Abstract
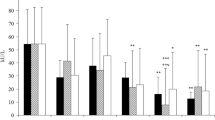
Taurine (2-aminoethanesulfonic acid) is a free sulfur-containing β-amino acid which has antioxidant, antiinflammatory and detoxificant properties. In the present study, the role of endotoxemia on peroxynitrite formation via 3-nitrotyrosine (3-NT) detection, and the possible antioxidant effect of taurine in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated guinea pigs were aimed. 40 adult male guinea pigs were divided into four groups; control, endotoxemia, taurine and taurine+endotoxemia. Animals were administered taurine (300 mg/kg), LPS (4 mg/kg) or taurine plus LPS intraperitoneally. After 6 h of incubation, when highest blood levels of taurine and endotoxin were attained, the animals were sacrificed and spleen samples were collected. The amounts of 3-nitrotyrosine and taurine were measured by HPLC, and reactive nitrogen oxide species (NOx) which are stable end products of nitric oxide was measured spectrophotometrically in spleen tissues. LPS administration significantly decreased the concentration of taurine whilst increased levels of 3-NT and NOx compared with control group. It was determined that taurine treatment decreased the levels of 3-nitrotyrosine and NOx in taurine+endotoxemia group. The group in which taurine was administered alone, contradiction to well-known antioxidant effect, taurine caused elevated concentration of 3-NT and NOx. This data suggest that taurine protects spleen against oxidative damage in endotoxemic conditions. However, the effect of taurine is different when it is administered alone. In conclusion, taurine may act as an antioxidant during endotoxemia, and as a prooxidant in healthy subjects at this dose.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bian K, Murad F (2001) Diversity of endotoxin-induced nitrotyrosine formation in macrophage-endothelium-rich organs. Free Radic Biol Med 31:421–429
Lin NT, Yang FL, Lee RP, Peng TC, Chen HI (2006) Inducible nitric oxide synthase mediates cytokine release: the time course in conscious and septic rats. Life Sci 78:1038–1043
Yilmaz G, Gursoy-Ozdemir Y, Dogan AI, Gurdal H, Gedikoglu G, Dalkara T, Guc MO (2001) Spleen damage in endotoxaemic mice: the involvement of nitric oxide. J Physiol Pharmacol 52:729–744
Isobe H, Okajima K, Uchiba M, Mizutani A, Harada N, Nagasaki A, Okabe K (2001) Activated protein C prevents endotoxin-induced hypotension in rats by inhibiting excessive production of nitric oxide. Circulation 104:1171–1175
Liu S, Adcock IM, Old RW, Barnes PJ, Evans TW (1993) Lipopolysaccharide treatment in vivo induces widespread tissue expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase mRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 196:1208–1213
Duncan MW (2003) A review of approaches to the analysis of 3-nitrotyrosine. Amino Acids 25:351–361
Guc MO (1999) Endotoxin-endothelium interactions in low-perfusion state research. J Physiol Pharmacol 50:541–550
van der Vliet A, Eiserich JP, Kaur H, Cross CE, Halliwell B (1996) Nitrotyrosine as biomarker for reactive nitrogen species. Methods Enzymol 269:175–184
Parratt JR (1997) Nitric oxide: a key mediator in sepsis and endotoxaemia? J Physiol Pharmacol 48:493–506
Sakemi K, Ohno Y, Tsuda M (1998) Nitrite/nitrate levels in blood and principal organs in rats treated with lipopolysaccharide. Kokuritsu Iyakuhin Shokuhin Eisei Kenkyusho Hokoku 116:101–106
Hofmann AF, Small DM (1967) Detergent properties of bile salts: correlation with physiological function. Annu Rev Med 18:333–376
Timbrell JA, Waterfield CJ (1996) Changes in taurine as an indicator of hepatic dysfunction and biochemical perturbations. Studies in vivo and in vitro Adv Exp Med Biol 403:125–134
Wu C, Miyagawa C, Kennedy DO, Yano Y, Otoni S, Matsui-Yuasa I (1997) Involvement of polyamines in the protection of taurine against the cytotoxicity of hydrazine or carbon tetrachloride in isolated rat hepatocytes. Chem Biol Interact 103:213–224
Thurston JH, Hauhart RE, Dirgo JA (1980) Taurine: a role in osmotic regulation of mammalian brain and possible clinical significance. Life Sci 26:1561–1568
Schuller-Levis GB, Park E (2004) Taurine and its chloramine: modulators of immunity. Neurochem Res 29:117–126
Pasantes-Morales H, Wright CE, Gaull GE (1985) Taurine protection of lymphoblastoid cells from iron-ascorbate induced damage. Biochem Pharmacol 34:2205–2207
Takahashi K, Harada H, Schaffer SW, Azuma J (1992) Effect of taurine on intracellular calcium dynamics of cultured myocardial cells during the calcium paradox. Adv Exp Med Biol 315:153–161
Hayes KC, Stephan ZF, Sturman JA (1980) Growth depression in taurinedepleted infant monkeys. J Nutr 110:2058–2064
Kulakowski EC, Maturo J (1984) Hypoglycemic properties of taurine not mediated by enhanced insulin release. Biochem Pharmacol 33:2835–2838
Silva LA, Silveira PC, Ronsani MM, Souza PS, Scheffer D, Vieira LC, Benetti M, De Souza CT, Pinho RA (2011) Taurine supplementation decreases oxidative stress in skeletal muscle after eccentric exercise. Cell Biochem Funct 29:43–49
Mehta TR, Dawson R (2001) Taurine is a weak scavenger of peroxynitrite and does not attenuate sodium nitroprusside toxicity to cells in culture. Amino Acids 20:419–433
Tappaz ML (2004) Taurine biosynthetic enzymes and taurine transporter: molecular identification and regulations. Neurochem Res 29:83–96
Duffy AJ, Nolan B, Sheth K, Collette H, De M, Bankey PE (2000) Inhibition of alveolar neutrophil immigration in endotoxemia is macrophage inflammatory protein 2 independent. J Surg Res 90:51–57
Egan BM, Abdih H, Kelly CJ, Condron C, Bouchier-Hayes DJ (2001) Effect of intravenous taurine on endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in sheep. Eur J Surg 167:575–580
Kamisaki Y, Wada K, Nakamoto K, Kishimoto Y, Kitano M, Itoh T (1996) Sensitive determination of nitrotyrosine in humans by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B Biomed Appl 685:343–347
Maruyama W, Hashizume Y, Matsubara K, Naoi M (1996) Identification of 3-nitro-l-tyrosine, a product of nitric oxide and superoxide, as an indicator of oxidative stress in the human brain. J Chromatogr B Biomed Appl 676:153–158
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR (1982) Analyses of nitrate, nitrite and [15N] nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 126:131–138
McMahon GP, O’Kennedy R, Kelly MT (1996) High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of taurine in human plasma using pre-column extraction and derivatization. J Pharm Biomed Anal 14:1287–1294
Nusetti S, Obregon F, Lima L (2006) Neuritic outgrowth from goldfish retinal explants, interaction of taurine and zinc. Adv Exp Med Biol 583:435–440
Romanovsky AA, Petersen SR (2003) The spleen: another mystery about its function. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 284:1378–1379
Molina PE, Qian L, Schuhlein D, Naukam R, Wang H, Tracey KJ, Abumrad NN (1998) CNI-1493 attenuates hemodynamic and pro-inflammatory responses to lps. Shock 10:329–334
Kan W, Zhao KS, Jiang Y, Yan W, Huang Q, Wang J, Qin Q, Huang X, Wang S (2004) Lung, spleen, and kidney are the major places for inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in endotoxic shock: role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in signal transduction of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression. Shock 21:281–287
Sanikidze TV, Tkhilava NG, Papava MB, Datunashvili IV, Gongadze MT, Gamrekelashvili DD, Bakhutashvili VI (2006) Role of free nitrogen and oxygen radicals in the pathogenesis of lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxemia. Bull Exp Biol Med 142:211–215
Erdem A, Sevgili AM, Akbiyik F, Atilla P, Cakar N, Balkanci ZD, Iskit AB, Guc MO (2008) The effect of taurine on mesenteric blood flow and organ injury in sepsis. Amino Acids 35:403–410
Erdamar H, Turkozkan N, Balabanli B, Ozan G, Bircan FS (2007) The relationship between taurine and 3-nitrotyrosine level of hepatocytes in experimental endotoxemia. Neurochem Res 32:1965–1968
Marcinkiewicz J, Grabowska A, Bereta J, Bryniarski K, Nowak B (1998) Taurine chloramine down-regulates the generation of murine neutrophil inflammatory mediators. Immunopharmacology 40:27–38
Nagl M, Hess MW, Pfaller K, Hengster P, Gottardi W (2000) Bactericidal activity of micromolar n-chlorotaurine: evidence for its antimicrobial function in the human defense system. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44:2507–2513
Kim C, Chung JK, Jeong JM, Chang YS, Lee YJ, Kim YJ, Lee MC, Koh CS, Kim BK (1998) Uptake of taurine and taurine chloramine in murine macrophages and their distribution in mice with experimental inflammation. Adv Exp Med Biol 442:169–176
Marcinkiewicz J, Nowak B, Grabowska A, Bobek M, Petrovska L, Chain B (1999) Regulation of murine dendritic cell functions in vitro by taurine chloramine, a major product of the neutrophil myeloperoxidase-halide system. Immunology 98:371–378
Park E, Quinn MR, Wright CE, Schuller-Levis G (1993) Taurine chloramine inhibits the synthesis of nitric oxide and the release of tumor necrosis factor in activated RAW 264.7 cells. J. Leukoc Biol 54:119–124
Kim C, Park E, Quinn MR, Schuller-Levis G (1996) The production of superoxide anion and nitric oxide by cultured murine leukocytes and the accumulation of TNF-α in the conditoned media is inhibited by taurine chloramine. Immunopharmacology 34:89–95
Janssen HF, Lombardini JB, Lust RM (1983) Cardiac taurine levels during endotoxemia. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 172:407–411
Engel JM, Muhling J, Weiss S, Karcher B, Lohr T, Menges T, Little S, Hempelmann G (2006) Relationship of taurine and other amino acids in plasma and in neutrophils of septic trauma patients. Amino Acids 30:87–94
Chiarla C, Giovannini I, Siegel JH (2003) Co-variation of plasma sodium, taurine and other amino acid levels in critical illness. Amino Acids 24:89–93
Stapleton PP, Redmond HP, Bouchier-Hayes DJ (1997) Taurine and inflammation-A new approach to an old problem? J Leukoc Biol 61:231–232
Houdijk AP, Oostering SJ, Siroen MP, de Jong S, Richir M, Rijssenbeck AL, Teerlink T, van Leeuwen PA (2006) Hypertaurinemia in bile duct-ligated rats after surgery: the effect of gut endotoxin restriction on organ fluxes and oxidative status. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 30:186–193
Parildar-Karpuzoglu H, Mehmetcik G, Ozdemirler-Erata G, Dogru-Abbasoglu S, Kocak-Toker N, Uysal M (2008) Effect of taurine treatment on pro-oxidantant/oxidant balance in livers and brains of old rats. Pharmacol Rep 60:673–678
Parildar H, Dogru-Abbasoglu S, Mehmetcik G, Ozdemirler G, Kocak-Toker N, Uysal M (2008) Lipid peroxidation potential and antioxidants in the heart tissue of β-alanine or taurine-treated old rats. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 54:61–65
Uchida S, Kwon HM, Yamauchi A, Preston AS, Marumo F, Handler JS (1992) Molecular cloning of the cDNA for an MDCK cell Na+ and Cl− dependent taurine transporter that is regulated by hypetonicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:8230–8234
Jones DP, Miller LA, Chesney RW (1995) The relative roles of external taurine concentration and medium osmolality in the regulation of taurine transport in LLC-PKI and MDCK cells. Pediatr Res 37:227–232
Bridges CC, Ola MS, Prasad PD (2001) Regulation of taurine transporter expression by NO in cultured human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 281:C1825–C1836
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Gazi University, Department of Scientific Research Projects Unit. The authors thank TUBITAK (The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey) for the fellowship to F.S.B.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bircan, F.S., Balabanli, B., Turkozkan, N. et al. Effects of Taurine on Nitric Oxide and 3-Nitrotyrosine Levels in Spleen During Endotoxemia. Neurochem Res 36, 1978–1983 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-011-0521-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-011-0521-3