Abstract
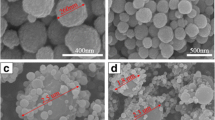
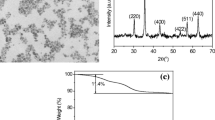
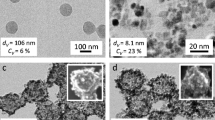
The addition of superparamagnetic iron nanoparticles into polystyrene matrix allows for the modification of the physical properties as well as the implementation of new features in the hybrid nanomaterials. These materials have excellent potential for biomedical and bioengineering applications. Nevertheless, it is necessary to achieve a good dispersion of magnetic nanoparticles for its successful incorporation into polymer particles. This can be obtained through the use of a stabilizer, which provides stability against aggregation. In this work, magnetic nanoparticles were dispersed using different stabilizers. Subsequently, ferrofluids stabilized using the mixture of ABEX/IGEPAL and acrylic acid (AA) were used to synthesize PS-Fe3O4 nanocomposites, through miniemulsion and emulsion polymerization conventional techniques. Semicontinuous and batch processes were compared, by varying surfactants and their concentrations. The PS-Fe3O4 nanoparticles were characterized by dynamic light scattering, scanning electron microscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and vibrating sample magnetometer. Magnetic nanoparticle dispersions show better results when the anionic and nonionic surfactants are used as a mixture rather than when used alone. Results of DLS showed that the semicontinuous process allowed obtaining monodisperse materials, whereas polidisperse systems are generated in batch process. Raman spectroscopy confirmed the presence of magnetite and polystyrene in the nanocomposites. PS-Fe3O4 nanoparticles showed superparamagnetic behavior with final magnetization of around 0.01 emu/g and low coercivity, properties that make them suitable for applications in wide fields of technology. Particle size (Dz), was lower than 300 nm in all cases. Moreover, the use of AA as stabilizer allows enhancing the PS-Fe3O4 composite properties. These findings showed that particle size, morphology, and agglomeration are directly influenced by the concentration and the type of surfactant employed.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arosio P, Mosconi M, Storti G, Morbidelli M (2011) Precipitation copolymerization of vinyl-imidazole and vinyl-pyrrolidone, 1-experimental analysis. Macromol React Eng 5:490–500
Buendía S, Cabañas G, Álvarez-Lucio G, Montiel-Sánchez H, Navarro-Clemente ME, Corea M (2011) Preparation of magnetic polymer particles with nanoparticles of Fe(0). J Colloid Interf Sci 354:139–143
Chakka VM, Altuncevahir B, Jin ZQ, Li Y, Liu JP (2006) Magnetic nanoparticles produced by surfactant-assisted ball milling. J Appl Phys 99(08E912):1–3
Chauvierre C, Labarre D, Couvreur P, Vauthier C (2003) Plug-in spectrometry with optical fibers as a novel analytical tool for nanoparticles technology: application to the investigation of the emulsion polymerization of the alkylcyanoacrylate. J Nanopart Res 5:365–371
Chokprasombata K, Sirisathitkula C, Hardinga P, Chandarakb S, Yimnirunb R (2013) Monodisperse magnetic nanoparticles: effects of surfactants on the reaction between iron acetylacetonate and platinum acetylacetonate. Rev Mex Fis 59:224–228
Conley Robert F (1996) Practical dispersion: a guide to understanding and formulating slurries. Wiley, Hoboken
El-Aasser MS, Sudol ED (2004) Miniemulsions: overview of research and applications. J Coat Technol Res 1:20–31
Erdem D, Sudol ED, Dimonie VL, El-Aasser MS (2000) Encapsulation of inorganic particles via miniemulsion polymerization, III. characterization of encapsulation. J Polym Sci Part A1 38:4441–4450
Fainerman VB, Mobius D, Miller R (2001) Surfactants: chemistry, interfacial properties, applications. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Ghorbani Z, Baharvand H, Nezhati MN, Panahi HA (2013) Magnetic polymer particles modified with β-cyclodextrin. J Polym Res 20(199):1–8
Goodwin J (2009) Colloids and interfaces surfactants and polymers. Wiley, New York
Gregorio-Jauregui KM, Pineda MG, Rivera-Salinas JE, Hurtado G, Saade H, Martínez JL, Ilyina A, López RG (2012) One-Step method for preparation of magnetic nanoparticles coated with chitosan. J Nanomater 2012:1–8
Guo Z, Park S, Hahn HT (2007) Magnetic and electromagnetic evaluation of the magnetic nanoparticles filled polyurethane nanocomposites. J Appl Phys 101:09m511–09m513
Hai NH, Luong N, Chau N, Tai NQ (2009) Preparation of magnetic nanoparticles embedded in polystyrene microspheres. J Phys Conf Ser JPCS 187(012009):1–6
Hanemann T, Szabó DV (2010) Polymer-Nanoparticle composites: from synthesis to modern applications. Materials 3:3468–3517
Hanesch M (2009) Raman spectroscopy of iron oxides and (oxy)hydroxides at low laser power and possible applications in environmental magnetic studies. Geophys J Int 177:941–948
Hwang Y-J, Oh C, Oh S-G (2005) Controlled release of retinol from silica particles prepared in O/W/O emulsion: the effects of surfactants and polymers. J Control Release 106:339–349
Koo HY, Chang ST, Choi WS, Park JH, Kim D-Yu, Velev OD (2006) Emulsion-Based synthesis of reversibly swellable, magnetic nanoparticle-embedded polymer microcapsules. Chem Mater 18:3308–3313
Kordás K, Kukkola J, Tóth G, Jantunen H, Szabó M, Sápi A, Kukovecz A, Kónya Z, Mikkola JP (2013) Springer Handbook of nanomaterials. Nanoparticle dispersions. Springer, Berlin, pp 729–776
Liu X, Hu Q, Fang Z, Zhang X, Zhang B (2009) Magnetic chitosan nanocomposites: a useful recyclable tool for heavy metal ion removal. Langmuir 25:3–8
Loo AL, Pineda GM, Saade H, Treviño ME, López RG (2008) Synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles in bicontinuous microemulsions. Effect of surfactant concentration. J Mater Sci 43:3649–3654
Martínez JR, de Alba JR, Blanco-Esqueda IG, Guerrero-Serrano A, Ortega-Zarzosa G (2013) Coercivity values enhancement by incorporation of magnetic powders in inorganic matrix hosts. NJGC 3:1–5
Nomura M, Tobita H, Suzuki K (2005) Emulsion polymerization: kinetic and mechanistic aspects. Adv Polym Sci 175:1–128
Novakov IA, Dang NK, Vaniev MA, Sidorenko NV (2013) On the stabilization and methods for modification of nanosize particles used for the preparation of polymerinorganic nanocomposites. Russ Chem Bull 62:276–284
Osuna Y, Gregorio-Jáuregui KM, Gaona-Lozano JG, Garza-Garcia IM, Ilyina A, Barriga-Castro ED, Saade H, López RG (2012) Chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles with low chitosan content prepared in one-step. J Nanomater 2012:1–7
Palm A (1951) Raman spectrum of polystyrene. J Phys Chem 55:1320–1324
Philippova O, Barabanova A, Molchanov V, Khokhlov A (2011) Magnetic polymer beads: recent trends and developments in synthetic design and applications. Eur Polym J 47:542–559
Racles C, Iacob M, Butnaru M, Sacarescu L, Cazacu M (2014) Aqueous dispersion of metal oxide nanoparticles, using siloxane surfactants. Colloid Surf A 448:160–168
Ramírez LP, Landfester K (2003) Magnetic polystyrene nanoparticles with a high magnetite content obtained by miniemulsion processes. Macromol Chem Phys 204:22–31
Sarkar S, Guibal E, Quignard F, SenGupta AK (2012) Polymer-supported metals and metal oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and applications. J Nanopart Res 14:715
Schork FJ, Luo Y, Smulders W, Russum JP, Butté A, Fontenot K (2005) Miniemulsion polymerization. Adv Polym Sci 175:129–255
Singh RP, Jain S, Ramarao P (2013) Surfactant-assisted dispersion of carbon nanotubes: mechanism of stabilization and biocompatibility of the surfactant. J Nanopart Res 15:1985
Sis H, Birinci M (2009) Effect of nonionic and ionic surfactants on zeta potential and dispersion properties of carbon black powders. Colloid Surf A 341:60–67
Skoglund S, Lowe TA, Hedberg J, Blomberg E, Wallinder IO, Wold S, Lundin M (2013) Effect of laundry surfactants on surface charge and colloidal stability of silver nanoparticles. Langmuir 29:8882–8891
Teja AS, Koh P-Y (2009) Synthesis, properties, and applications of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Prog Cryst Growth Charact 55:22–45
van Herk AM, Landfester K (2010) Advances in Polymer Science: Hybrid latex particles preparation with (Mini)emulsion polymerization. Springer, Berlin
Wang Y, Li Y, Rong C, Liu JP (2007) Sm–Co hard magnetic nanoparticles prepared by surfactant-assisted ball milling. Nanotechnology 18(465701):1–4
Wang Z, Lam A, Acosta E (2013) Suspensions of iron oxide nanoparticles stabilized by anionic surfactants. J Surfactants Deterg 16:397–407
Wilcoxon JP, Provencio PP (1999) Use of surfactant micelles to control the structural phase of nanosized iron clusters. J Phys Chem B 103:9809–9812
Wilson JL, Poddar P, Frey NA, Srikantha H (2004) Synthesis and magnetic properties of polymer nanocomposites with embedded iron nanoparticles. J Appl Phys 95:1439–1443
Xing S, Zhao G (2007) Stability and particle size of polypyrrole dispersion using sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate as surfactant. e-Polymers 18:1–9
Yang J, Lee H, Hyung W, Park SB, Haam S (2005) Magnetic PECA nanoparticles as drug carriers for targeted delivery: synthesis and release characteristics. J Microencapsul 23:203–212
Zhang DH, Qin JG (2000) Study on the concentration dependence on orientation of polystyrene on silver by the sers technique. Chin J Polym Sci 18:177–180
Zhou J, Ralston J, Sedev R, Beattie DA (2009) Functionalized gold nanoparticles: synthesis, structure and colloidal stability. J Colloid Interface Sci 331:251–262
Acknowledgments
The author Karla M. Gregorio-Jauregui is grateful to the National Council of Science and Technology (CONACyT) for the postdoctoral scholarship awarded to him.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Puentes-Vara, L.A., Gregorio-Jauregui, K.M., Bolarín, A.M. et al. Effects of surfactant and polymerization method on the synthesis of magnetic colloidal polymeric nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 18, 212 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3524-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3524-9