Abstract
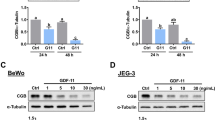
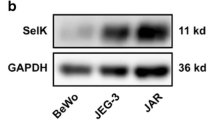
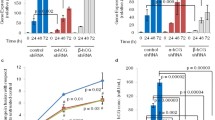
Human chorionic gonadotropin β (hCGβ) promotes tumorigenesis in a variety of tumors including glioblastoma, breast and prostate cancer cells, etc. However, the involved mechanisms remain elusive. Distinct from the other tumors, glioblastoma is a highly invasive brain tumor; invasion causes high recurrence and mortality. Characterization of hCGβ signaling is to determine therapeutic targets to inhibit invasion and lower recurrence. Through both a stable cell line over-expressing hCGβ and hCGβ standards, we tested hCGβ signaling, migration and invasion in human glioblastoma U87MG cells. ELISA showed that hCGβ secreted into culture medium at an amount of 237.8 ± 7.8 ng/107 cells in hCGβ transfected stable cells after the cells were grown for 24 h. Through Western blot and Gelatin zymography, we found that hCGβ standards phosphorylated ERK1/2 and upregulated MMP-2 expression in dose- and time-dependent manners. Meanwhile, overexpressed hCGβ phosphorylated ERK1/2, and upregulated MMP-2 expression and activity, whereas ERK1/2 blocker PD98059 (25 μM) significantly decreased both ERK1/2 and MMP-2 expression and activity. In addition, in the same conditions as the signaling test, hCGβ promoted cell migration and invasion, whereas the PD98059 diminished these effects. These findings demonstrated that hCGβ phosphorylated ERK1/2 upregulating MMP-2 expression and activity leading to cell migration and invasion, suggesting that hCGβ, ERK1/2 and MMP-2 are the potential targets to inhibit glioblastoma invasion.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stenman UH, Alfthan H, Hotakainen K (2004) Human chorionic gonadotropin in cancer. Clin Biochem 37(7):549–561
Iles RK, Delves PJ, Butler SA (2010) Does hCG or hCGbeta play a role in cancer cell biology? Mol Cell Endocrinol 329(1–2):62–70
Acevedo HF, Hartsock RJ, Maroon JC (1997) Detection of membrane-associated human chorionic gonadotropin and its subunits on human cultured cancer cells of the nervous system. Cancer Detect Prev 21(4):295–303
Ruddon RW, Bryan AH, Meade-Cobun KS, Pollack VA (1980) Production of human chorionic gonadotropin and its subunits by human tumors growing in nude mice. Cancer Res 40(11):4007–4012
Hotakainen K, Ljungberg B, Paju A, Rasmuson T, Alfthan H, Stenman UH (2002) The free beta-subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin as a prognostic factor in renal cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer 86(2):185–189
Lundin M, Nordling S, Lundin J, Alfthan H, Stenman UH, Haglund C (2001) Tissue expression of human chorionic gonadotropin beta predicts outcome in colorectal cancer: a comparison with serum expression. Int J Cancer 95(1):18–22
Djurdjevic S, Maksimovic M, Pantelic M, Golubovic A, Curcic A (2011) Usefulness of beta hCG as tumor marker in the diagnosis and follow up of patients with ovarian cancer. J BUON 16(4):715–721
Sheaff MT, Martin JE, Badenoch DF, Baithun SI (1996) Beta hCG as a prognostic marker in adenocarcinoma of the prostate. J Clin Pathol 49(4):329–332
Venyo AK, Herring D, Greenwood H, Maloney DJ (2010) The expression of beta human chorionic gonadotrophin (beta-hCG) in human urothelial carcinoma. Pan Afr Med J 7:20
Oberg K, Wide L (1981) hCG and hCG subunits as tumour markers in patients with endocrine pancreatic tumours and carcinoids. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 98(2):256–260
Wu W, Walker AM (2006) Human chorionic gonadotropin beta (hCGbeta) down-regulates E-cadherin and promotes human prostate carcinoma cell migration and invasion. Cancer 106(1):68–78
Srisuparp S, Strakova Z, Brudney A, Mukherjee S, Reierstad S, Hunzicker-Dunn M, Fazleabas AT (2003) Signal transduction pathways activated by chorionic gonadotropin in the primate endometrial epithelial cells. Biol Reprod 68(2):457–464
Maymo JL, Perez Perez A, Sanchez-Margalet V, Duenas JL, Calvo JC, Varone CL (2009) Up-regulation of placental leptin by human chorionic gonadotropin. Endocrinology 150(1):304–313
Huang C, Jacobson K, Schaller MD (2004) MAP kinases and cell migration. J Cell Sci 117(Pt 20):4619–4628
Coutts AS, Murphy LC (1998) Elevated mitogen-activated protein kinase activity in estrogen-nonresponsive human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 58(18):4071–4074
Adeyinka A, Nui Y, Cherlet T, Snell L, Watson PH, Murphy LC (2002) Activated mitogen-activated protein kinase expression during human breast tumorigenesis and breast cancer progression. Clin Cancer Res 8(6):1747–1753
Lin HC, Song TY, Hu ML (2009) S-Adenosylhomocysteine promotes the invasion of C6 glioma cells via increased secretion of matrix metalloproteinase-2 in murine microglial BV2 cells. Toxicol Sci 112(2):322–330
Bergman MR, Cheng S, Honbo N, Piacentini L, Karliner JS, Lovett DH (2003) A functional activating protein 1 (AP-1) site regulates matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2) transcription by cardiac cells through interactions with JunB-Fra1 and JunB-FosB heterodimers. Biochem J 369(Pt 3):485–496
Yao J, Xiong S, Klos K, Nguyen N, Grijalva R, Li P, Yu D (2001) Multiple signaling pathways involved in activation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) by heregulin-beta1 in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 20(56):8066–8074
Bauvois B (2012) New facets of matrix metalloproteinases MMP-2 and MMP-9 as cell surface transducers: outside-in signaling and relationship to tumor progression. Biochim Biophys Acta 1825(1):29–36
Gialeli C, Theocharis AD, Karamanos NK (2011) Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression and their pharmacological targeting. FEBS J 278(1):16–27
Chang MC, Chen CA, Chen PJ, Chiang YC, Chen YL, Mao TL, Lin HW, Lin Chiang WH, Cheng WF (2012) Mesothelin enhances invasion of ovarian cancer by inducing MMP-7 through MAPK/ERK and JNK pathways. Biochem J 442(2):293–302
Watanabe T, Yasue A, Fujihara S, Tanaka E (2012) PERIOSTIN regulates MMP-2 expression via the alphavbeta3 integrin/ERK pathway in human periodontal ligament cells. Arch Oral Biol 57(1):52–59
Hu B, Jarzynka MJ, Guo P, Imanishi Y, Schlaepfer DD, Cheng SY (2006) Angiopoietin 2 induces glioma cell invasion by stimulating matrix metalloprotease 2 expression through the alphavbeta1 integrin and focal adhesion kinase signaling pathway. Cancer Res 66(2):775–783
Fluhr H, Bischof-Islami D, Krenzer S, Licht P, Bischof P, Zygmunt M (2008) Human chorionic gonadotropin stimulates matrix metalloproteinases-2 and -9 in cytotrophoblastic cells and decreases tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1, -2, and -3 in decidualized endometrial stromal cells. Fertil Steril 90(4 Suppl):1390–1395
Chueh FS, Chen YY, Huang AC, Ho HC, Liao CL, Yang JS, Kuo CL, Chung JG (2011) Bufalin-inhibited migration and invasion in human osteosarcoma U-2 OS cells is carried out by suppression of the matrix metalloproteinase-2, ERK, and JNK signaling pathways. Environ Toxicol. doi:10.1002/tox.20769
Ma CY, Ji WT, Chueh FS, Yang JS, Chen PY, Yu CC, Chung JG (2011) Butein inhibits the migration and invasion of SK-HEP-1 human hepatocarcinoma cells through suppressing the ERK, JNK, p38, and uPA signaling multiple pathways. J Agric Food Chem 59(16):9032–9038
Deryugina EI, Quigley JP (2006) Matrix metalloproteinases and tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 25(1):9–34
Gessi S, Sacchetto V, Fogli E, Merighi S, Varani K, Baraldi PG, Tabrizi MA, Leung E, Maclennan S, Borea PA (2010) Modulation of metalloproteinase-9 in U87MG glioblastoma cells by A3 adenosine receptors. Biochem Pharmacol 79(10):1483–1495
Bandopadhyaya G, Arora G, Shukla J, Ghosh S (2012) Recognition based hormonal 95 kDa monoclonal antibody on three human cancer cell lines for developing targeted radio-immuno-imaging and therapy. Hellenic J Nuc Med 15(2):108
Cole LA (2009) Human chorionic gonadotropin and associated molecules. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 9(1):51–73
Kim EK (1802) Choi EJ (2010) Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 4:396–405
Meng XL, Rennert OM, Chan WY (2007) Human chorionic gonadotropin induces neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells through activation of stably expressed lutropin/choriogonadotropin receptor. Endocrinology 148(12):5865–5873
Hua H, Li M, Luo T, Yin Y, Jiang Y (2011) Matrix metalloproteinases in tumorigenesis: an evolving paradigm. Cell Mol Life Sci 68(23):3853–3868
Rucci N, Sanita P, Angelucci A (2011) Roles of metalloproteases in metastatic niche. Curr Mol Med 11(8):609–622
Li R, Li G, Deng L, Liu Q, Dai J, Shen J, Zhang J (2010) IL-6 augments the invasiveness of U87MG human glioblastoma multiforme cells via up-regulation of MMP-2 and fascin-1. Oncol Rep 23(6):1553–1559
Kesanakurti D, Chetty C, Dinh DH, Gujrati M, Rao JS (2012) Role of MMP-2 in the regulation of IL-6/Stat3 survival signaling via interaction with alpha5beta1 integrin in glioma. Oncogene. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.52
Deshane J, Garner CC, Sontheimer H (2003) Chlorotoxin inhibits glioma cell invasion via matrix metalloproteinase-2. J Biol Chem 278(6):4135
Friedl P, Wolf K (2003) Tumour-cell invasion and migration: diversity and escape mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer 3(5):362–374
Wolf K, Mazo I, Leung H, Engelke K, Von Andrian UH, Deryugina EI, Strongin AY, Bröcker EB, Friedl P (2003) Compensation mechanism in tumor cell migration. J Cell Biol 160(2):267–277
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to Dr. Ameae Walker, University of California at Riverside for her assistance in the experiments. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No: 81272843).
Conflict of interest
None to declare.
Open access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Du, L., Li, C. et al. Human chorionic gonadotropin β induces cell motility via ERK1/2 and MMP-2 activation in human glioblastoma U87MG cells. J Neurooncol 111, 237–244 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-012-1017-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-012-1017-y