Verkman AS (2003) Role of aquaporin water channels in eye function. Exp Eye Res 76:137–143
Farjo R, Peterson WM, Naash MI (2008) Expression profiling after retinal detachment and reattachment: a possible role for aquaporin-0. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 49:511–521
Qin Y, Fan J, Ye X, Xu G, Liu W, Da C (2009) High salt loading alters the expression and localization of glial aquaporins in rat retina. Exp Eye Res 89:88–94
Kim IB, Lee FJ, Oh SJ, Park CB, Pow DV, Chun MH (2002) Light and electron microscopic analysis of aquaporin 1-like-immunoreactive amacrine cells in the rat retina. J Comp Neurol 452:178–191
Patil RV, Saito I, Yang X, Wax MB (1997) Expression of aquaporins in the rat ocular tissue. Exp Eye Res 64:203–209
Hamann S, Zeuthen T, La Cour M, Nagelhus EA, Ottersen OP, Agre P, Nielsen S (1998) Aquaporins in complex tissues: distribution of aquaporins 1-5 in human and rat eye. Am J Physiol 274:1332–1345
Nagelhus EA, Veruki ML, Torp R, Haug FM, Laake JH, Nielsen S, Agre P, Ottersen OP (1998) Aquaporin-4 water channel protein in the rat retina and optic nerve: polarized expression in Müller cells and fibrous astrocytes. J Neurosci 18:2506–2519
Nagelhus EA, Mathiisen TM, Ottersen OP (2004) Aquaporin-4 in the central nervous system: cellular and subcellular distribution and coexpression with KIR4.1. Neuroscience 129:905–913
Hombrebueno JR, Lee EJ, Martínez-Ruiz N, García-Alcázar A, Grzywacz NM, De Juan J (2012) Aquaporin-4 immunoreactivity in Müller and amacrine cells of marine teleost fish retina. Brain Res 1432:46–55
Zichichi R, Magnoli D, Montalbano G, Laurà R, Vega JA, Ciriaco E, Germanà A (2011) Aquaporin 4 in the sensory organs of adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Brain Res 1384:23–28
Ortaka H, Caylib S, Ocaklıb S, Söğütc E, Ekicid F, Tas U, Demir S (2013) Age-related changes of aquaporin expression patterns in the postnatal rat retina. Acta Histochem 115:382–388
Iandiev I, Biedermann B, Reichenbach A, Wiedemann P, Bringmann A (2006) Expression of aquaporin-9 immunoreactivity by catecholaminergic amacrine cells in the rat retina. Neurosci Lett 398:264–267
Badaut J, Lasbennes F, Magistretti PJ, Regli L (2002) Aquaporins in brain: distribution, physiology, and pathophysiology. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22:367–378
Wang D, Owler BK (2011) Expression of AQP1 and AQP4 in paediatric brain tumours. J Clin Neurosci 18:122–127
Fukuda M, Nakanishi Y, Fuse M, Yokoi N, Hamada Y, Fukagawa M, Negi A, Nakamura M (2010) Altered expression of aquaporins 1 and 4 coincides with neurodegenerative events in retinas of spontaneously diabetic Torii rats. Exp Eye Res 90:17–25
Nagelhus EA, Veruki ML, Torp R, Haug FM, Laake JH, Nielsen S, Agre P, Ottersen OP (1998) Aquaporin-4 water channel protein in the rat retina and optic nerve: polarized expression in Müller cells and fibrous astrocytes. J Neurosci 18:2506–2519
Nagelhus EA, Horio Y, Inanobe A, Fujita A, Haug FM, Nielsen S, Kurachi Y, Ottersen OP (1999) Immunogold evidence suggests that coupling of K+ siphoning and water transport in rat retinal Müller cells is mediated by a coenrichment of Kir4.1 and AQP4 in specific membrane domains. Glia 26:47–54
Li XM, Wendu RL, Yao J, Ren Y, Zhao YX, Cao GF, Qin J, Yan B (2014) Abnormal glutamate metabolism in the retina of aquaporin 4 (AQP4) knockout mice upon light damage. Neurol Sci 35:847–853
Kumar B, Gupta SK, Srinivasan BP, Nag TC, Srivastava S, Saxena R, Jha KA (2013) Hesperetin rescues retinal oxidative stress, neuroinflammation and apoptosis in diabetic rats. Microvasc Res 87:65–74
Goodyear MJ, Crewther SG, Junghans BM (2009) A role for aquaporin-4 in fluid regulation in the inner retina. Vis Neurosci 26:159–165
Goodyear MJ, Crewther SG, Murphy MJ, Giummarra L, Hazi A, Junghans BM, Crewther DP (2010) Spatial and temporal dissociation of AQP4 and Kir4.1 expression during induction of refractive errors. Mol Vis 16:1610–1619
Iandiev I, Wurm A, Hollborn M, Wiedemann P, Grimm C, Remé CE, Reichenbach A, Pannicke T, Bringmann A (2008) Müller cell response to blue light injury of the rat retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 49:3559–3567
Da T, Verkman AS (2004) Aquaporin-4 gene disruption in mice protects against impaired retinal function and cell death after ischemia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45:4477–4483
Dibas A, Yang MH, He S, Bobich J, Yorio T (2008) Changes in ocular aquaporin-4 (AQP4) expression following retinal injury. Mol Vis 14:1770–1783
Organisciak DT, Vaughan DK (2010) Retinal light damage: mechanisms and protection. Prog Retin Eye Res 29:113–134
Basha AA, Mathangi DC, Shyamala R, Rao RK (2014) Protective effect of light emitting diode phototherapy on fluorescentlight induced retinal damage in Wistar strain albino rats. Ann Anat 196:312–316
Reese CD (2008) Industrial safety and health for administrative services. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Li T, Troilo D, Glasser A, Howland HC (1995) Constant light produces severe corneal flattening and hyperopia in chickens. Vision Res 35:1203–1209
Kitano S, Morgan J, Caprioli J (1996) Hypoxic and excitotoxic damage to cultured rat retinal ganglion cells. Exp Eye Res 63:105–112
Izumi Y, Kirby CO, Benz AM, Olney JW, Zorumski CF (1999) Müller cell swelling, glutamate uptake, and excitotoxic neurodegeneration in the isolated rat retina. Glia 25:379–389
Vitry FD, Picart R, Jacque C, Tixier-Vidal A (1981) Glial fibrillary acidic protein. Dev Neurosci 4:457–460
Morris VB, Shorey CD (1967) An electron microscope study of types of receptor in the chick retina. J Comp Neurol 129:13–340
Marshall J, Mellerio J, Palmer DA (1972) Damage to pigeon retinae by moderate illumination from fluorescent lamps. Exp Eye Res 14:164–169
Thomson LR, Toyoda Y, Langner A, Delori FC, Garnett KM, Craft N, Nichols CR, Cheng KM, Dorey CK (2002) Elevated retinal zeaxanthin and prevention of light-induced photoreceptor cell death in quail. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43:3538–3549
Lauber JK (1987) Light-induced avian glaucoma as an animal model for human primary glaucoma. J Ocul Pharmacol 3:77–100
Montiani-Ferreira F, Fischer A, Cernuda-Cernuda R, Kiupel M, DeGrip WJ, Sherry D, Cho SS, Shaw GC, Evans MG, Hocking PM, Petersen-Jones SM (2005) Detailed histopathologic characterization of the retinopathy, globe enlarged (rge) chick phenotype. Mol Vis 11:11–27
Brison E, Jacomy H, Desforges M, Talbot PJ (2014) Novel treatment with neuroprotective and antiviral properties against a neuroinvasive human respiratory virus. J Virol 88:1548–1563
Cebulla CM, Zelinka CP, Scott MA, Lubow M, Bingham A, Rasiah S, Mahmoud AM, Fischer AJ (2012) A chick model of retinal detachment: cone rich and novel. PLoS One 7:e44257
Kanan Y, Wicker LD, Al-Ubaidi MR, Mandal NA, Kasus-Jacobi A (2008) Retinal dehydrogenase RDH1 and RDH2 in the mouse retina: expression levels during development and regulation by oxidative stress. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 49:1071–1078
Roehlecke C, Schumann U, Ader M, Brunssen C, Bramke S, Morawietz H, Funk RH (2013) Stress reaction in outer segments of photoreceptors after blue light irradiation. PLoS One 8:e71570
Li T, Howland HC, Troilo D (2000) Diurnal illumination patterns affect the development of the chick eye. Vision Res 40:2387–2393
Dunaief JL, Dentchev T, Ying GS, Milam AH (2002) The role of apoptosis in age-related macular degeneration. Arch Ophthalmol 120:1435–1442
Li XM, Wendu RL, Yao J, Ren Y, Zhao YX, Cao GF, Qin J, Yan B (2014) Abnormal glutamate metabolism in the retina of aquaporin 4 (AQP4) knockout mice upon light damage. Neurol Sci 35:847–853
Dai M, Xia XB, Xiong SQ (2012) BDNF regulates GLAST and glutamine synthetase in mouse retinal Müller cells. J Cell Physiol 227:596–603
Crewther SG, Liang H, Junghans BM, Crewther DP (2006) Ionic control of ocular growth and refractive change. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:15663–15668
Zeng XN, Sun XL, Gao L, Fan Y, Ding JH, Hu G (2007) Aquaporin-4 deficiency down-regulates glutamate uptake and GLT-1 expression in astrocytes. Mol Cell Neurosci 34:34–39
Verkman AS, Ruiz-Ederra J, Levin MH (2008) Functions of aquaporins in the eye. Prog Retin Eye Res 27:420–433
Iandiev I, Pannicke T, Biedermann B, Wiedemann P, Reichenbach A, Bringmann A (2006) Ischemia–reperfusion alters the immunolocalization of glial aquaporins in rat retina. Neurosci Lett 408:108–112
Ruiz-Ederra J, Zhang H, Verkman AS (2007) Evidence against functional interaction between aquaporin-4 water channels and Kir4.1 potassium channels in retinal Müller cells. J Biol Chem 282:21866–21872
Yuan S, Zhang W, Ding J, Yao J, Jiang Q, Hu G (2009) Increased sensitivity to retinal light damage in aquaporin-4 knockout mice. Exp Eye Res 89:119–122
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the SERB (DST, Government of India, New Delhi, No. AS-27/2012; TCN) for the financial support. KAJ, PK and VK received fellowships from UGC, AIIMS and CSIR, respectively. The TEM work was done at SAIF (DST), AIIMS-New Delhi, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jha, K.A., Nag, T.C., Kumar, V. et al. Differential Expression of AQP1 and AQP4 in Avascular Chick Retina Exposed to Moderate Light of Variable Photoperiods. Neurochem Res 40, 2153–2166 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1698-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1698-7