Abstract
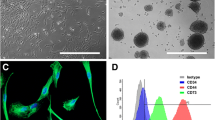
Umbilical cord blood-derived marrow stromal cells (UCB-MSCs) with high proliferation capacity and immunomodulatory properties are considered to be a good candidate for cell-based therapies. But until now, little work has been focused on the differentiation of UCB-MSCs. In this work, UCB-MSCs were demonstrated to be negative for CD34 and CD45 expression but positive for CD90 and CD105 expression. The gate values of UCB-MSCs for CD90 and CD105 were 99.3 and 98.6 %, respectively. Two weeks after treatment, the percentage of neuron-like cells differentiated from UCB-MSCs was increased to 84 ± 12 % in the experimental group [treated with olfactory ensheathing cells (OECs)-conditioned medium] and they were neuron-specific enolase positive; few neuron-like cells were found in the control group (without OECs-conditioned medium). Using whole-cell recording, sodium and potassium currents were recorded in UCB-MSCs after differentiation by OECs. Thus, human UCB-MSCs could be differentiated to neural cells by secreted secretion from OECs and exhibited electrophysiological properties similar to mature neurons after 2 weeks post-induction. These results imply that OECs can be used as a new strategy for stem cell differentiation and provide an alternative neurogenesis pathway for generating sufficient numbers of neural cells for cell therapy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ao Q, Wang AJ, Chen GQ, Wang SJ, Zuo HC, Zhang XF (2007) Combined transplantation of neural stem cells and olfactory ensheathing cells for the repair of spinal cord injuries. Med Hypotheses 69:1234–1237
Bieback K, Kern S, Klüter H, Eichler H (2004) Critical parameters for the isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood. Stem Cells 22:525–634
Capelli C, Gotti E, Morigi M, Rota C, Weng L, Dazzi F, Spinelli O, Cazzaniga G, Trezzi R, Gianatti A, Rambaldi A, Golay J, Introna M (2011) Minimally manipulated whole human umbilical cord is a rich source of clinical-grade human mesenchymal stromal cells expanded in human platelet lysate. Cytotherapy 13:786–801
Duan D, Rong M, Zeng Y, Teng X, Zhao Z, Liu B, Tao X, Zhou R, Fan M, Peng C, Chen P, Liang S, Lu M (2011) Electrophysiological characterization of NSCs after differentiation induced by OEC conditioned medium. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 153:2085–2090
Erices A, Conget P, Minguell JJ (2000) Mesenchymal progenitor cells in human umbilical cord blood. Br J Haematol 109:235–242
Fu YS, Cheng YC, Lin MY, Cheng H, Chu PM, Chou SC, Shih YH, Ko MH, Sung MS (2006) Conversion of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in Wharton’s jelly to dopaminergic neurons in vitro: potential therapeutic application for Parkinsonism. Stem Cells 24:115–124
Gang EJ, Hong SH, Jeong JA, Hwang SH, Kim SW, Yang IH, Ahn C, Han H, Kim H (2004) In vitro mesengenic potential of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 321:102–108
Goldman S (2005) Stem and progenitor cell-based therapy of the human central nervous system. Nat Biotechnol 23:862–871
Greco SJ, Zhou C, Ye JH, Rameshwar P (2007) An interdisciplinary approach and characterization of neuronal cells transdifferentiated from human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev 16:811–826
Harris DT (2008) Cord blood stem cells: a review of potential neurological applications. Stem Cell Res 4:269–274
Jurga M, Lipkowski AW, Lukomska B, Buzanska L, Kurzepa K, Sobanski T, Habich A, Coecke S, Gajkowska B, Domanska-Janik K (2009) Generation of functional neural artificial tissue from human umbilical cord blood stem cells. Tissue Eng Part C Methods 15:365–372
Koch TG, Heerkens T, Thomsen PD, Betts DH (2007) Isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from equine umbilical cord blood, BMC. Biotechnology 7:1–9
Lee OK, Kuo TK, Chen WM, Lee KD, Hsieh SL, Chen TH (2004) Isolation of multipotentmesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood. Blood 103:1669–1675
Lee H, Bae JS, Jin HK (2010) Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve neurological abnormalities of Niemann-Pick type C mouse by modulation of neuroinflammatory condition. J Vet Med Sci 72:709–717
Lee HJ, Lee JK, Lee H, Carter JE, Chang WJ, Oh W, Yang YS, Suh JG, Lee BH, Jin HK, Bae JS (2012) Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve neuropathology and cognitive impairment in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model through modulation of neuroinflammation. Neurobiol Aging 33:588–602
Liu Y, Teng X, Yang X, Song Q, Lu R, Xiong J, Liu B, Zeng N, Zeng Y, Long J, Cao R, Lin Y, He Q, Chen P, Lu M, Liang S (2010) Shotgun proteomics and network analysis between plasma membrane and extracellular matrix proteins from rat olfactory ensheathing cells. Cell Transpl 19:133–146
Moore NH, Costa LG, Shaffer SA, Goodlett DR, Guizzetti M (2009) Shotgun proteomics implicates extracellular matrix proteins and protease systems in neuronal development induced by astrocyte cholinergic stimulation. J Neurochem 108:891–908
Ni WF, Yin LH, Lu J, Xu HZ, Chi YL, Wu JB, Zhang N (2010) In vitro neural differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells induced by Cocultured olfactory ensheathing cells. Neurosci Lett 475:99–103
Park SI, Lim JY, Jeong CH, Kim SM, Jun JA, Jeun SS, Oh WI (2012) Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell therapy promotes functional recovery of contused rat spinal cord through enhancement of endogenous cell proliferation and oligogenesis. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012:362473
Peters R, Wolf MJ, van den Broek M, Nuvolone M, Dannenmann S, Stieger B, Rapold R, Konrad D, Rubin A, Bertino JR, Aguzzi A, Heikenwalder M, Knuth AK (2010) Efficient generation of multipotentmesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood in stroma-free liquid culture. PLoS One 5:e15689
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S, Marshak DR (1999) Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 284:143–147
Quirici N, Soligo D, Bossolasco P, Servida F, Lumini C, Deliliers GL (2002) Isolation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by anti-nerve growth factor receptor antibodies. Exp Hematol l30:783–791
Rao MS, Mattson MP (2001) Stem cells and aging: expanding the possibilities. Mech Ageing Dev 1227:13–734
Rojas-Mayorquín AE, Torres-Ruíz NM, Ortuño-Sahagún D, Gudiño-Cabrera G (2008) Microarray analysis of striatal embryonic stem cells induced to differentiate by ensheathing cell conditioned media. Dev Dyn 237:979–994
Sanchez-Ramos JR, Song S, Kamath SG, Zigova T, Willing A, Cardozo-Pelaez F, Stedeford T, Chopp M, Sanberg PR (2001) Expression of neural markers in human umbilical cord blood. Exp Neurol 171:109–115
Shukla S, Chaturvedi RK, Seth K, Roy NS, Agrawal AK (2009) Enhanced survival and function of neural stem cells-derived dopaminergic neurons under influence of olfactory ensheathing cells in parkinsonian rats. J Neurochem 109:436–451
Srivastava N, Seth K, Khanna VK, Ansari RW, Agrawal AK (2009) Long-term functional restoration by neural progenitor cell transplantation in rat model of cognitive dysfunction: co-transplantation with olfactory ensheathing cells for neurotrophic factor support. Int J Dev Neurosci 27:103–110
Tio M, Tan KH, Lee W, Wang TT, Udolph G (2010) Roles of db-cAMP, IBMX and RA in aspects of neural differentiation of cord blood derived mesenchymal-like stem cells. PLoS One 5:e9398
Torrente Y, Polli E (2008) Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Transpl 17:1103–1113
Yang SE, Ha CW, Jung M, Jin HJ, Lee M, Song H, Choi S, Oh W, Yang YS (2004) Mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells developed in cultures from UC blood. Cytotherapy 6:476–486
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, Y., Rong, M., Liu, Y. et al. Electrophysiological Characterisation of Human Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Induced by Olfactory Ensheathing Cell-Conditioned Medium. Neurochem Res 38, 2483–2489 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1186-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1186-x