Abstract
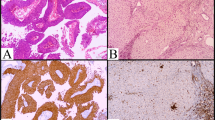
Signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 (STAT3) are activated by various cytokines and oncogenes; however, the activity and pathogenesis of STAT3 in diffuse large B cell lymphoma of the central nervous system have not been thoroughly elucidated. We investigated the phosphorylation levels of STAT3 in 40 specimens of primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (PCNS DLBCL) and analyzed the association between phsopho-STAT3 (pSTAT3) expression and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) concentration of interleukin-10 (IL-10) or IL-6. Immunohistochemistry and Western blot analysis revealed that most of the specimens in PCNS DLBCL expressed pSTST3 protein, and a strong phosphorylation levels of STAT3 was statistically associated with high CSF IL-10 levels, but not with CSF IL-6 levels. Next, we demonstrated that recombinant IL-10 and CSF containing IL-10 induced the phosphorylation of STAT3 in PCNS DLBCL cells. Furthermore, molecular subtype classified by Hans’ algorithm was correlated with pSTAT3 expression levels and CSF IL-10 levels. These results suggest that the STAT3 activity is correlated with CSF IL-10 level, which is a useful marker for STAT3 activity in PCNS DLBCLs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prodduturi P, Bierman PJ (2012) Current and emerging pharmacotherapies for primary CNS lymphoma. Clin Med Insights Oncol 6:219–231
Yu H, Pardoll D, Jove R (2009) STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev Cancer 9:798–809
Gupta M, Han JJ, Stenson M et al (2012) Elevated serum IL-10 levels in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a mechanism of aberrant JAK2 activation. Blood 119:2844–2853
Lee SW, Ahn YY, Kim YS et al (2012) The Immunohistochemical expression of STAT3, Bcl-xL, and MMP-2 proteins in colon adenoma and adenocarcinoma. Gut liver 6:45–51
Morikawa T, Baba Y, Yamauchi M et al (2011) STAT3 expression, molecular features, inflammation patterns, and prognosis in a database of 724 colorectal cancers. Clin Cancer 17:1452–1462
Seki Y, Suzuki N, Imaizumi M et al (2004) STAT3 and MAPK in human lung cancer tissues and suppression of oncogenic growth by JAB and dominant negative STAT3. Int J Oncol 24:931–934
Barton BE, Karras JG, Murphy TF et al (2004) Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) activation in prostate cancer: direct STAT3 inhibition induces apoptosis in prostate cancer lines. Mol Cancer Ther 3:11–20
Lin TS, Mahajan S, Frank DA (2000) STAT signaling in the pathogenesis and treatment of leukemias. Oncogene 19:2496–2504
Vainchenker W, Constantinescu SN (2013) JAK/STAT signaling in hematological malignancies. Oncogene 32:2601–2613
Tsutsui M, Yasuda H, Suto H et al (2010) Frequent STAT3 activation is associated with Mcl-1 expression in nasal NK-cell lymphoma. Int J Lab Hematol 32:419–426
Wu ZL, Song YQ, Shi YF et al (2011) High nuclear expression of STAT3 is associated with unfavorable prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Hematol Oncol 4:31
Sasayama T, Nakamizo S, Nishihara M et al (2012) Cerebrospinal fluid interleukin-10 is a potentially useful biomarker in immunocompetent primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL). Neuro-Oncology 14:368–380
Gupta M, Maurer MJ, Wellik LE et al (2012) Expression of Myc, but not pSTAT3, is an adverse prognostic factor for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with epratuzumab/R-CHOP. Blood 120:4400–4406
Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC et al (2004) Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood 103:275–282
Vajpayee N, Hussain J, Tolocica I et al (2010) Expression of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) in primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a retrospective analysis of 17 cases. J Neurooncol 100:249–253
Komohara Y, Horlad H, Ohnishi K et al (2011) M2 macrophage/microglial cells induce activation of Stat3 in primary central nervous system lymphoma. J Clin Exp Hematopathol 51:93–99
Yu H, Kortylewski M, Pardoll D (2007) Crosstalk between cancer and immune cells: role of STAT3 in the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Immunol 7:41–51
Williams LM, Ricchetti G, Sarma U et al (2004) Interleukin-10 suppression of myeloid cell activation–a continuing puzzle. Immunology 113:281–292
Frank DA (2007) STAT3 as a central mediator of neoplastic cellular transformation. Cancer Lett 251:199–210
Ding BB, Yu JJ, Yu RY et al (2008) Constitutively activated STAT3 promotes cell proliferation and survival in the activated B-cell subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood 111:1515–1523
Scuto A, Kujawski M, Kowolik C et al (2011) STAT3 inhibition is a therapeutic strategy for ABC-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Res 71:3182–3188
Xu YH, Lu S (2014) A meta-analysis of STAT3 and phospho-STAT3 expression and survival of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. European J Surg Oncol 40:311–317
Jahnke K, Thiel E, Martus P et al (2006) Relapse of primary central nervous system lymphoma: clinical features, outcome and prognostic factors. J Neurooncol 80:159–165
Lam LT, Wright G, Davis RE et al (2008) Cooperative signaling through the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and nuclear factor-κB pathways in subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 111:3701–3713
Hedvat M, Huszar D, Herrmann A et al (2009) The JAK2 inhibitor AZD1480 potently blocks Stat3 signaling and oncogenesis in solid tumors. Cancer Cell 16:487–497
Xin H, Herrmann A, Reckamp K et al (2011) Antiangiogenic and antimetastatic activity of JAK inhibitor AZD1480. Cancer Res 71:6601–6610
Conflict of interest
None.
Funding
This study was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research to Eiji Kohmura (25293309), Takashi Sasayama (25462258), and Kazuhiro Tanaka (24791501) from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (TIFF 842 kb)
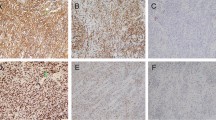
Supplementary Fig. 1 Histological examinations of HKBML tumors implanted into nude mice. HKBML PCNSL cells (5 x 106/200 μl) were injected s.c. into the right flank of nude mice (BALB-c nu/nu). After 2 weeks, the tumor was removed, fixed, and analyzed by immunohistochemistry. The HKBML tumor was identified as a non-GCB type tumor. (Original magnification: × 400)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mizowaki, T., Sasayama, T., Tanaka, K. et al. STAT3 activation is associated with cerebrospinal fluid interleukin-10 (IL-10) in primary central nervous system diffuse large B cell lymphoma. J Neurooncol 124, 165–174 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1843-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1843-9