Abstract
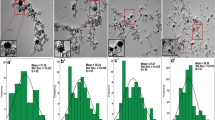
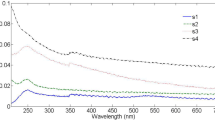
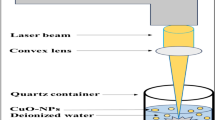
Pulsed laser ablation in liquid (PLAL) has been widely applied for the generation of nanoparticles (NPs). We report on the generation of NiO NPs using a high-power, high-brightness continuous wave (CW) fiber laser source at a wavelength of 1,070 nm. Characterization of such NPs in terms of size distribution, shape, chemical composition, and phase structure was carried out by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), high-resolution TEM equipped with energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX), and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The results revealed the formation of NiO NPs in water with an average size of 12.6 nm. The addition of anionic surfactant sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) reduced the size of NiO NPs down to 10.4 nm. The shape of the NPs was also affected by the SDS, showing the change of shapes from spherical domination in water to tetragonal with increased SDS concentrations. Furthermore, the NiO NPs generated in water and SDS solutions were dual phase containing both cubic and rhombohedral structures. It was also found that the NiO NPs were single crystalline in nature irrespective of the size and shape.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdolvand A, Khan SZ et al (2007) Efficient generation of titanium oxide nanomaterials using a continuous wave high-power fiber laser. Conference on lasers and electro-optics (CLEO Europe), Munich, Germany
Abdolvand A, Khan SZ et al (2008) Generation of titanium-oxide nanoparticles in liquid using a high-power, high-brightness continuous-wave fiber laser. Appl Phys A 91(3):365–368. doi:10.1007/s00339-008-4448-8
Bernand-Mantel A, Seneor P et al (2006) Evidence for spin injection in a single metallic nanoparticle: a step towards nanospintronics. J Appl Phys Lett 89(6):062502. doi:10.1063/1.2236293
Boschloo G, Hagfeldt A (2001) Spectroelectrochemistry of nanostructured NiO. J Phys Chem B 105(15):3039–3044. doi:10.1021/jp003499s
Ditlbacher H, Krenn JR et al (2000) Spectrally coded optical data storage by metal nanoparticles. Opt Lett 25(8):563–565. doi:10.1364/OL.25.000563
Fojtik A, Henglein A (1993) Laser ablation of films and suspended particles in a solvent. Formation of cluster and colloid solutions. Ber Bunsen-Ges Phys Chem 97(2):252
Gleiter H (1989) Nanocrystalline materials. Prog Mater Sci 33(4):223–315. doi:10.1016/0079-6425(89)90001-7
Golightly JS, Castleman AW Jr (2006) Analysis of titanium nanoparticles created by laser irradiation under liquid environment. J Phys Chem B 110(40):19979–19984. doi:10.1021/jp062123x
Jin Z, Lan CQ (2008) Nickel and cobalt nanoparticles produced by laser ablation of solids in organic solution. Mat Lett 62(10–11):1521–1524
Kim S, Yoo BK et al (2005) Catalytic effect of laser ablated Ni nanoparticles in the oxidative addition reaction for a coupling reagent of benzylchloride and bromoacetonitrile. J Mol Catal Chem 226(2):231–234. doi:10.1016/j.molcata.2004.10.038
Kumar S, Nann T (2006) Shape control of II–VI semiconductor nanomaterials. Small 2(3):316–329. doi:10.1002/smll.200500357
Liu B, Hu Z et al (2007) Nanoparticle generation in ultrafast pulsed laser ablation of nickel. Appl Phys Lett 90(4):044103. doi:10.1063/1.2434168
Mafune F, Kohno J-Y et al (2000a) Formation and size control of silver nanoparticles by laser ablation in aqueous solution. J Phys Chem B 104(39):9111–9117. doi:10.1021/jp001336y
Mafune F, Kohno J-Y et al (2000b) Structure and stability of silver nanoparticles in aqueous solution produced by laser ablation. J Phys Chem B 104(35):8333–8337. doi:10.1021/jp001803b
Mafune F, Kohno J-Y et al (2003) Formation of stable platinum nanoparticles by laser ablation in water. J Phys Chem B 107(18):4218–4223. doi:10.1021/jp021580k
Mahfouz R, Cadete Santos Aires FJ et al (2008) Synthesis and physico-chemical characteristics of nanosized particles produced by laser ablation of a nickel target in water. Appl Surf Sci 254(16):5181–5190
Neddersen J, Chumanov G et al (1993) Laser ablation of metals. A new method for preparing SERS active colloids. Appl Spectrosc 47(12):1959. doi:10.1366/0003702934066460
Prochazka M, Stepanek J et al (1997) Laser ablation: preparation of ‘chemically pure’ Ag colloids for surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy. J Mol Struct 410–411:213–216. doi:10.1016/S0022-2860(96)09467-7
Sakiyama K, Koga K et al (2004) Formation of size-selected Ni/Nio core-shell particles by pulsed laser ablation. J Phys Chem B 108(2):523–529. doi:10.1021/jp035339x
Sakka T, Iwanaga S et al (2000) Laser ablation at solid-liquid interfaces: an approach from optical emission spectra. J Chem Phys 112(19):8645–8653. doi:10.1063/1.481465
Sasaki T, Liang C et al (2004) Fabrication of oxide base nanostructures using pulsed laser ablation in aqueous solutions. J Appl Phys A 79:1489–1492
Sasaki T, Shimizu Y et al (2006) Preparation of metal oxide-based nanomaterials using nanosecond pulsed laser ablation in liquids. J Photochem Photobiol Chem 182(3):335–341. doi:10.1016/j.jphotochem.2006.05.031
Seto T, Koga K et al (2004) Laser synthesis and magnetic properties of monodispersed core-shell nanoparticles. J Appl Phys A 79:1165–1167
Sibbald MS, Chumanov G et al (1996) Reduction of cytochrome c by halide-modified, laser-ablated silver colloids. J Phys Chem 100(11):4672. doi:10.1021/jp953248x
Swihart MT (2003) Vapor-phase synthesis of nanoparticles. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 8(1):127–133. doi:10.1016/S1359-0294(03)00007-4
Tartaj P, Del Puerto Morales M et al (2003) The preparation of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine. J Phys D Appl Phys 36(13):182–197. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/36/13/202
Tsuji T, Kakita T et al (2003) Preparation of nano-size particles of silver with femtosecond laser ablation in water. Appl Surf Sci 206(1–4):314–320. doi:10.1016/S0169-4332(02)01230-8
Willard MA, Kurihara LK et al (2004) Chemically prepared magnetic nanoparticles. Int Mater Rev 49(3–4):125–170. doi:10.1179/095066004225021882
Zbroniec L, Martucci A et al (2004) Optical CO gas sensing using nanostructured NiO and NiO/SiO2 nanocomposites fabricated by PLD and sol-gel methods. J Appl Phys A 79(4–6):1303–1305
Zbroniec L, Sasaki T et al (2005) Parameter dependence of nickel oxide nanoparticles prepared by pulsed-laser ablation. J Ceram Process Res 6(2):134–137
Acknowledgments
This work is conducted by the Northwest Laser Engineering Consortium, funded by the Northwest Development Agency (NWDA) of the UK. The authors are thankful to Ms Judith Shackleton for her help with XRD. S.Z. Khan is thankful for research funding by National University of Sciences and Technology (Pakistan) and The University of Manchester (UK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, S.Z., Yuan, Y., Abdolvand, A. et al. Generation and characterization of NiO nanoparticles by continuous wave fiber laser ablation in liquid. J Nanopart Res 11, 1421–1427 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-008-9530-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-008-9530-9