Abstract
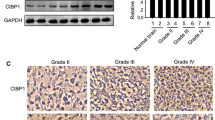
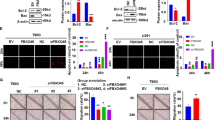
We previously reported that loss of Nrdp1 contributes to human glioma progression by reducing apoptosis. However, the role of Nrdp1 in glioma migration and invasion has not been investigated. Here, we report that ErbB3, a substrate of Nrdp1, is undetectable in normal brain tissues and grade II/III glioma tissues, but is abundant in a certain percentage of grade IV glioma tissues and is associated with the loss of Nrdp1. This suggests that Nrdp1 may be involved in glioma migration and invasion by regulating ErbB3. Thus, the role of Nrdp1/ErbB3 signaling in glioma cell migration and invasion was investigated using Nrdp1 loss- and gain-of-function. The results show that down-regulation of Nrdp1 by use of short hairpin RNA promoted glioma cell migration and invasion. In contrast, overexpression of Nrdp1 significantly inhibited glioma cell migration and invasion. Further investigation on molecular targets revealed that Nrdp1 decreased the level of ErbB3, which resulted in decreasing p-AKT thereby reducing cytoplasmic p27Kip1. Taken together, these findings suggest that Nrdp1-mediated ErbB3 degradation suppresses glioma migration and invasion and that loss of Nrdp1 may amplify ErbB3 signaling to contribute to glioma migration and invasion. These findings suggest that Nrdp1 may be a target for glioma therapy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wen PY, Kesari S (2008) Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med 359(5):492–507
Clarke J, Butowski N, Chang S (2010) Recent advances in therapy for glioblastoma. Arch Neurol 67(3):279–283
Holand K, Salm F, Arcaro A (2011) The phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling pathway as a therapeutic target in grade IV brain tumors. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 11(8):894–918
Buonanno A, Fischbach GD (2001) Neuregulin and ErbB receptor signaling pathways in the nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol 11(3):287–296
Burden S, Yarden Y (1997) Neuregulins and their receptors: a versatile signaling module in organogenesis and oncogenesis. Neuron 18(6):847–855
Stern DF (2003) ErbBs in mammary development. Exp Cell Res 284(1):89–98
Yen L et al (2006) Loss of Nrdp1 enhances ErbB2/ErbB3-dependent breast tumor cell growth. Cancer Res 66(23):11279–11286
Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX (2001) Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2(2):127–137
Salomon DS et al (1995) Epidermal growth factor-related peptides and their receptors in human malignancies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 19(3):183–232
Holbro T et al (2003) The ErbB2/ErbB3 heterodimer functions as an oncogenic unit: ErbB2 requires ErbB3 to drive breast tumor cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(15):8933–8938
Mujoo K et al (2014) Regulation of ERBB3/HER3 signaling in cancer. Oncotarget 5(21):10222–10236
Qiu XB, Goldberg AL (2002) Nrdp1/FLRF is a ubiquitin ligase promoting ubiquitination and degradation of the epidermal growth factor receptor family member, ErbB3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(23):14843–14848
Lu H et al (2014) Nrdp1 inhibits growth of colorectal cancer cells by nuclear retention of p27. Tumour Biol 35(9):8639–8643
Shi H et al (2014) Lower expression of Nrdp1 in human glioma contributes tumor progression by reducing apoptosis. IUBMB Life 66(10):704–710
Fry WH et al (2011) Quantity control of the ErbB3 receptor tyrosine kinase at the endoplasmic reticulum. Mol Cell Biol 31(14):3009–3018
Andersson U et al (2004) Epidermal growth factor receptor family (EGFR, ErbB2-4) in gliomas and meningiomas. Acta Neuropathol 108(2):135–142
Berezowska S, Schlegel J (2011) Targeting ErbB receptors in high-grade glioma. Curr Pharm Des 17(23):2468–2487
Yarden Y, Pines G (2012) The ERBB network: at last, cancer therapy meets systems biology. Nat Rev Cancer 12(8):553–563
Junttila TT et al (2009) Ligand-independent HER2/HER3/PI3 K complex is disrupted by trastuzumab and is effectively inhibited by the PI3K inhibitor GDC-0941. Cancer Cell 15(5):429–440
Lahlou H et al (2012) Uncoupling of PI3 K from ErbB3 impairs mammary gland development but does not impact on ErbB2-induced mammary tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 72(12):3080–3090
Tao JJ et al (2014) Antagonism of EGFR and HER3 enhances the response to inhibitors of the PI3K-AKT pathway in triple-negative breast cancer. Sci Signal 7(318):r29
Shin I et al (2002) PKB/AKT mediates cell-cycle progression by phosphorylation of p27(Kip1) at threonine 157 and modulation of its cellular localization. Nat Med 8(10):1145–1152
Liang J et al (2002) PKB/AKT phosphorylates p27, impairs nuclear import of p27 and opposes p27-mediated G1 arrest. Nat Med 8(10):1153–1160
Knighton DR et al (1993) Structural features that specify tyrosine kinase activity deduced from homology modeling of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(11):5001–5005
Nourse J et al (1994) Interleukin-2-mediated elimination of the p27Kip1 cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor prevented by rapamycin. Nature 372(6506):570–573
Coats S et al (1996) Requirement of p27Kip1 for restriction point control of the fibroblast cell cycle. Science 272(5263):877–880
McAllister SS et al (2003) Novel p27(kip1) C-terminal scatter domain mediates Rac-dependent cell migration independent of cell cycle arrest functions. Mol Cell Biol 23(1):216–228
Besson A et al (2004) p27Kip1 modulates cell migration through the regulation of RhoA activation. Genes Dev 18(8):862–876
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81201264, 81272777 and 81400127), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2014M551662) and Jiangsu Planned Projects for Postdoctoral Research Funds.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hengliang Shi and Hui Gong have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
a The GFP photograph shows the stable cell line with silenced Nrdp1 in A172 cells; bar 50 μm. b The GFP photograph shows the stable cell line with silenced Nrdp1 in U118 cells; bar 50 μm. c Representative blots show the silencing efficiency of Nrdp1 shRNA and the up-regulation of ErbB3 upon silencing of Nrdp1 in A172 cells. d Representative blots show the silencing efficiency of Nrdp1 shRNA and the up-regulation of ErbB3 upon silencing of Nrdp1 in U118 cells. Supplementary material 1 (TIFF 11,096 kb)
Fig. S2
a The GFP image shows the efficiency of plasmid transfection; bar 100 μm. b The overexpression of Flag-Nrdp1 is shown by immunofluorescence staining with anti-Flag antibody; bar 100 μm. c Representative blots show the expression efficiency of Nrdp1 and the down-regulation of ErbB3 upon overexpression of Nrdp1. Supplementary material 2 (TIFF 12,574 kb)
Fig. S3
a The expression profiles of Nrdp1, ErbB3 and p27Kip1 in U251, U87, SHG44, A172, and U118 cell lines. b Knockdown of endogenous Nrdp1 in U251, U87 and SHG44 cells resulted in an increase of ErbB3 expression in these three cell lines. Supplementary material 3 (TIFF 2073 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, H., Gong, H., Cao, K. et al. Nrdp1-mediated ErbB3 degradation inhibits glioma cell migration and invasion by reducing cytoplasmic localization of p27Kip1 . J Neurooncol 124, 357–364 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1851-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1851-9