Abstract
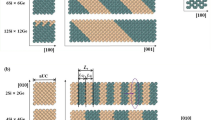
The electronic properties of saturated and unsaturated twinned SiC nanowires grown along [111] direction and surrounded by {111} facets are investigated using first-principles calculations with density functional theory and generalized gradient approximation. All the nanowires considered, including saturated and unsaturated ones, exhibit semiconducting characteristics. The saturated nanowires have a direct band gap and the band gap decreases with increasing diameters of the nanowires. The hexagonal (2H) stacking inside the cubic (3C) stacking has no effect on electronic properties of the SiC nanowires. The highest occupied molecular orbitals and the lowest unoccupied molecular orbitals are distributed along the nanowire axis uniformly, which indicates that the twinned SiC nanowires are good candidates in realizing nano-optoelectronic devices.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Algra RE, Verheijen MA, Borgström MT, Feiner L-F, Immink G, van Enckevort WJP, Vlieg E, Bakkers EPAM (2008) Twinning superlattices in indium phosphide nanowires. Nature 456:369–372
Bechstedt F, Kächell P, Zywietz A, Karch K, Adolph B, Tenelsen K, Furthmüller J (1997) Polytypism and properties of silicon carbide. Phys Stat Sol (B) 202:35–62
Chen CC, Yeh CC, Chen CH, Yu MY, Liu HL, Wu JJ, Chen KH, Chen LC, Peng JY, Chen YF (2001) Catalytic growth and characterization of gallium nitride nanowires. J Am Chem Soc 123:2791–2798
Choyke WJ, Hamilton DR, Patrick L (1964) Optical properties of cubic SiC—luminescence of nitrogen-exciton complexes + interband absorption. Phys Rev A 133:1163
Colli A, Hofmann S, Ferrari AC, Ducati C, Martelli F, Rubini S, Cabrini S, Franciosi A, Robertson J (2005) Low-temperature synthesis of ZnSe nanowires and nanosaws by catalyst-assisted molecular-beam epitaxy. Appl Phys Lett 86:153103
Cui Y, Lieber CM (2001) Functional nanoscale electronic devices assembled using silicon nanowire building blocks. Science 291:851–853
Dai H, Wong EW, Lu YZ, Fan SS, Lieber CM (1995) Synthesis and characterization of carbide nanorods. Nature 375:769–772
Dick KA, Deppert K, Mårtensson T, Mandl B, Samuelson L, Seifert W (2005) Failure of the Vapor–Liquid–Solid mechanism in Au-assisted MOVPE growth of InAs nanowires. Nano Lett 5(4):761–764
Fissel A, Schröter B, Richter W (1995) Low-temperature growth of SiC thin films on Si and 6H–SiC by solid-source molecular beam epitaxy. Appl Phys Lett 66:3182–3184
Gali A (2007) Ab initio theoretical study of hydrogen and its interaction with boron acceptors and nitrogen donors in single-wall silicon carbide nanotubes. Phys Rev B 75:085416
Hao YF, Meng GW, Wang ZL, Ye CH, Zhang LD (2006) Periodically twinned nanowires and polytypic nanobelts of ZnS: The role of mass diffusion in vapor–liquid–solid growth. Nano Lett 6(8):1650–1655
Harmand JC, Patriarche G, Péré-Laperne N, Mérat-Combes MN, Travers L, Glas F (2005) Analysis of vapor–liquid–solid mechanism in Au-assisted GaAs nano-wire growth. Appl Phys Lett 87:203101
Hu JT, Ouyang M, Yang PD, Lieber CM (1999) Controlled growth and electrical properties of heterojunctions of carbon nanotubes and silicon nanowires. Nature 399:48–51
Huang Y, Duan XF, Cui Y, Lieber CM (2002) Gallium nitride nanowire nanodevices. Nano Lett 2(2):101–104
Jensen LE, Björk MT, Jeppesen S, Persson AI, Ohlsson BJ, Samuelson L (2004) Role of surface diffusion in chemical beam epitaxy of InAs nanowires. Nano Lett 4(10):1961–1964
Kächell P, Wenzien B, Bechstedt F (1994) Electronic properties of cubic and hexagonal SiC polytypes from ab initio calculations. Phys Rev B 50:10761–10768
Kohn W, Beche AD, Parr RG (1996) Density functional theory of electronic structure. J Phys Chem 100:12974–12980
Kresse G, Furthmüller J (1996) Efficiency of ab initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comput Mater Sci 6:15–50
Kresse G, Joubert D (1999) From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys Rev B 59:1758–1775
Li Q, Gong XG, Wang CR, Wang J, Ip K, Hark S (2004) Size-dependent periodically twinned ZnSe nanowires. Adv Mater 16:1436–1440
Li J, Zhu XL, Ding P, Chen YP (2009) The synthesis of twinned silicon carbide nanowires by a catalyst-free pyrolytic deposition technique. Nanotechnology 20:145602
Makeev MA, Srivastava D, Menon M (2006) Silicon carbide nanowires under external loads: an atomistic simulation study. Phys Rev B 74:165303
Moewe M, Chuang LC, Dubrovskii VG, Chang-Hasnain C (2008) Growth mechanisms and crystallographic structure of InP nanowires on lattice-mismatched substrates. J Appl Phys 104:044313
Pack JD, Monkhorst HJ (1977) “Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations”—a reply. Phys Rev B 16:1748–1749
Pan ZW, Lai HL, Frederick CK, Au K, Duan XF, Zhou WY, Shi WS, Wang N, Lee CS, Wong NB, Lee ST, Xie SS (2000) Oriented silicon carbide nanowires: synthesis and field emission properties. Adv Mater 12:1186–1190
Perdew JP, Wang Y (1986) Accurate and simple density functional for the electronic exchange energy: generalized gradient approximation. Phys Rev B 33:8800–8802
Seong HK, Choi HJ, Lee SK, Lee JI, Choi DJ (2004) Optical and electrical transport properties in silicon carbide nanowires. Appl Phys Lett 85:1256–1258
Shen GZ, Bando Y, Ye CH, Liu BD, Golberg D (2006) Synthesis, characterization and field-emission properties of bamboo-like β-SiC nanowires. Nanotechnology 17:3468–3472
Shim HW, Huang HC (2007) Three-stage transition during silicon carbide nanowire growth. Appl Phys Lett 90:083106
Shim HW, Zhang YF, Huang HC (2008) Twin formation during SiC nanowire synthesis. J Appl Phys 104:063511
Sun XH, Li CP, Wong NB, Lee CS, Lee ST, Teo BK (2002) Templating effect of hydrogen-passivated silicon nanowires in the production of hydrocarbon nanotubes and nanoonions via sonochemical reactions with common organic solvents under ambient conditions. J Am Chem Soc 124(50):14856–14857
Taguchi T, Igawa N, Yamamoto H, Jitsukawa S (2005) Synthesis of silicon carbide nanotubes. J Am Ceram Soc 88(2):459–461
Wang DH, Xu D, Wang Q, Hao YJ, Jin GQ, Guo XY, Tu KN (2008a) Periodically twinned SiC nanowires. Nanotechnology 19:215602
Wang ZG, Zu XT, Gao F, Weber WJ (2008b) Atomistic simulations of the mechanical properties of silicon carbide nanowires. Phys Rev B 77:224113
Wang ZH, Zhao MW, He T, Zhang HY, Zhang XJ, Xi ZX, Yan SS, Liu XD, Xia YY (2009) Orientation-dependent stability and quantum-confinement effects of silicon carbide nanowires. J Phys Chem C 113:12731–12735
Wang ZG, Li JB, Gao F, Weber WJ (2010) Tensile and compressive mechanical behavior of twinned silicon carbide nanowires. Acta Mater 58(6):1963–1971
Wong EW, Sheehan PE, Lieber CM (1997) Nanobeam mechanics: elasticity, strength, and toughness of nanorods and nanotubes. Science 277:1971–1975
Wong KW, Zhou XT, Frederick CK, Au K, Lai HL, Lee CS, Lee ST (1999) Field-emission characteristics of SiC nanowires prepared by chemical-vapor deposition. Appl Phys Lett 75:2918–2920
Wu ZH, Mei XY, Kim D, Blumin M, Ruda HE (2002) Growth of Au-catalyzed ordered GaAs nanowire arrays by molecular-beam epitaxy. Appl Phys Lett 81:5177–5179
Wu RB, Pan Y, Yang GY, Gao MX, Wu LL, Chen JJ, Zhai R, Lin J (2007) Twinned SiC zigzag nanoneedles. J Phys Chem C 111(17):6233–6237
Yan BH, Zhou G, Duan WH, Wu J, Gu BL (2006) Uniaxial-stress effects on electronic properties of silicon carbide nanowires. Appl Phys Lett 89:023104
Yang GY, Wu RB, Chen JJ, Pan Y, Zhai R, Wu LL, Lin J (2007) Growth of SiC nanowires/nanorods using a Fe-Si solution method. Nanotechnology 18:155601
Zhang Y, Suenaga K, Colliex C, Iijima S (1998) Coaxial nanocable: silicon carbide and silicon oxide sheathed with boron nitride and carbon. Science 281:973–975
Zhang DQ, Alkhateeb A, Han HM, Mahmood H, Mcllroy DN, Norton MG (2003) Silicon carbide nanosprings. Nano Lett 3(7):983–987
Acknowledgments
Z. Wang was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (10704014) and the Young Scientists Foundation of Sichuan (09ZQ026-029) and UESTC (JX0731). J. Li gratefully acknowledges financial support from the “One-Hundred Talents Plan” of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholar (Grants No.60925016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Wang, S., Zhang, C. et al. First principles study of the electronic properties of twinned SiC nanowires. J Nanopart Res 13, 185–191 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-0017-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-0017-0