Abstract
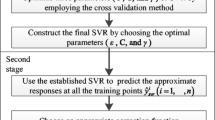
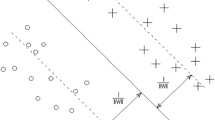
Traditional methods of constructing of least square support vector regression (LSSVR) do not consider the gradients of the true function but just think about the exact responses at samples. If gradient information is easy to get, it should be used to enhance the surrogate. In this paper, the gradient-enhanced least square support vector regression (GELSSVR) is developed with a direct formulation by incorporating gradient information into the traditional LSSVR. The efficiencies of this technique are compared by analytical function fitting and two real life problems (the recent U.S. actuarial life table and Borehole). The results show that GELSSVR provides more reliable prediction results than LSSVR alone.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander IJ, Forrester AJK (2009) Recent advances in surrogate-based optimization. Prog Aerosp Sci 45:50–79
Ankenman BE, Nelson BL, Staum J (2010) Stochastic kriging for simulation metamodeling. Oper Res 58(2):371–382
Bendtsen C, Stauning O (1996) Fadbad, a flexible c++ package for automatic differentiation. Tech. rep., Technical University of Denmark, IMM, Departement of Mathematical Modeling
Bischof C, Khademi P, Mauer A, Carle A (1996) Adifor 2.0: Automatic differentiation of fortran 77 programs. Comput Sci Eng, IEEE 3(3):18–32
Bischof CH, Roh L, Mauer-Oats AJ (1997) Adic: an extensible automatic differentiation tool for ansi-c. Softw Pract Exp 27(12):1427–1456
Bischof CH, Bucker H, Lang B, Rasch A, Vehreschild A (2002) Combining source transformation and operator overloading techniques to compute derivatives for matlab programs. In: Source Code Analysis and Manipulation, 2002. Proceedings. Second IEEE International Workshop on, IEEE, pp 65–72
Chen X, Ankenman BE, Nelson BL (2013) Enhancing stochastic kriging metamodels with gradient estimators. Oper Res 61(2):512–528
Chung HS, Alonso JJ (2001) Using gradients to construct response surface models for high-dimensional design optimization problems. In: 39th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, AIAA, Reno, NV, USA
Chung HS, Alonso JJ (2002a) Design of a low-boom supersonic business jet using cokriging approximation models. In: 9th AIAA/ISSMO Symposium on Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization, AIAA, Atlanta, GA, USA
Chung HS, Alonso JJ (2002b) Using gradients to construct cokriging approximation models for high-dimensional design optimization problems. In: 40th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, AIAA, Reno, NV, USA
Coleman TF, Verma A (2000) Admit-1: automatic differentiation and matlab interface toolbox. ACM Trans Math Softw 26(1):150–175
Giering R, Kaminski T (1998) Recipes for adjoint code construction. ACM Trans Math Softw 24(4):437–474
Giles MB, Pierce NA (2000) An introduction to the adjoint approach to design. Flow, Turbul Combust 65(3–4):393–415
Golub GH, Van Loan CF (1989) Matrix computations. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
Griewank A (2000) Evaluating derivatives: principles and techniques of algorithmic differentiation. SIAM, Philadelphia, PA, USA
Griewank A, Juedes D, Utke J (1996) Adol-c, a package for the automatic differentiation of algorithms written in c/c++. ACM Trans Math Softw 22(2):131–167
Han ZH, Gortz S, Zimmermann R (2009) On improving efficiency and accuracy of variable-fidelity surrogate modeling in aero-data for loads context. In: Proceedings of European Air and Space Conference, CEAS, Manchester, UK
Hascot L (2004) Tapenade: a tool for automatic differentiation of programs. In: Proceedings of 4th European congress on computational methods, ECCOMAS, Jyvaskyla, Finland, pp 1–14
Jones BL, Mereu JA (2002) A critique of fractional age assumptions. Insur Math Econ 30:363–370
Laurenceau J, Sagaut P (2008) Building efficient response surfaces of aerodynamic functions with kriging and cokriging. AIAA J 46(2):498–507
Leary SJ, Bhaskar A, Keane AJ (2004) A derivative based surrogate model for approximating and optimizing the output of an expensive computer simulation. J Global Optim 30(1):39–58
Liu W, Batill S (2000) Gradient-enhanced neural network response surface approximations. In: 8th AIAA/ISSMO Symposium and Exhibit on Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization, AIAA, Long Beach, California, USA
Liu W, Batill SM (2002) Gradient-enhanced response surface approximations using kriging models. In: 9th AIAA/ISSMO Symposium and Exhibit on Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization, AIAA, Atlanta, Georgia, USA
Luo Y, Tao D, Geng B, Xu C, Maybank SJ (2013a) Manifold regularized multitask learning for semi-supervised multilabel image classification. Image Proc IEEE Trans 22(2):523–536
Luo Y, Tao D, Xu C, Xu C, Liu H, Wen Y (2013b) Multiview vector-valued manifold regularization for multilabel image classification. IEEE Trans Neural Networks Learn Syst 24(5):709–722
McKay MD, Bechman RJ, Conover WJ (1979) A comparison of three methods for selecting values of input variables in the analysis of output from a computer code. Technometrics 21(2):239–245
Mitra NJ, Nguye A (2003) Estimating surface normals in noisy point cloud data. Int J Comput Geom Appl 14:261–276
Morris MD, Mitchell TJ, Ylvisaker D (1993) Bayesian design and analysis of computer experiments: use of derivatives in surface prediction. Technometrics 35(3):243–255
NLBowers, Gether HU, Hiekman JC, Jones DA, Nesbi CJ (1986) Actuarial mathematics. Society of Actuaries Schaumburg
Saunders C, Gammerman A, Vovk V (1998) Ridge regression learning algorithm in dual variables. In: (ICML-1998) Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Machine Learning, Morgan Kaufmann, Madison, Wisconsin, USA, pp 515–521
Shiriaev D, Griewank A (1996) Adol-f automatic differentiation of fortran codes. In: Computational differentiation: techniques, applications, and tools, SIAM, Philadelphia, PA, USA, pp 375–384
Smola AJ, Schlkopf B (2004) A tutorial on support vector regression. Stat Comput 14(3):199–222
Sobester A (2003) Enhancements to global design optimization techniques. PhD thesis
Stephenson G (2010) Using derivative information in the statistical analysis of computer models. PhD thesis
Van KF, Vervenne K (2004) Gradient-enhanced response surface building. Struct Multi Optim 27:337–351
Vapnik VN (1995) The nature of statistical learning theory. Springer, New York
Wang GG, Shan S (2007) Review of metamodeling techniques in support of engineering design optimization. J Mech Des 129(4):370–381
Yamazaki W, Rumpfkeil MP, Mavriplis DJ (2010) Design optimization utilizing gradient/hessian enhanced surrogate model. In: 28th AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference, AIAA, Chicago, Illinois, USA
Zhou XJ, Ma YZ (2013) A study on smo algorithm for solving -svr with non-psd kernels. Commun Stat Simul Comput 40(10):2175–2196
Zhou XJ, Ma YZ, Li XF (2011) Ensemble of surrogates with recursive arithmetic average. Struct Multi Optim 44(5):651–671
Zhou XJ, Ma YZ, Tu YL, Feng Y (2012) Ensemble of surrogates for dual response surface modeling in robust parameter design. Qual Reliab Eng Int 29(2):173–197
Acknowledgments
The funding provided for this study by National Science Foundation for Young Scientists of China under Grant NO.71401080, the University Social Science Foundation of Jiangsu under Grant NO.2013SJB6300072 & NO.TJS211021, the University Science Foundation of Jiangsu under Grant NO.12KJB630002, and the Talent Introduction Foundation of Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications under Grant NO.NYS212008 & NO.D/2013/01/104 are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X.J., Jiang, T. Enhancing Least Square Support Vector Regression with Gradient Information. Neural Process Lett 43, 65–83 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-014-9402-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-014-9402-5