Abstract
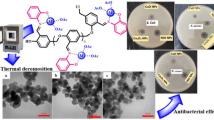
We explored here the synthesis of copper nanoparticles (CuNPs) by thermal decomposition of copper(II) acetate in diphenyl ether in the presence of different capping ligands. To look for any specific role in thermal decomposition, we performed reactions in the presence of oleic acid, oleylamine, and 1,2-octanediol, or in the presence of different combinations of these capping ligands, or in the absence of them. The CuNPs obtained in the presence of oleic acid and oleylamine (in the presence or absence of 1,2-octanediol) were stabilized as Cu(0) NPs, and the “naked” NPs prepared in solvent only easily oxidized to CuO. Therefore, both oleic acid and oleylamine can act as capping ligands to prepare air-stable Cu(0) NPs. The 1,2-alkyldiol is not necessary for metal reduction during the synthesis, but its presence improves size and morphology control. The presence of capping ligands significantly reduced the bactericidal activity exhibited by the Cu NPs against the gram-negative bacteria Escherichia coli.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alivisatos AP (1996) Semiconductor clusters, nanocrystals, and quantum dots. Science 271:933–937
Avery SV, Howlett NG, Radice S (1996) Copper toxicity towards Saccharomyces cerevisiae: dependence on plasma membrane fatty acid composition. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:3960–3966
Bao N, Shen L, Wang Y, Padhan P, Gupta A (2007) A facile thermolysis route to monodisperse ferrite nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc 129:12374–12375
Borel J-P (1981) Thermodynamical size effect and the structure of metallic clusters. Surf Sci 106:1–9
Chen S, Sommers JM (2001) Alkanethiolate-protected copper nanoparticles: spectroscopy, electrochemistry, and solid-state morphological evolution. J Phys Chem B 105:8816–8820
Chen X, Tian X, Shin I, Yoon J (2011) Fluorescent and luminescent probes for detection of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Chem Soc Rev 40:4783–4804
Cioffi N, Torsi L, Ditaranto N, Tantillo G, Ghibelli L, Sabbatini L (2005) Copper nanoparticles/polymer composites with antifungal and bacteriostatic properties. Chem Mater 17:5255–5262
Crouse CA, Barron AR (2008) Reagent control over the size, uniformity, and composition of Co-Fe-O nanoparticles. J Mater Chem 18:4146–4153
Daniel M-C, Astruc D (2004) Gold nanoparticles: assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem Rev 104:293–346
Dhas NA, Raj CP, Gedanken A (1998) Synthesis, characterization, and properties of metallic copper nanoparticles. Chem Mater 10:1446–1452
Gamerith S, Klug A, Scheiber H, Scherf U, Moderegger E, List EJ (2007) Direct ink-jet printing of Ag–Cu nanoparticle and Ag-precursor based electrodes for OFET applications. Adv Funct Mater 17:3111–3118
Hiramatsu H, Osterloh FE (2004) A simple large-scale synthesis of nearly monodisperse gold and silver nanoparticles with adjustable sizes and with exchangeable surfactants. Chem Mater 16:2509–2511
Huber DL (2005) Synthesis, properties, and applications of iron nanoparticles. Small 1:482–501
Jeong S et al (2008) Controlling the thickness of the surface oxide layer on Cu nanoparticles for the fabrication of conductive structures by ink-jet printing. Adv Funct Mater 18:679–686
Kawasaki H, Kosaka Y, Myoujin Y, Narushima T, Yonezawa T, Arakawa R (2011) Microwave-assisted polyol synthesis of copper nanocrystals without using additional protective agents. Chem Commun 47:7740–7742
Kent PD, Mondloch JE, Finke RG (2014) A four-step mechanism for the formation of supported-nanoparticle heterogenous catalysts in contact with solution: the conversion of Ir(1,5-COD)Cl/γ-Al2O3 to Ir(0)(~170)/γ-Al2O3. J Am Chem Soc 136:1930–1941
Lee Y, J-r Choi, Lee KJ, Stott NE, Kim D (2008) Large-scale synthesis of copper nanoparticles by chemically controlled reduction for applications of inkjet-printed electronics. Nanotechnology 19:415604
Lima E Jr et al (2009) Single-step chemical synthesis of ferrite hollow nanospheres. Nanotechnology 20:045606
Lisiecki I, Sack-Kongehl H, Weiss K, Urban J, Pileni M-P (2000) Annealing process of anisotropic copper nanocrystals. 1. Cylinders Langmuir 16:8802–8806
Liu X, Atwater M, Wang J, Dai Q, Zou J, Brennan JP, Huo Q (2007) A study on gold nanoparticle synthesis using oleylamine as both reducing agent and protecting ligand. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 7:3126–3133
Lu A-H, Salabas EL, Schüth F (2007) Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:1222–1244
Matsumoto T, Fujii H, Ueda T, Kamai M, Nogi K (2005) Measurement of surface tension of molten copper using the free-fall oscillating drop method. Meas Sci Technol 16:432
Mitsudome T, Mikami Y, Ebata K, Mizugaki T, Jitsukawa K, Kaneda K (2008) Copper nanoparticles on hydrotalcite as a heterogeneous catalyst for oxidant-free dehydrogenation of alcohols. Chem Commun 39:4804–4806
Mott D, Galkowski J, Wang L, Luo J, Zhong C-J (2007) Synthesis of size-controlled and shaped copper nanoparticles. Langmuir 23:5740–5745
Mott D et al (2009) From ultrafine thiolate-capped copper nanoclusters toward copper sulfide nanodiscs: a thermally activated evolution route. Chem Mater 22:261–271
Murray CB, Kagan C, Bawendi M (2000) Synthesis and characterization of monodisperse nanocrystals and close-packed nanocrystal assemblies. Annu Rev Mater Sci 30:545–610
Nagaraju G, Ebeling G, Gonçalves RV, Teixeira SR, Weibel DE, Dupont J (2013) Controlled growth of TiO2 and TiO2–RGO composite nanoparticles in ionic liquids for enhanced photocatalytic H2 generation. J Mol Catal A: Chem 378:213–220
Park J et al (2004) Ultra-large-scale syntheses of monodisperse nanocrystals. Nat Mater 3:891–895
Park J, Joo J, Kwon SG, Jang Y, Hyeon T (2007) Synthesis of monodisperse spherical nanocrystals. Angewandte Chemie-Int Ed 46:4630–4660
Raffi M, Mehrwan S, Bhatti TM, Akter JI, Hameed A, Yawar W, Hasan M (2010) Investigations into the antibacterial behavior of copper nanoparticles against Escherichia coli. Ann Microbiol 60:75–80
Roucoux A, Schulz J, Patin H (2002) Reduced transition metal colloids: a novel family of reusable catalysts? Chem Rev 102:3757–3778
Schmid G (1992) Large clusters and colloids. Metals in the embryonic state. Chem Rev 92:1709–1727
Sun SH, Zeng H (2002) Size-controlled synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 124:8204–8205
Sun SH, Murray CB, Weller D, Folks L, Moser A (2000) Monodisperse FePt nanoparticles and ferromagnetic FePt nanocrystal superlattices. Science 287:1989–1992
Wang X, Zhuang J, Peng Q, Li Y (2005) A general strategy for nanocrystal synthesis. Nature 437:121–124
Wang C, Daimon H, Lee Y, Kim J, Sun S (2007) Synthesis of monodisperse Pt nanocubes and their enhanced catalysis for oxygen reduction. J Am Chem Soc 129:6974–6975
Wei Y, Chen S, Kowalczyk B, Huda S, Gray TP, Grzybowski BA (2010) Synthesis of stable, low-dispersity copper nanoparticles and nanorods and their antifungal and catalytic properties. J Phys Chem C 114:15612–15616
Woo K, Kim D, Kim JS, Lim S, Moon J (2008) Ink-Jet printing of Cu—Ag-based highly conductive tracks on a transparent substrate. Langmuir 25:429–433
Xu Z, Shen C, Hou Y, Gao H, Sun S (2009) Oleylamine as both reducing agent and stabilizer in a facile synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles. Chem Mater 21:1778–1780
Yin Y, Alivisatos AP (2005) Colloidal nanocrystal synthesis and the organic-inorganic interface. Nature 437:664–670
Zhu H, Zhang C, Yin Y (2005) Novel synthesis of copper nanoparticles: influence of the synthesis conditions on the particle size. Nanotechnology 16:3079
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Brazilian agencies FAPESP and CNPq for financial support. We also thank Prof. Ana Maria Ferreira (Instituto de Química, Universidade de São Paulo) for TG-MS measurements (FAPESP Grant 05/60596-8). MTM and LMR are members of the NAPCatSinQ-USP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest Editors: Carlos Lodeiro Espiño, José Luis Capelo Martinez
This article is part of the topical collection on Composite Nanoparticles
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Effenberger, F.B., Sulca, M.A., Machini, M.T. et al. Copper nanoparticles synthesized by thermal decomposition in liquid phase: the influence of capping ligands on the synthesis and bactericidal activity. J Nanopart Res 16, 2588 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2588-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2588-7