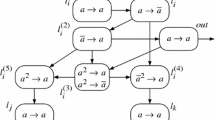
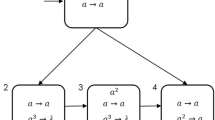
Abstract
Spiking neural P systems with inhibitory synapses (ISN P systems, for short) are a class of discrete neural-like computing models, which are inspired by the way of biological neurons storing and processing information and communication by means of excited and inhibitory impulses. In this work, we prove that ISN P systems can compute and accept any set of Turing computable numbers by using one type of neurons, thus can achieve Turing universality. Such systems are called homogenous ISN P systems. The results give a positive answer to an open problem left in (Pan and Păun, Int J Comput Commun 4(3):273–282, 2009) that “whether the number of types of neurons in universal SN P systems can be decreased by using inhibitory synapses”. The obtained result is optimal in the sense of having minimal number of types of neurons in Turing universal SN P systems.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rozenberg G, Bck T, Kok JN (2011) Handbook of natural computing. Springer, Berlin
Păun G (2000) Computing with membranes. J Comput Syst Sci 61(1):108–143
Freund R, Păun G, Pérez-Jiménez MJ (2005) Tissue-like P systems with channel-states. Theor Comput Sci 330:101–116
Ionescu M, Păun G, Yokomori T (2006) Spiking neural P systems. Fund Inf 71(2–3):279–308
Nishida TY (2004) An approximate algorithm for NP-complete optimization problems exploiting P systems. In Proceedings of Brainstorming Workshop on Uncertainty in Membrane, Computing, 185–192
Zhang G, Cheng J, Gheorghe M, Meng Q (2013) A hybrid approach based on differential evolution and tissue membrane systems for solving constrained manufacturing parameter optimization problems. Appl Soft Comput 13(3):1528–1542
Păun G, Rozenberg G, Salomaa A (2010) The Oxford handbook of membrane computing. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Siegelmann HT, Sontag ED (1995) On the computational power of neural nets. J Comput System Sci 50(1):132–150
Pan L, Zeng X (2010) A note on small universal spiking neural P systems. LNCS 5957:436–447
Pollack JB (1991) The induction of dynamical recognizers. Mach Learn 7(2–3):227–252
Giles CL, Omlin CW (1992), Inserting rules into recurrent neural networks. Neural Networks for Signal Processing II. In Proceedings of the Signal Processing, Workshop, 13–22
Hyoetyniemi H (1996) Turing machines are recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of Genes, Nets And Symbols. Helsinki, Finland: Finnish Artificial Intelligence Society, 13–24
Moore C (1998) Dynamical recognizers: real-time language recognition by analog computers. Theor Comput Sci 201:99–136
Maass W (1997) Networks of spiking neurons: the third generation of neural network models. Neural Netw 10:1659–1671
Maass W, Schmitt M (1999) On the complexity of learning for spiking neurons with temporal coding. Inf Comput 153(1):26–46
Natschläger T, Maass W (2002) Spiking neurons and the induction of finite state machines. Theor Comput Sci 287(1):251–265
Ghosh DS, Adeli H (2009) Spiking neural networks. Int J Neural Syst 19(4):295–308
Pan L, Păun G (2010) Spiking neural P systems: an improved normal form. Theor Comput Sci 411(6):906–918
Zeng X, Pan L (2009) Homogeneous spiking neural P systems. Fund Inf 97:275–294
Chen H, Freund R, Ionescu M et al (2007) On string languages generated by spiking neural P systems. Fund Inf 75(1–4):141–162
Zhang X, Zeng X, Pan L (2008) On string languages generated by SN P systems with exhaustive use of rules. Nat Comput 7(4):535–549
Pan L, Zeng X (2011) Small universal spiking neural P systems working in exhaustive mode. IEEE Trans Nanobiosci 10(2):99–105
Păun A, Păun G (2007) Small universal spiking neural P systems. Biosystems 90:48–60
Ishdorj TO, Leporati A, Pan L et al (2010) Deterministic solutions to QSAT and Q3SAT by spiking neural P systems with pre-computed resources. Theor Comput Sci 411(25):2345–2358
Pan L, Păun G, Pérez-Jiménez MJ (2011) Spiking neural P systems with neuron division and budding. Sci China Inform Sci 54(8):1596–1607
Ionescu M, Sburlan D (2007) Some applications of spiking neural P systems. In Proceedings of the Eighth Workshop on Membrane Computing, Thessaloniki, 383–394
Cavaliere M, Ibarra OH, Păun G (2009) Asynchronous spiking neural P systems. Theor Comput Sci 410:2352–2364
Song T, Pan L, Păun G (2013) Asynchronous spiking neural P systems with local synchronization. Inf Sci 219:197–207
Pan L, Wang J, Hoogeboom HJ (2012) Spiking neural P systems with astrocytes. Neural Comput 24:1–24
Macías-Ramos LF, Pérez-Jiménez MJ (2013) Spiking neural P systems with functional astrocytes. LNCS 7762:228–242
Păun G (2007) Spiking neural P systems with astrocyte-like control. J Univers Comput Sci 13(11):1707–1721
Song T, Pan L (2014) Spiking neural P systems with rules on synapses. Theor Comput Sci 529:82–95
Pan L, Păun G (2009) Spiking neural P systems with anti-spikes. Int J Comput Commun 4(3):273–282
Song T, Pan L, Wang J et al (2012) Normal forms of spiking neural P systems with anti-spikes. IEEE Trans Nanobiosci 4(11):352–359
Rozenberg G, Salomaa A (1997) Handbook of formal languages. Springer, Berlin
Minsky M (1967) Computation: finite and infinite machines. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Păun G (2002) Membrane computing: an introduction. Springer, Berlin
Cavaliere M, Egecioglu O, Ibarra OH et al (2009) Asynchronous spiking neural P systems. Theor Comput Sci 410:2352–2364
Song T, Wang X, Zhang Z et al (2013) Homogenous spiking neural P systems with anti-spikes. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-013-1397-8
Nishida TY (2006) Membrane algorithms: approximate algorithms for np-complete optimization problems. Applications of membrane computing. Springer, Berlin
Zhang G, Gheorghe M, Li Y (2012) A membrane algorithm with quantum-inspired subalgorithms and its application to image processing. Nat Comput 11(4):701–717
Zhao J, Wang N (2011) Hybrid optimization method based on membrane computing. Ind Eng Chem Res 50(3):1691–1704
Wang K, Wang N (2011) A protein inspired RNA genetic algorithm for parameter estimation in hydrocracking of heavy oil. Chem Eng J 167(1):228–239
Xiao J, Zhang X, Xu J (2012) A membrane evolutionary algorithm for DNA sequence design in DNA computing. Chin Sci Bull 57(1):698–706
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (61033003, 91130034, 61100145, 61202011 and 61272071), Ph.D. Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (20100142110072 and 2012014213 008), and Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (2011CDA027).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, T., Wang, X. Homogenous Spiking Neural P Systems with Inhibitory Synapses. Neural Process Lett 42, 199–214 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-014-9352-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-014-9352-y