Abstract
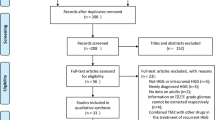
To perform a systematic review and meta-analysis of severe adverse events (SAE) reported in early trials combining molecularly targeted therapies (MTT) with radiotherapy (RT), and to compare them to standard therapy. A summary data meta-analysis was performed and compared to the historical standard. Inclusion criteria were phase I and/or II trials published between 2000 and 2011, with glioblastoma multiforme patients treated with RT and MTT. Pooled incidence rates (IR) of SAE were estimated as well as the pooled median progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). Nineteen prospective trials (9 phase I, 1 phase I/II and 9 phase II) out of 29 initially selected were included (n = 755 patients). The exact number of patients who had experienced SAE was mentioned in 37 % of the trials, concerning only 17 % of the patients. Information such as the period during which adverse events were monitored, the planned treatment duration, and late toxicity were not reported in the trials. The pooled IR of overall SAE was 131.2 (95 % CI 88.8–193.7) per 1000 person-months compared to 74.7 (63.6–87.8) for standard therapy (p < 0.01). Significant differences were observed for gastrointestinal events (p = 0.05) and treatment-related deaths (p = 0.02), in favour of standard therapy. No significant difference was observed in PFS and OS. Reporting a summary of toxicity data in early clinical trials should be stringently standardized. The use of MTT with RT compared to standard therapy increased SAE while yielded comparable survival in glioblastoma multiforme patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Angelis LM (2001) Brain tumours. N Eng J Med 344:114–123
Omuro AMP, Faivre S, Raymond E (2007) Lessons learned in the development of targeted therapy for malignant gliomas. Mol Cancer Ther 6:1909–1919
Stupp R, Mason W, Bent M et al (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Eng J Med 352:987–996
Agrawal M, Grady C, Fairclough DL et al (2006) Patients’ decision-making process regarding participation in phase I oncology research. J Clin Oncol 24:4479–4484
Deutsch E, Soria JC, Armand JP (2005) New concepts for phase I trials: evaluating new drugs combined with radiation therapy. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 2:456–465
Ioannidis JP, Evans SJ, Gotzsche PC et al (2004) Better reporting of harms in randomized trials: an extension of the CONSORT statement. Ann Intern Med 141:781–788
Postel-Vinay S, Gomez-Roca C, Molife LR et al (2011) Phase I trials of molecularly targeted agents: should we pay more attention to late toxicities? J Clin Oncol 29:1728–1735
Common Toxicity Manual.: http://ctep.cancer.gov/protocoldevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/ctcmanual_v4_10-4-99.pdf
Sutton AJ, Abrams KR, Jones et al (2000) Methods for meta-analysis in medical research. Wiley, Chichester
Michiels S, Piedbois P, Burdett S, Syz N et al (2005) Meta-analysis when only the median survival times are known: a comparison with individual patient data results. Int J Technol Assess Health Care 21:119–125
Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ et al (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327:557–560
Thompson SG, Higgins JPT (2002) How should meta-regression analyses be undertaken and interpreted? Stat Med 21:1559–1573
Viechtbauer W (2010) Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metaphor package. J Stat Softw 36:1–48
Drappatz J, Wong E, Schiff D et al (2009) A pilot safety study of lenalidomide and radiotherapy for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 73:222–227
Kubicek G, Werner-Wasik M, Machtay M et al (2009) Phase I trial using proteasome inhibitor bortezomib and concurrent temozolomide and radiotherapy for central nervous system malignancies. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 74:433–439
Brandes AA, Stupp R, Hau P et al (2010) EORTC Study 26041-22041: phase I/II study on concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide and radiotherapy with vatalanib in newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Eur J Cancer 46:348–354
Drappatz J, Norden A, Wong E et al (2010) Phase I study of vandetanib with radiotherapy and temozolomide for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 78:85–90
Peereboom DM, Shepard DR, Manmeet S et al (2010) Phase II trial of erlotinib with temozolomide and radiation in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurooncol 98:93–99
Stupp R, Hegi M, Heyns B et al (2010) Phase I/IIa study of cilengitide and temozolomide with concomitant radiotherapy followed by cilengitide and temozolomide maintenance therapy In patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 28:2712–2718
Gerstner ER, Eichler AF, Plotkin SR et al (2011) Phase I trial of vatalanib (PTK787) in combination with standard radiation and temozolomide in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 103:325–332
Lai A, Tran A, Nghiemphu PP et al (2011) Phase II study of bevacizumab plus temozolomide during and after radiation therapy for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme. J Clin Oncol 29:142–148
Vredenburgh JJ, Desjardins A, Reardon DA et al (2011) The addition of bevacizumab to standard radiation therapy and temozolomide followed by bevacizumab, temozolomide, and irinotecan for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 17:4119–4124
Hainsworth JD, Shih KC, Shepard GC et al (2012) Phase II study of concurrent radiation therapy, temozolomide, and bevacizumab followed by bevacizumab/everolimus as first-line treatment for patients with Glioblastoma. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 10:240–246
Vredenburgh JJ, Desjardins A, Reardon DA, et al (2011) The addition of bevacizumab to temozolomide and radiation therapy followed by bevacizumab, temozolomide, and oral topotecan for newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme. Neuro Oncol 13S:AbstractOT-19
Liebross RH, Birhiray R, Schultz S et al (2011) A feasibility trial of concurrent radiation, temozolomide, and bevacizumab followed by temozolomide and bevacizumab for resectable and unresectable glioblastoma multiforme of the brain. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81:S275
Nghiemphu PL, Wen PY, Lamborn KR et al (2011) A phase I trial of tipifarnib with radiation therapy, with and without temozolomide, for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81:1422–1427
Chang S, Lamborn K, Malec M et al (2004) Phase II study of temozolomide and thalidomide with radiation therapy for newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 60:353–357
Brown P, Krishnan S, Sarkaria J et al (2008) Phase I/II trial of erlotinib and temozolomide with RT in treatment of newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme: NCCT Groups Study N0177. J Clin Oncol 26:5603–5609
Narayana A, Golfinos J, Fischer I et al (2008) Feasibility of using bevacizumab with radiation therapy and temozolomide in newly diagnosed high-grade glioma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 72:383–389
Krishnan S, Brown P, Ballman K et al (2006) Phase I trial of erlotinib with radiation therapy in patients with glioblastoma multiforme: results of the North Central Centre Treatment Group Protocol N0177. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 65:1192–1199
Moyal ECJ, Laprie A, Delannes M et al (2007) Phase I trial of tipifarnib (r115777) concurrent with radiotherapy in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 68:1396–1401
Chinot OL, Wick W, Mason W et al (2014) Bevacizumab plus radiotherapy-temozolomide for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 370:709–722
Gilbert MR, Dignam JJ, Armstrong TS et al (2014) A randomized trial of bevacizumab for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 370:699–708
Ree AH, Hollywood D (2013) Design and conduct of early-phase radiotherapy trials with targeted therapeutics: lessons from the PRAVO experience. Radiother Oncol 108:3–16
Dixit S, Baker L, Walmsley V et al (2012) Temozolomide-related idiosyncratic and other uncommon toxicities: a systematic review. Anticancer Drugs 23:1099–1106
Berlin JA, Crowe BJ, Whalen E et al (2013) Meta-analysis of clinical trial safety data in a drug development program: answers to frequently asked questions. Clin Trials 10:20–31
Wen PY, Macdonald DR, Reardon DA et al (2010) Updated response assessment criteria for high-grade gliomas: response assessment in neuro-oncology working group. J Clin Oncol 28:1963
Ferté C, Fernandez M, Hollebecque A et al (2014) Tumor growth rate is an early indicator of antitumor drug activity in phase I clinical trials. Clin Cancer Res 20:246–252
Santos MA, Lefeuvre D, Le Teuff G et al (2012) Meta-analysis of toxicities in phase I or II trials studying the use of targeted therapy combined to radiotherapy in patients with locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorax Oncol 7S:S234–S235
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Ligue Nationale Contre le Cancer (French Cancer League) and by a grant for EURONCO/DUERTECC.
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Eric Deutsch and Gwénaël Le Teuff: Co-senior author.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
dos Santos, M.A., Pignon, JP., Blanchard, P. et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of phase I/II targeted therapy combined with radiotherapy in patients with glioblastoma multiforme: quality of report, toxicity, and survival. J Neurooncol 123, 307–314 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1802-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1802-5