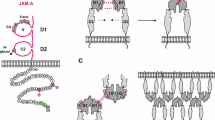
Abstract
To perform their diverse biological functions the adhesion activities of the cell adhesion molecules of the immunoglobulin superfamily (IgCAMs) might be regulated by local clustering, proteolytical shedding of their ectodomains or rapid recycling to and from the plasma membrane. Another form of regulation of adhesion might be obtained through flexible ectodomains of IgCAMs which adopt distinct conformations and which in turn modulate their adhesion activity. Here, we discuss variations in the conformation of the extracellular domains of CEACAM1 and CAR that might influence their binding and signaling activities. Furthermore, we concentrate on alternative splicing of single domains and short segments in the extracellular regions of L1 subfamily members that might affect the organization of the N-terminal located Ig-like domains. In particular, we discuss variations of the linker sequence between Ig-like domains 2 and 3 (D2 and D3) that is required for the horseshoe conformation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brümmendorf T, Rathjen FG (1996) Structure/function relationships of axon-associated adhesion receptors of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Curr Opin Neurobiol 6:584–593
Zonta B, Desmazieres A, Rinaldi A, Tait S, Sherman DL, Nolan MF, Brophy PJ (2011) A critical role for Neurofascin in regulating action potential initiation through maintenance of the axon initial segment. Neuron 69:945–956
Kriebel M, Metzger J, Trinks S, Chugh D, Harvey RJ, Harvey K, Volkmer H (2011) The cell adhesion molecule neurofascin stabilizes axo-axonic GABAergic terminals at the axon initial segment. J Biol Chem 286:24385–24393
Cohen NR, Taylor JS, Scott LB, Guillery RW, Soriano P, Furley AJ (1998) Errors in corticospinal axon guidance in mice lacking the neural cell adhesion molecule L1. Curr Biol 8:26–33
Brümmendorf T, Kenwrick S, Rathjen FG (1998) Neural cell recognition molecule L1: from cell biology to human hereditary brain malformations. Curr Opin Neurobiol 8:87–97
Maness PF, Schachner M (2007) Neural recognition molecules of the immunoglobulin superfamily: signaling transducers of axon guidance and neuronal migration. Nat Neurosci 10:19–26
Stoeckli ET (2010) Neural circuit formation in the cerebellum is controlled by cell adhesion molecules of the Contactin family. Cell Adh Migr 4:523–526
Bizzoca A, Corsi P, Gennarini G (2009) The mouse F3/contactin glycoprotein: structural features, functional properties and developmental significance of its regulated expression. Cell Adh Migr 3:53–63
Robbins EM, Krupp AJ, de Perez AK, Ghosh AK, Fogel AI, Boucard A, Sudhof TC, Stein V, Biederer T (2010) SynCAM 1 adhesion dynamically regulates synapse number and impacts plasticity and learning. Neuron 68:894–906
Marg A, Sirim P, Spaltmann F, Plagge A, Kauselmann G, Buck F, Rathjen FG, Brümmendorf T (1999) Neurotractin, a novel neurite outgrowth-promoting Ig-like protein that interacts with CEPU-1 and LAMP. J Cell Biol 145:865–876
Ango F, Di Cristo G, Higashiyama H, Bennett V, Wu P, Huang ZJ (2004) Ankyrin-based subcellular gradient of neurofascin, an immunoglobulin family protein, directs GABAergic innervation at purkinje axon initial segment. Cell 119:257–272
Schaefer AW, Kamei Y, Kamiguchi H, Wong EV, Rapoport I, Kirchhausen T, Beach CM, Landreth G, Lemmon SK, Lemmon V (2002) L1 endocytosis is controlled by a phosphorylation-dephosphorylation cycle stimulated by outside-in signaling by L1. J Cell Biol 157:1223–1232
Schafer MK, Altevogt P (2010) L1CAM malfunction in the nervous system and human carcinomas. Cell Mol Life Sci 67(14):2425–2437
Maretzky T, Schulte M, Ludwig A, Rose-John S, Blobel C, Hartmann D, Altevogt P, Saftig P, Reiss K (2005) L1 is sequentially processed by two differently activated metalloproteases and presenilin/gamma-secretase and regulates neural cell adhesion, cell migration, and neurite outgrowth. Mol Cell Biol 25:9040–9053
Mechtersheimer S, Gutwein P, Agmon-Levin N, Stoeck A, Oleszewski M, Riedle S, Postina R, Fahrenholz F, Fogel M, Lemmon V, Altevogt P (2001) Ectodomain shedding of L1 adhesion molecule promotes cell migration by autocrine binding to integrins. J Cell Biol 155:661–673
Matsumoto-Miyai K, Ninomiya A, Yamasaki H, Tamura H, Nakamura Y, Shiosaka S (2003) NMDA-dependent proteolysis of presynaptic adhesion molecule L1 in the hippocampus by neuropsin. J Neurosci 23:7727–7736
Yap CC, Vakulenko M, Kruczek K, Motamedi B, Digilio L, Liu JS, Winckler B (2012) Doublecortin (DCX) Mediates Endocytosis of Neurofascin Independently of Microtubule Binding. J Neurosci 32:7439–7453
Gray-Owen SD, Blumberg RS (2006) CEACAM1: contact-dependent control of immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 6:433–446
Brümmendorf T, Rathjen FG (1995) Cell adhesion molecules 1: immunoglobulin superfamily. Protein Profile 2:963–1108
Klaile E, Vorontsova O, Sigmundsson K, Muller MM, Singer BB, Ofverstedt LG, Svensson S, Skoglund U, Obrink B (2009) The CEACAM1N-terminal Ig domain mediates cis- and trans-binding and is essential for allosteric rearrangements of CEACAM1 microclusters. J Cell Biol 187:553–567
Kostrewa D, Brockhaus M, D’Arcy A, Dale GE, Nelboeck P, Schmid G, Mueller F, Bazzoni G, Dejana E, Bartfai T, Winkler FK, Hennig M (2001) X-ray structure of junctional adhesion molecule: structural basis for homophilic adhesion via a novel dimerization motif. EMBO J 20:4391–4398
Soroka V, Kolkova K, Kastrup JS, Diederichs K, Breed J, Kiselyov VV, Poulsen FM, Larsen IK, Welte W, Berezin V, Bock E, Kasper C (2003) Structure and interactions of NCAM Ig1-2-3 suggest a novel zipper mechanism for homophilic adhesion. Structure 11:1291–1301
Mortl M, Sonderegger P, Diederichs K, Welte W (2007) The crystal structure of the ligand-binding module of human TAG-1 suggests a new mode of homophilic interaction. Protein Sci 16:2174–2183
Muller MM, Klaile E, Vorontsova O, Singer BB, Obrink B (2009) Homophilic adhesion and CEACAM1-S regulate dimerization of CEACAM1-L and recruitment of SHP-2 and c-Src. J Cell Biol 187:569–581
Bergelson JM, Cunningham JA, Droguett G, Kurt-Jones EA, Krithivas A, Hong JS, Horwitz MS, Crowell RL, Finberg RW (1997) Isolation of a common receptor for Coxsackie B viruses and adenoviruses 2 and 5. Science 275:1320–1323
Tomko RP, Xu R, Philipson L (1997) HCAR and MCAR: the human and mouse cellular receptors for subgroup C adenoviruses and group B coxsackieviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:3352–3356
Cohen CJ, Gaetz J, Ohman T, Bergelson JM (2001) Multiple regions within the coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor cytoplasmic domain are required for basolateral sorting. J Biol Chem 276:25392–25398
Excoffon KJ, Hruska-Hageman A, Klotz M, Traver GL, Zabner J (2004) A role for the PDZ-binding domain of the coxsackie B virus and adenovirus receptor (CAR) in cell adhesion and growth. J Cell Sci 117:4401–4409
Honda T, Saitoh H, Masuko M, Katagiri-Abe T, Tominaga K, Kozakai I, Kobayashi K, Kumanishi T, Watanabe YG, Odani S, Kuwano R (2000) The coxsackievirus-adenovirus receptor protein as a cell adhesion molecule in the developing mouse brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 77:19–28
Patzke C, Max KEA, Behlke J, Schreiber J, Schmidt H, Dorner AA, Kroger S, Henning M, Otto A, Heinemann U, Rathjen FG (2010) The coxsackievirus-adenovirus receptor reveals complex homophilic and heterophilic interactions on neural cells. J Neurosci 30:2897–2910
Zen K, Liu Y, McCall IC, Wu T, Lee W, Babbin BA, Nusrat A, Parkos CA (2005) Neutrophil migration across tight junctions is mediated by adhesive interactions between epithelial coxsackie and adenovirus receptor and a junctional adhesion molecule-like protein on neutrophils. Mol Biol Cell 16:2694–2703
Witherden DA, Verdino P, Rieder SE, Garijo O, Mills RE, Teyton L, Fischer WH, Wilson IA, Havran WL (2010) The junctional adhesion molecule JAML is a costimulatory receptor for epithelial gammadelta T cell activation. Science 329:1205–1210
van Raaij MJ, Chouin E, van der ZH, Bergelson JM, Cusack S (2000) Dimeric structure of the coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor D1 domain at 1.7 A resolution. Structure 8:1147–1155
Verdino P, Witherden DA, Havran WL, Wilson IA (2010) The molecular interaction of CAR and JAML recruits the central cell signal transducer PI3K. Science 329:1210–1214
Prota AE, Campbell JA, Schelling P, Forrest JC, Watson MJ, Peters TR, Aurrand-Lions M, Imhof BA, Dermody TS, Stehle T (2003) Crystal structure of human junctional adhesion molecule 1: implications for reovirus binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:5366–5371
Staunton DE, Dustin ML, Erickson HP, Springer TA (1990) The arrangement of the immunoglobulin-like domains of ICAM-1 and the binding sites for LFA-1 and rhinovirus. Cell 61:243–254
Kulahin N, Kristensen O, Rasmussen KK, Olsen L, Rydberg P, Vestergaard B, Kastrup JS, Berezin V, Bock E, Walmod PS, Gajhede M (2011) Structural model and trans-interaction of the entire ectodomain of the olfactory cell adhesion molecule. Structure 19:203–211
Su XD, Gastinel LN, Vaughn DE, Faye I, Poon P, Bjorkman PJ (1998) Crystal structure of hemolin: a horseshoe shape with implications for homophilic adhesion. Science 281:991–995
Freigang J, Proba K, Leder L, Diederichs K, Sonderegger P, Welte W (2000) The crystal structure of the ligand binding module of axonin-1/TAG-1 suggests a zipper mechanism for neural cell adhesion. Cell 101:425–433
Rader C, Kunz B, Lierheimer R, Giger RJ, Berger P, Tittmann P, Gross H, Sonderegger P (1996) Implications for the domain arrangement of axonin-1 derived from the mapping of its NgCAM binding site. EMBO J 15:2056–2068
Liu H, Focia PJ, He X (2011) Homophilic adhesion mechanism of neurofascin, a member of the L1 family of neural cell adhesion molecules. J Biol Chem 286:797–805
Schurmann G, Haspel J, Grumet M, Erickson HP (2001) Cell adhesion molecule L1 in folded (horseshoe) and extended conformations. Mol Biol Cell 12:1765–1773
Hall H, Bozic D, Fauser C, Engel J (2000) Trimerization of cell adhesion molecule L1 mimics clustered L1 expression on the cell surface: influence on L1-ligand interactions and on promotion of neurite outgrowth. J Neurochem 75:336–346
He Y, Jensen GJ, Bjorkman PJ (2009) Cryo-electron tomography of homophilic adhesion mediated by the neural cell adhesion molecule L1. Structure 17:460–471
Sasakura H, Inada H, Kuhara A, Fusaoka E, Takemoto D, Takeuchi K, Mori I (2005) Maintenance of neuronal positions in organized ganglia by SAX-7, a Caenorhabditis elegans homologue of L1. EMBO J 24:1477–1488
Wang X, Kweon J, Larson S, Chen L (2005) A role for the C. elegans L1CAM homologue lad-1/sax-7 in maintaining tissue attachment. Dev Biol 284:273–291
Wang X, Zhang W, Cheever T, Schwarz V, Opperman K, Hutter H, Koepp D, Chen L (2008) The C. elegans L1CAM homologue LAD-2 functions as a coreceptor in MAB-20/Sema2 mediated axon guidance. J Cell Biol 180:233–246
Pocock R, Benard CY, Shapiro L, Hobert O (2008) Functional dissection of the C. elegans cell adhesion molecule SAX-7, a homologue of human L1. Mol Cell Neurosci 37:56–68
Volkmer H, Hassel B, Wolff JM, Frank R, Rathjen FG (1992) Structure of the axonal surface recognition molecule neurofascin and its relationship to a neural subgroup of the immunoglobulin superfamily. J Cell Biol 118:149–161
Kriebel M, Wuchter J, Trinks S, Volkmer H (2012) Neurofascin: a switch between neuronal plasticity and stability. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 44:694–697
Hassel B, Rathjen FG, Volkmer H (1997) Organization of the neurofascin gene and analysis of developmentally regulated alternative splicing. J Biol Chem 272:28742–28749
Pruss T, Kranz EU, Niere M, Volkmer H (2006) A regulated switch of chick neurofascin isoforms modulates ligand recognition and neurite extension. Mol Cell Neurosci 31:354–365
Volkmer H, Leuschner R, Zacharias U, Rathjen FG (1996) Neurofascin induces neurites by heterophilic interactions with axonal NrCAM while NrCAM requires F11 on the axonal surface to extend neurites. J Cell Biol 135:1059–1069
Volkmer H, Zacharias U, Norenberg U, Rathjen FG (1998) Dissection of complex molecular interactions of neurofascin with axonin-1, F11, and tenascin-R, which promote attachment and neurite formation of tectal cells. J Cell Biol 142:1083–1093
Pruss T, Niere M, Kranz EU, Volkmer H (2004) Homophilic interactions of chick neurofascin in trans are important for neurite induction. Eur J Neurosci 20:3184–3188
Grumet M, Mauro V, Burgoon MP, Edelman GM, Cunningham BA (1991) Structure of a new nervous system glycoprotein, Nr-CAM, and its relationship to subgroups of neural cell adhesion molecules. J Cell Biol 113:1399–1412
Kayyem JF, Roman JM, de la Rosa EJ, Schwarz U, Dreyer WJ (1992) Bravo/Nr-CAM is closely related to the cell adhesion molecules L1 and Ng-CAM and has a similar heterodimer structure. J Cell Biol 118:1259–1270
Wang B, Williams H, Du JS, Terrett J, Kenwrick S (1998) Alternative splicing of human NrCAM in neural and nonneural tissues. Mol Cell Neurosci 10:287–295
Jouet M, Rosenthal A, Kenwrick S (1995) Exon 2 of the gene for neural cell adhesion molecule L1 is alternatively spliced in B cells. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 30:378–380
De Angelis E, Brümmendorf T, Cheng L, Lemmon V, Kenwrick S (2001) Alternative use of a mini exon of the L1 gene affects L1 binding to neural ligands. J Biol Chem 276:32738–32742
Jacob J, Haspel J, Kane-Goldsmith N, Grumet M (2002) L1 mediated homophilic binding and neurite outgrowth are modulated by alternative splicing of exon 2. J Neurobiol 51:177–189
Johnson CP, Fujimoto I, Perrin-Tricaud C, Rutishauser U, Leckband D (2004) Mechanism of homophilic adhesion by the neural cell adhesion molecule: use of multiple domains and flexibility. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:6963–6968
Carafoli F, Saffell JL, Hohenester E (2008) Structure of the tandem fibronectin type 3 domains of neural cell adhesion molecule. J Mol Biol 377:524–534
Plagge A, Brümmendorf T (1997) The gene of the neural cell recognition molecule F11: conserved exon-intron arrangement in genes of neural members of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Gene 192:215–225
Kozlov SV, Giger RJ, Hasler T, Korvatska E, Schorderet DF, Sonderegger P (1995) The human TAX1 gene encoding the axon-associated cell adhesion molecule TAG-1/axonin-1: genomic structure and basic promoter. Genomics 30:141–148
Lee S, Takeda Y, Kawano H, Hosoya H, Nomoto M, Fujimoto D, Takahashi N, Watanabe K (2000) Expression and regulation of a gene encoding neural recognition molecule NB-3 of the contactin/F3 subgroup in mouse brain. Gene 245:253–266
De BL, Polizzi A, Cangiano G, Buttiglione M, Arbia S, Storlazzi CT, Rocchi M, Gennarini G (2001) Alternative promoters drive the expression of the gene encoding the mouse axonal glycoprotein F3/contactin. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 95:55–74
Acknowledgments
The authors’ work was supported by a grant from DFG (Ra424/5-1). The critical reading of the manuscript by Dr Alistair Garratt is greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special Issue: In Honor of Elisabeth Bock.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Volkmer, H., Schreiber, J. & Rathjen, F.G. Regulation of Adhesion by Flexible Ectodomains of IgCAMs. Neurochem Res 38, 1092–1099 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0888-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0888-9