Abstract
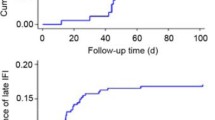
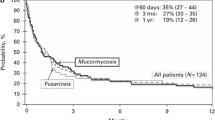
Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT) recipients are at increased risk of invasive fungal infections (IFI), which are associated with a high mortality rate. We evaluated the impact of IFI in allogeneic HCT patients. In total, 541 consecutive allogeneic HCT recipients were included. The cumulative incidence of any IFI and mold infections at 1-year post-HCT was 10 and 7%, respectively. Median times to IFI and mold infection were 200 and 210 days, respectively. There was a trend toward fewer IFI and mold infections in the last several years. Both acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) (OR 1.83, p = 0.05) and corticosteroid duration (OR 1.0, p = 0.026) were significantly associated with increased risk of IFI, acute GVHD (OR 2.3, p = 0.027) emerged as the most important association with mold infections. Any IFI [HR 4.1 (2.79–6.07), p < 0.0001] and mold infections [HR 3.34 (2.1–5.1), p < 0.0001] were independently associated with non-relapse mortality (NRM). This association persisted in the setting of both acute and chronic GVHD. Corticosteroid treatment for >90 days was also significantly associated with higher NRM [HR 1.9 (1.3–2.6), p < 0.0001]. This study highlights the impact of IFI on NRM among HCT patients. The decrease in number of IFI and mold infections over the last several years may reflect the benefit of prophylaxis with mold-active antifungal agents.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Neofytos D, Horn D, Anaissie E, Steinbach W, Olyaei A, Fishman J, et al. Epidemiology and outcome of invasive fungal infection in adult hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients: analysis of Multicenter Prospective Antifungal Therapy (PATH) Alliance registry. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;48:265–73.
Kontoyiannis DP, Marr KA, Park BJ, Alexander BD, Anaissie EJ, Walsh TJ, et al. Prospective surveillance for invasive fungal infections in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients, 2001–2006: overview of the Transplant-Associated Infection Surveillance Network (TRANSNET) Database. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;50:1091–100.
Ullmann AJ, Lipton JH, Vesole DH, Chandrasekar P, Langston A, Tarantolo SR, et al. Posaconazole or fluconazole for prophylaxis in severe graft-versus-host disease. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:335–47.
Malani AN, Kerr LE, Kauffman CA. Voriconazole: How to use this antifungal agent and What to expect. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2015;36:786–95.
Clark NM, Grim SA, Lynch JP 3rd. Posaconazole: use in the prophylaxis and treatment of fungal infections. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2015;36:767–85.
De Pauw B, Walsh TJ, Donnelly JP, Stevens DA, Edwards JE, Calandra T, et al. Revised definitions of invasive fungal disease from the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Invasive Fungal Infections Cooperative Group and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study Group (EORTC/MSG) Consensus Group. Clin Infect Dis Off Publ Infect Dis Soc Am. 2008;46:1813–21.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J, et al. 1994 Consensus conference on acute GVHD grading. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995;15:825–8.
Filipovich AH, Weisdorf D, Pavletic S, Socie G, Wingard JR, Lee SJ, et al. National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. Diagnosis and staging working group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2005;11:945–56.
Akan H, Antia VP, Kouba M, Sinko J, Tanase AD, Vrhovac R, et al. Preventing invasive fungal disease in patients with haematological malignancies and the recipients of haematopoietic stem cell transplantation: practical aspects. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013;68:iii5–16.
Bow EJ. Invasive fungal infection in haematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients: epidemiology from the transplant physician’s viewpoint. Mycopathologia. 2009;168:283–97.
Omer AK, Ziakas PD, Anagnostou T, Coughlin E, Kourkoumpetis T, McAfee SL, et al. Risk factors for invasive fungal disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a single center experience. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013;19:1190–6.
Slavin S, Naparstek E, Nagler A, Ackerstein A, Kapelushnik J, Or R. Allogeneic cell therapy for relapsed leukemia after bone marrow transplantation with donor peripheral blood lymphocytes. Exp Hematol. 1995;23:1553–62.
Baddley JW, Stroud TP, Salzman D, Pappas PG. Invasive mold infections in allogeneic bone marrow transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:1319–24.
Marr KA, Carter RA, Crippa F, Wald A, Corey L. Epidemiology and outcome of mould infections in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;34:909–17.
Jantunen E, Ruutu P, Niskanen L, Volin L, Parkkali T, Koukila-Kahkola P, et al. Incidence and risk factors for invasive fungal infections in allogeneic BMT recipients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1997;19:801–8.
Martino R, Bautista G, Parody R, Garcia I, Esquirol A, Rovira M, et al. Severe infections after single umbilical cord blood transplantation in adults with or without the co-infusion of CD34+ cells from a third-party donor: results of a multicenter study from the Grupo Espanol de Trasplante Hematopoyetico (GETH). Transpl Infect Dis. 2015;17:221–33.
Junghanss C, Marr KA, Carter RA, Sandmaier BM, Maris MB, Maloney DG, et al. Incidence and outcome of bacterial and fungal infections following nonmyeloablative compared with myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a matched control study. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2002;8:512–20.
Mikulska M, Raiola AM, Bruno B, Furfaro E, Van Lint MT, Bregante S, et al. Risk factors for invasive aspergillosis and related mortality in recipients of allogeneic SCT from alternative donors: an analysis of 306 patients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2009;44:361–70.
Miceli MH, Diaz JA, Lee SA. Emerging opportunistic yeast infections. Lancet Infect Dis. 2011;11:142–51.
Miceli MH, Lee SA. Emerging moulds: epidemiological trends and antifungal resistance. Mycoses. 2011;54:e666–78.
Kauffman CA. Zygomycosis: reemergence of an old pathogen. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39:588–90.
Park BJ, Pappas PG, Wannemuehler KA, Alexander BD, Anaissie EJ, Andes DR, et al. Invasive non-Aspergillus mold infections in transplant recipients, United States, 2001–2006. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:1855–64.
Horn DL, Freifeld AG, Schuster MG, Azie NE, Franks B, Kauffman CA. Treatment and outcomes of invasive fusariosis: review of 65 cases from the PATH Alliance registry. Mycoses. 2014;57:652–8.
Rowley S, Friedman TM, Korngold R. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for malignant diseases. In: Rich R, editor. Clinical immunology principles and practice. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Mosby-Elsevier; 2008. p. 1223–36.
Buttgereit F, Seibel MJH, Bijlsma JWJ. Glucocorticoids. In: Rich R, editor. Clinical immunology principles and practice. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Mosby-Elsevier; 2008. p. 1293–305.
Gyetvai A, Emri T, Fekete A, Varga Z, Gazdag Z, Pesti M, et al. High-dose methylprednisolone influences the physiology and virulence of Candida albicans ambiguously and enhances the candidacidal activity of the polyene antibiotic amphotericin B and the superoxide-generating agent menadione. FEMS Yeast Res. 2007;7:265–75.
Farmakiotis D, Shirazi F, Zhao Y, Saad PJ, Albert ND, Roilides E, et al. Methylprednisolone enhances the growth of Exserohilum rostratum in vitro, attenuates spontaneous apoptosis, and increases mortality rates in immunocompetent Drosophila flies. J Infect Dis. 2014;210:1471–5.
Cordonnier C, Ribaud P, Herbrecht R, Milpied N, Valteau-Couanet D, Morgan C, et al. Prognostic factors for death due to invasive aspergillosis after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a 1-year retrospective study of consecutive patients at French transplantation centers. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;42:955–63.
Marr KA, Carter RA, Boeckh M, Martin P, Corey L. Invasive aspergillosis in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients: changes in epidemiology and risk factors. Blood. 2002;100:4358–66.
Bhatti Z, Shaukat A, Almyroudis NG, Segal BH. Review of epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment of invasive mould infections in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Mycopathologia. 2006;162:1–15.
Girmenia C, Raiola AM, Piciocchi A, Algarotti A, Stanzani M, Cudillo L, et al. Incidence and outcome of invasive fungal diseases after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a prospective study of the Gruppo Italiano Trapianto Midollo Osseo (GITMO). Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20:872–80.
Hou CY, Xu LL, Chen H, Liu N, Jiang M, Wang GQ, et al. Intestinal aGVHD and infection after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Med Sci Monit. 2013;19:802–6.
Henden AS, Hill GR. Cytokines in graft-versus-host disease. J Immunol. 2015;194:4604–12.
Shoham S, Levitz SM. The immune response to fungal infections. Br J Haematol. 2005;129:569–82.
Bettelli E, Carrier Y, Gao W, Korn T, Strom TB, Oukka M, et al. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature. 2006;441:235–8.
Zelante T, De Luca A, Bonifazi P, Montagnoli C, Bozza S, Moretti S, et al. IL-23 and the Th17 pathway promote inflammation and impair antifungal immune resistance. Eur J Immunol. 2007;37:2695–706.
Malard F, Bossard C, Brissot E, Chevallier P, Guillaume T, Delaunay J, et al. Increased Th17/Treg ratio in chronic liver GVHD. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014;49:539–44.
Serody JS, Hill GR. The IL-17 differentiation pathway and its role in transplant outcome. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2012;18:S56–61.
Gregg KS, Kauffman CA. Invasive aspergillosis: epidemiology, clinical aspects, and treatment. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2015;36:662–72.
Upton A, Kirby KA, Carpenter P, Boeckh M, Marr KA. Invasive aspergillosis following hematopoietic cell transplantation: outcomes and prognostic factors associated with mortality. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44:531–40.
Baddley JW, Andes DR, Marr KA, Kontoyiannis DP, Alexander BD, Kauffman CA, et al. Factors associated with mortality in transplant patients with invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;50:1559–67.
Acknowledgement
Funding was provided by National Institutes of Health (Grant No. CA46592).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Marisa H. Miceli, Tracey Churay, Thomas Braun, and Carol A. Kauffman have no conflicts to report. Daniel R. Couriel is an active member of Merck, Inc. Advisory Board.
Additional information
Marisa H. Miceli and Tracey Churay have contributed equally to the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miceli, M.H., Churay, T., Braun, T. et al. Risk Factors and Outcomes of Invasive Fungal Infections in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplant Recipients. Mycopathologia 182, 495–504 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-017-0115-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-017-0115-y