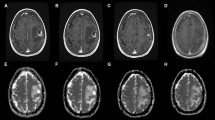
Abstract
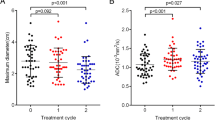
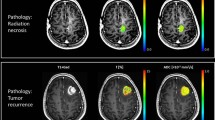
To evaluate the effect of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) on intracranial metastases with diffusion-weighted imaging/apparent diffusion coefficient maps. A total of 107 patients with 144 metastases larger than 1 cm in diameter were retrospectively reviewed. We calculated the DWITumor/white matter ratios (DWIT/WM ratio) between the metastases and the normal, contralateral frontal white matter at each time point. We also recorded the ADC values for metastases (ADCT values). The DWIT/WM ratio and ADCT values were assessed for correlation with the patients’ tumor response, brain edema, and survival. A decrease in DWIT/WM ratios was seen in the controlled metastases, and an increase in the DWIT/WM ratio were seen in the metastases with poor tumor control. On the other hand, an increase in ADCT values was seen in the controlled metastases, and a decrease in ADCT values was seen in the metastases with poor control. The differences were significant (p value: 0.001 and 0.002, respectively). Sensitivity of a decrease in the DWIT/WM ratio to make an early prediction of tumor control was 83.9 %, and specificity was 88.5 %. When using the initial ADCT values of metastases to predict tumor response, sensitivity and specificity were 85.5 and 72.7 %, respectively. DWI/ADC is a practical method for studying the efficacy of SRS and predicting early metastases response progression. A decrease signal on DWI and increased ADC values are indicators of good tumor control, and reflect the beneficial effect of SRS.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADC:
-
Apparent diffusion coefficient
- ARE:
-
Adverse radiation effect
- CTP:
-
Computed tomography perfusion
- DWI:
-
Diffusion-weighed images
- FDG-PET:
-
Positron emission tomography with 18Ffluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose
- FLAIR:
-
Fluid attenuated inversion recovery
- GI:
-
Gastrointestinal
- GKS:
-
Gamma-knife surgery
- Gy:
-
Gray
- KPS:
-
Karnofsky Performance Scale
- MET-PET:
-
Positron emission tomography with 11Cmethyl-l-methionine
- MR:
-
Magnetic resonance
- MRP:
-
Magnetic resonance perfusion
- MRS:
-
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- rCBV:
-
Relative cerebral blood volume
- SCLC:
-
Small cell lung cancer
- SPECT:
-
Single photon emission computed tomography
- SRS:
-
Stereotactic radiosurgery
- T1WI:
-
T1-weighted images
- T2WI:
-
T2-weighted images
- WBRT:
-
Whole brain radiotherapy
- WM:
-
White mater
References
Walker AE, Robins M, Weinfeld FD (1985) Epidemiology of brain tumors: the national survey of intracranial neoplasms. Neurology 35:219–226
Davis FG, Dolecek TA, McCarthy BJ, Villano JL (2012) Toward determining the lifetime occurrence of metastatic brain tumors estimated from 2007 United States cancer incidence data. Neuro Oncol 14:1171–1177
Sugahara T, Korogi Y, Kochi M, Ikushima I, Shigematu Y, Hirai T, Okuda T, Liang L, Ge Y, Komohara Y, Ushio Y, Takahashi M (1999) Usefulness of diffusion-weighted MRI with echo-planar technique in the evaluation of cellularity in gliomas. J Magn Reson Imaging 9:53–60
Kono K, Inoue Y, Nakayama K, Shakudo M, Morino M, Ohata K, Wakasa K, Yamada R (2001) The role of diffusion-weighted imaging in patients with brain tumors. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1081–1088
Guo AC, Cummings TJ, Dash RC, Provenzale JM (2002) Lymphomas and high-grade astrocytomas: comparison of water diffusibility and histologic characteristics. Radiology 224:177–183
Higano S, Yun X, Kumabe T, Watanabe M, Mugikura S, Umetsu A, Sato A, Yamada T, Takahashi S (2006) Malignant astrocytic tumors: clinical importance of apparent diffusion coefficient in prediction of grade and prognosis. Radiology 241:839–846
Da Silva AN, Nagayama K, Schlesinger D, Sheehan JP (2009) Early brain tumor metastasis reduction following Gamma Knife surgery. J Neurosurg 110:547–552
Jagannathan J, Yen CP, Ray DK, Schlesinger D, Oskouian RJ, Pouratian N, Shaffrey ME, Larner J, Sheehan JP (2009) Gamma knife radiosurgery to the surgical cavity following resection of brain metastases. J Neurosurg 111:431–438
Basina BR, Olson C, Roy DK, Yen CP, Schlesinger D, Nagayama K, Sheehan JP (2010) Radiation dose and incidence of new metastasis in the anterior temporal lobe structures of radiosurgically treated patients. J Neurosurg 112:122–129
Stinauer MA, Diot Q, Westerly DC, Schefter TE, Kavanagh BD (2012) Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography response and normal tissue regeneration after stereotactic body radiotherapy to liver metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 83:e613–e618
Murakami R, Hirai T, Sugahara T, Fukuoka H, Toya R, Nishimura S, Kitajima M, Okuda T, Nakamura H, Oya N, Kuratsu J, Yamashita Y (2009) Grading astrocytic tumors by using apparent diffusion coefficient parameters: superiority of a one- versus two-parameter pilot method. Radiology 251:838–845
Wu CC, Guo WY, Chen MH, Ho DM, Hung AS, Chung HW (2012) Direct measurement of the signal intensity of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for preoperative grading and treatment guidance for brain gliomas. J Chin Med Assoc 75:581–588
Hein PA, Eskey CJ, Dunn JF, Hug EB (2004) Diffusion-weighted imaging in the follow-up of treated high-grade gliomas: tumor recurrence versus radiation injury. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:201–209
Asao C, Korogi Y, Kitajima M, Hirai T, Baba Y, Makino K, Kochi M, Morishita S, Yamashita Y (2005) Diffusion-weighted imaging of radiation-induced brain injury for differentiation from tumor recurrence. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1455–1460
Mardor Y, Pfeffer R, Spiegelmann R, Roth Y, Maier SE, Nissim O, Berger R, Glicksman A, Baram J, Orenstein A, Cohen JS, Tichler T (2003) Early detection of response to radiation therapy in patients with brain malignancies using conventional and high b-value diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. J Clin Oncol 21:1094–1100
Mardor Y, Roth Y, Ochershvilli A, Spiegelmann R, Tichler T, Daniels D, Maier SE, Nissim O, Ram Z, Baram J, Orenstein A, Pfeffer R (2004) Pretreatment prediction of brain tumors’ response to radiation therapy using high b-value diffusion-weighted MRI. Neoplasia 6:136–142
Tomura N, Narita K, Izumi J, Suzuki A, Anbai A, Otani T, Sakuma I, Takahashi S, Mizoi K, Watarai J (2006) Diffusion changes in a tumor and peritumoral tissue after stereotactic irradiation for brain tumors: possible prediction of treatment response. J Comput Assist Tomogr 30:496–500
Huang CF, Chou HH, Tu HT, Yang, Lee JK, Lin LY (2008) Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging as an evaluation of the response of brain metastases treated by stereotactic radiosurgery. Surg Neurol 69:62–68 discussion 68
Goldman M, Boxerman JL, Rogg JM, Noren G (2006) Utility of apparent diffusion coefficient in predicting the outcome of Gamma knife-treated brain metastases prior to changes in tumor volume: a preliminary study. J Neurosurg 105(Suppl):175–182
Chernov M, Hayashi M, Izawa M, Ochiai T, Usukura M, Abe K, Ono Y, Muragaki Y, Kubo O, Hori T, Takakura K (2005) Differentiation of the radiation-induced necrosis and tumor recurrence after gamma knife radiosurgery for brain metastases: importance of multi-voxel proton MRS. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 48:228–234
Kang TW, Kim ST, Byun HS, Jeon P, Kim K, Kim H, Lee JI (2009) Morphological and functional MRI, MRS, perfusion and diffusion changes after radiosurgery of brain metastasis. Eur J Radiol 72:370–380
Nagel FJ, Van As H, Tramper J, Rinzema A (2002) Water and glucose gradients in the substrate measured with NMR imaging during solid-state fermentation with Aspergillus oryzae. Biotechnol Bioeng 79:653–663
Gao X, Zhang XN, Zhang YT, Yu CS, Xu DS (2011) Magnetic resonance imaging in assessment of treatment response of gamma knife for brain tumors. Chin Med J (Engl) 124:1906–1910
Young GS (2007) Advanced MRI of adult brain tumors. Neurol Clin 25:947–973 viii
Hamstra DA, Chenevert TL, Moffat BA, Johnson TD, Meyer CR, Mukherji SK, Quint DJ, Gebarski SS, Fan X, Tsien CI, Lawrence TS, Junck L, Rehemtulla A, Ross BD (2005) Evaluation of the functional diffusion map as an early biomarker of time-to-progression and overall survival in high-grade glioma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:16759–16764
Hamstra DA, Galban CJ, Meyer CR, Johnson TD, Sundgren PC, Tsien C, Lawrence TS, Junck L, Ross DJ, Rehemtulla A, Ross BD, Chenevert TL (2008) Functional diffusion map as an early imaging biomarker for high-grade glioma: correlation with conventional radiologic response and overall survival. J Clin Oncol 26:3387–3394
Murakami R, Sugahara T, Nakamura H, Hirai T, Kitajima M, Hayashida Y, Baba Y, Oya N, Kuratsu J, Yamashita Y (2007) Malignant supratentorial astrocytoma treated with postoperative radiation therapy: prognostic value of pretreatment quantitative diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Radiology 243:493–499
Barajas RF Jr, Rubenstein JL, Chang JS, Hwang J, Cha S (2010) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging derived apparent diffusion coefficient is predictive of clinical outcome in primary central nervous system lymphoma. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:60–66
Berghoff AS, Spanberger T, Ilhan-Mutlu A, Magerle M, Hutterer M, Woehrer A, Hackl M, Widhalm G, Dieckmann K, Marosi C, Birner P, Prayer D, Preusser M (2013) Preoperative diffusion-weighted imaging of single brain metastases correlates with patient survival times. PLoS ONE 8:e55464
Yoshii Y, Satou M, Yamamoto T, Yamada Y, Hyodo A, Nose T, Ishikawa H, Hatakeyama R (1993) The role of thallium-201 single photon emission tomography in the investigation and characterisation of brain tumours in man and their response to treatment. Eur J Nucl Med 20:39–45
Shah AH, Snelling B, Bregy A, Patel PR, Tememe D, Bhatia R, Sklar E, Komotar RJ (2012) Discriminating radiation necrosis from tumor progression in gliomas: a systematic review what is the best imaging modality? J Neurooncol 112:141–152
Fatterpekar GM, Galheigo D, Narayana A, Johnson G, Knopp E (2012) Treatment-related change versus tumor recurrence in high-grade gliomas: a diagnostic conundrum–use of dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced (DSC) perfusion MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol 198:19–26
Kano H, Kondziolka D, Lobato-Polo J, Zorro O, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (2010) T1/T2 matching to differentiate tumor growth from radiation effects after stereotactic radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 66:486–491 discussion 491-482
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, CC., Wintermark, M., Xu, Z. et al. Application of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging to predict the intracranial metastatic tumor response to gamma knife radiosurgery. J Neurooncol 118, 351–361 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1439-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1439-9