Abstract
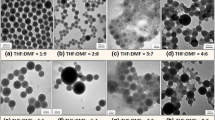
This paper describes the synthesis of adenine-mediated superparamagnetic β-FeOOH nanostructures in aqueous medium. Capping by adenine provides a synthetic control to manipulate their size, morphology, optical and magnetization properties. β-FeOOH binds to adenine mainly through –NH2, N(3); N(9)H and N(7) of the pyridine and imidazole rings, respectively. At low [adenine], it produces nanorods, but at higher [adenine] (>1 × 10−2 mol dm−3), increasing numbers of spherical nanoparticles encapsulating β-FeOOH with an average diameter of 2.5 nm in the core and adenine molecules in the shell are obtained, causing an increase in the specific surface area by about twofold. Dynamic light scattering technique also depicts a regular decrease in their hydrodynamic size with increasing [adenine] and exhibits the highest stability with a zeta potential of ~67 mV for the sample containing 2 × 10−2 mol dm−3 adenine (SP5). An increasing [adenine] from 1 × 10−3 to 2 × 10−2 mol dm−3 in these samples enhanced the value of saturation magnetization (M S), due to β-FeOOH, gradually from 2.0 to 6.9 emu g−1 at 300 K, but at <80 K, a magnetic reversal from superparamagnetic to ferromagnetic is observed. A correlation between morphology and magnetic properties of these nanostructures is discussed. The capping of colloidal β-FeOOH by adenine thus provides a synthetic control to produce novel biocompatible nanostructures exhibiting superparamagnetic behavior with high M S at 300 K having potential for environmental and biological applications.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berry CC, Curtis ASG (2003) Functionalization of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine. J Phys D Appl Phys 36:R198–R206. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/36/13/203
Blesa MA, Mijalchik M, Villegas M (1986) Transformation of akaganeite into magnetite in aqueous hydrazine suspensions. React Solids 2:85–94. doi:10.1016/0168-7336(86)80066-3
Brayner R, Yepremian C, Djediat C, Coradin T, Herbst F, Livage J, Fievet F, Coute A (2009) Photosynthetic microorganism-mediated synthesis of akaganeite (β-FeOOH) nanorods. Langmuir 25:10062–10067. doi:10.1021/la9010345
Cai J, Liu J, Gao Z, Navrotsky A, Suib SL (2001) Synthesis and anion exchange of tunnel structure akaganeite. Chem Mater 13:4595–4602. doi:10.1021/cm010310w
Chatterjee S, Sarkar S, Bhattacharyya SN (1993) Size effect in the photochemical generation of hydrogen from water by colloidal Fe2O3 particles. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 72:183–187. doi:10.1016/1010-6030(93)85027-6
Chaudhari NK, Yu JS (2008) Size control synthesis of uniform β-FeOOH to high coercive field porous magnetic α-Fe2O3 nanorods. J Phys Chem C 112:19957–19962. doi:10.1021/jp808589y
Cornell RM, Schwertmann U (2003) The iron oxides—structure, properties, reactions, occurrences and uses. Wiley-VCH, Darmstadt
de Faria DLA, Silva SV, Oliveira MT (1997) Raman microspectroscopy of some iron oxides and oxyhydroxides. J Raman Spectrosc 28:873–878. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4555(199711)28:11<867:AID-JRS175>3.0.CO;2-6
Deliyanni EA, Peleka EN, Matis KA (2007) Effect of cationic surfactant on the adsorption of arsenites onto akaganeite nanocrystals. Sep Sci Technol 42:993–1012. doi:10.1080/01496390701206306
Fang X-L, Li Y, Chen C, Kuang Q, Gao XZ, Xie SY, Huang RB, Zheng LS (2010) pH-induced simultaneous synthesis and self-assembly of 3D layered β-FeOOH nanorods. Langmuir 26:2745–2750. doi:10.1021/la902765p
Farrell D, Dennis CL, Lim J, Maetich SA (2009) Optical and electron microscopy studies of Schiller layer formation and structure. J Colloids Interface Sci 331:394–400. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2008.11.075
Gossuin Y, Colet JM, Roch A, Muller RN, Gills P (2002) Cesium adsorption in hydrated iron oxide particles suspensions: an NMR study. J Magn Reson 157:132–136. doi:10.1006/jmre.2002.2581
Gupta AK, Gupta M (2005) Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 26:3995–4021. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.10.012
Jana NR, Chen Y, Peng X (2004) Size- and shape-controlled magnetic (Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni) oxide nanocrystals via a simple and general approach. Chem Mater 16:3931–3935. doi:10.1021/cm049221k
Joly AG, Xiong G, Wang C, McCready DE, Beck KM, Hess WP (2007) Synthesis and photoexcited charge carrier dynamics of β-FeOOH nanorods. Appl Phys Lett 90:103504-1–103504-3. doi:10.1063/1.2711395
Katz E, Willner I (2004) Integrated nanoparticle–biomolecule hybrid systems: synthesis, properties, and applications. Angew Chem 43:6042–6108. doi:10.1002/anie.200400651
Kim J, Grey CP (2010) 2H and 7Li solid-state MAS NMR study of local environments and lithium adsorption on the iron(III) oxyhydroxide, akaganeite (β-FeOOH). Chem Mater 22:5453–5462. doi:10.1021/cm100816h
Klabunde KJ (2001) Nanoscale materials in chemistry. Wiley, New York
Kolbe F, Weiss H, Morgenstern P, Wennrich R, Lorenz W, Schurk K, Stanjek H, Daus B (2011) Sorption of aqueous antimony and arsenic species onto akaganeite. J Colloid Interface Sci 357:460–465. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2011.01.095
Kumar A, Singhal A (2007) Synthesis of colloidal β-Fe2O3 nanostructures—influence of addition of Co2+ on their morphology and magnetic behavior. Nanotechnology 18:475703. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/18/47/475703
Kumar A, Singhal A (2011a) Optical, photophysical and magnetic behavior of GMP-templated binary (β-Fe2O3/CdS) and ternary (β-Fe2O3/Ag/CdS) nanohybrids. J Mater Chem 21:481–496. doi:10.1039/c0jm01372b
Kumar A, Singhal A (2011b) Optical and magnetic behavior of Ag encapsulated β-Fe2O3 core–shell hollow Nanotubes. Mater Chem Phys 131:230–240. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2011.09.016
Kwon S-K, Kimijima K, Kanie K, Muramatsu A, Suzuki S, Matsubara E, Waseda Y (2005) Inhibition of conversion process from Fe(OH)3 to β-FeOOH and α-Fe2O3 by the addition of silicate ions. ISIJ Int 45:77–81. doi:10.2355/isijinternational.45.77
Laurent S, Forge D, Port M, Roch A, Robic C, Elst LV, Muller RN (2008) Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological application. Chem Rev 108:2064–2110. doi:10.1021/cr068445e
Lazaridis NK, Bakoyannakis DN, Deliyanni EA (2005) Chromium(VI) sorptive removal from aqueous solutions by nanocrystalline akaganèite. Chemosphere 58:65–73. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.09.007
Liu Y, Yu L, Hu Y, Guo C, Zhang F, Lou XW(D) (2012) A magnetically separable photocatalyst based on nest-like γ-Fe2O3/ZnO double-shelled hollow structures with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Nanoscale 4:183–187. doi:10.1039/C1NR11114K
Mazeina L, Deore S, Navrotsky A (2006) Energetics of bulk and nano-akaganeite, β-FeOOH: enthalpy of formation, surface enthalpy, and enthalpy of water adsorption. Chem Mater 18:1830–1838. doi:10.1021/cm052543j
Millan A, Urtizberea A, Natividad E, Luis F, Silva NJO, Palacio F, Mayoral I, Ruiz-Gonzalez ML, Gonzalez-Calbet JM, Lecante P, Serin V (2009) Akaganeite polymer nanocomposites. Polymer 50:1088–1094. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2009.01.034
Nakamura (1992) Acicular magnetic iron oxide particles and magnetic recording media using such particles. United States Patent No. 5,120,604
Ning J, Xiao G, Wang L, Zou B, Liu B, Zou G (2011) Facile synthesis of magnetic metal (Mn, Fe, Co, and Ni) oxides nanocrystals via a cation-exchange reaction. Nanoscale 3:741–745. doi:10.1039/c0nr00684j
Nowak MJ, Lapinski L, Kwiatkowski JS, Leszczynski J (1996) Molecular structure and infrared spectra of adenine. experimental matrix isolation and density functional theory study of adenine 15N isotopomers. J Phys Chem 100:3527–3534. doi:10.1021/jp9530008
NuLi Y, Zeng R, Zhang P, Guo Z, Liu H (2008) Controlled synthesis of α-Fe2O3 nanostructures and their size-dependent electrochemical properties for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 184:456–461. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.03.004
Prené P, Tronc E, Jolivet J-P, Livage J, Cherkaoui R, Noguks M, Dormann J-L (1993) Magnetic properties of isolated γ-Fe2O3 particles. IEEE Trans Magn 29:2658–2660. doi:10.1109/20.280834
Raj K, Moskowitz B, Casciari R (1995) Advances in ferrofluid technology. J Magn Magn Mater 149:174–180. doi:10.1016/0304-8853(95)00365-7
Santulli AC, Feygenson M, Camino FE, Aronson MC, Wong SS (2011) Synthesis and characterization of one-dimensional Cr2O3 nanostructures. Chem Mater 23:1000–1008. doi:10.1021/cm102930z
Schmid I, Kappenberger P, Hellwig O, Carey MJ, Fullerton EE, Hug HJ (2008) The role of uncompensated spins in exchange biasing. Europhys Lett 81:17001. doi:10.1209/0295-5075/81/17001
Shao HF, Qian XF, Yin J, Zhu ZK (2005) Controlled morphology synthesis of β-FeOOH and the phase transition to Fe2O3. J Solid State Chem 178:3130–3136. doi:10.1016/j.jssc.2005.07.011
Takagi J, Takakura S, Okada T, Kobayashi T, Ozaki M, Kihira H, Mizoguchi T (2008) Estimation of magneto-crystalline uniaxial anisotropy constant of β-FeOOH by Mössbauer spectroscopy. Corros Sci 50:1971–1974. doi:10.1016/j.corsci.2008.05.006
Tartaj P, Morales MP, Veintemillas-Verdaguer S, González-Carreno T, Serna CJ (2003) The preparation of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine. J Phys D Appl Phys 36:R182–R197. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/36/13/202
Williams DB, Carter CB (1996) Transmission electron microscopy. Plenum Publishing Corporation, New York
Xiong Y, Xie Y, Chen S, Li Z (2003) Fabrication of self-supported patterns of aligned β-FeOOH nanowires by a low-temperature solution reaction. Chem Eur J 9:4991–4996. doi:10.1002/chem.200305118
Yoon M, Kim Y, Kim YM, Volkov V, Song HJ, Park YJ, Park I-W (2005) Superparamagnetic properties of nickel nanoparticles in an ion-exchange polymer film. Mater Chem Phys 91:104–107. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2004.10.059
Yu M, Jeong Y, Park J, Park S, Kim J, Min J, Kim K, Jon S (2008) Drug-loaded superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for combined cancer imaging and therapy in vivo. Angew Chem Int Ed 47:5362–5365. doi:10.1002/anie.200800857
Zboril R, Mashlan M, Petridis D (2002) Iron(III) oxides from thermal processes-synthesis, structural and magnetic properties, Mössbauer spectroscopy characterization, and applications. Chem Mater 14:969–982. doi:10.1021/cm0111074
Zeng L, Ren W, Zheng J, Wu A, Cui P (2012) Synthesis of water soluble FeOOH nanospindles and their performance for magnetic resonance imaging. Appl Surf Sci 258:2570–2575. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.10.093
Zhang L-Y, Xue DS, Fen J (2006) Magnetic properties of amorphous β-FeOOH nanowire arrays. J Magn Magn Mater 305:228–232. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2006.01.006
Acknowledgments
SKG is thankful to MHRD, New Delhi for the award of SRF. Thanks is also due to the Heads, Center of Nanotechnology for Zetasizer, UV–Vis–NIR spectrophotometer and IIC, IITR, Roorkee for providing the facilities of XRD, FESEM, and SQUID magnetometer. The authors also acknowledge SAIF, AIIMS, New Delhi; Panjab University, Chandigarh; Metrohm India Ltd.; M/s Laser Spectra Sevices India Pvt. Ltd., Bangalore for providing facilities of TEM, surface area analysis, and Raman Spectroscopy, respectively. Help of Mr. Satyabadi Martha is also acknowledged for getting recorded Raman spectra.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A., Gupta, S.K. Synthesis of adenine mediated superparamagnetic colloidal β-FeOOH nanostructure(s): study of their morphological changes and magnetic behavior. J Nanopart Res 15, 1466 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1466-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1466-z