Abstract
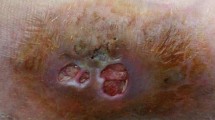
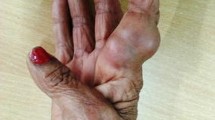
We report a rare case of subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Cladosporium cladosporioides. A 21-year-old man was presented to our clinic with the history of cysts and nodules on his face and neck for 5 years. He was diagnosed subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis according to the finding of fungal elements in histopathological examination and direct microscopic examination of cyst pus, which was confirmed by positive culture of the cyst pus. The isolate grown on culture was identified as C. cladosporioides on the basis of morphological characters and sequence of the ITS region of ribosomal DNA. After treatment with oral itraconazole, he almost completely resolved the inflammatory lesions. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case report of C. cladosporioides infection presented with multiple cysts and nodules like acne.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li DM, de Hoog GS. Cerebral phaeohyphomycosis: a cure at what lengths? Lancet Infect Dis. 2009;9:376–83.
Kwon-Chung KJ, Schwartz IS, Rybak BJ. A pulmonary fungus ball produced by Cladosporium cladosporioides. Am J Clin Pathol. 1975;64:564–8.
Polack FM, Siverio C, Bresky RH. Corneal chromomycosis: double infection by Phialophora verrucosa (Medlar) and Cladosporium cladosporioides (Frescenius). Ann Ophthalmol. 1976;8:139–44.
Gugnani HC, Gupta S, Talwar RS. Role of opportunistic fungi in ocular infections in Nigeria. Mycopathologia. 1978;65:155–66.
Drabick JJ, Gomatos PJ, Solis JB. Cutaneous cladosporiosis as a complication of skin testing in a man positive for human immunodeficiency virus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;22:135–6.
Annessi G, Cimitan A, Zambruno G, Di Silverio A. Cutaneous phaeohyphomycosis due to Cladosporium cladosporioides. Mycoses. 1992;35:243–6.
Pereiro M Jr, Jo-Chu J, Toribio J. Phaeohyphomycotic cyst due to Cladosporium cladosporioides. Dermatology. 1998;197:90–2.
Gugnani HC, Sood N, Singh B, Makkar R. Case report. Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis due to Cladosporium cladosporioides. Mycoses. 2000;43:85–7.
Vieira MR, Milheiro A, Pacheco FA. Phaeohyphomycosis due to Cladosporium cladosporioides. Med Mycol. 2001;39:135–7.
Kantarcioglu AS, Yücel A, de Hoog GS. Case report. Isolation of Cladosporium cladosporioides from cerebrospinal fluid. Mycoses. 2002;45:500–3.
Huang WM, Li W, Guo HW, Luo YC, Chen QX. A case of cutaneous phaeohyphomycosis due to Cladosporium cladosporioides [in Chinese]. Chin J Mycol. 2008;3:157–60.
Chew FL, Subrayan V, Chong PP, Goh MC, Ng KP. Cladosporium cladosporioides keratomycosis: a case report. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2009;53:657–9.
Yu J, Wan Z, Lu QY, Chen W, Wang XH. Onychomycosis caused by Trichophyton rubrum and Cladosporium cladosporioides in psoriasis patient: one case report [in Chinese]. Chin J Mycol. 2009;4:298–300.
Duquia RP, de Almeida HL, Jr Vettorato G, Rocha NM, de Castro LA. Ecthyma-like phaeohyphomycosis caused by Cladosporium cladosporioides. Mycoses. 2010;53:541–3.
Sang H, Zheng XE, Zhou WQ, He W, Lv GX, Shen YN, et al. A case of subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Cladosporium cladosporioides and its treatment. Mycoses. 2012;55:195–7.
Giri S, Kindo AJ, Rao S, Kumar AR. Unusual causes of fungal rhinosinusitis: a study from a tertiary care centre in South India. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2013;31:379–84.
Zeller S, Lempert S, Goebeler M, Hamm H, Kolb-Mäurer A. Cladosporium cladosporioides: a so far unidentified cause of white piedra. Mycoses. 2015;58:315–7.
Bordoloi P, Nath R, Borgohain M, Huda MM, Barua S, Dutta D, et al. Subcutaneous mycoses: an aetiological study of 15 cases in a tertiary care hospital at Dibrugarh, Assam, northeast India. Mycopathologia. 2015;179:425–35.
Nath R, Barua S, Barman J, Swargiary P, Borgohain M, et al. Subcutaneous Mycosis due to Cladosporium cladosporioides and Bipolaris cynodontis from Assam, North-East India and review of published. Mycopathologia. 2015;180:379–87.
Zhou YB, Chen P, Sun TT, Wang XJ, Li DM. Acne-like subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Cladosporium cladosporioides: a rare case report and review of published literatures. Mycopathologia. 2016. doi:10.1007/s11046-016-9995-5.
Acknowledgments
We thank the patient for providing permission to share his information. This work is supported by Project 81571967 of National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y.B., Chen, P., Sun, T.T. et al. Acne-Like Subcutaneous Phaeohyphomycosis Caused by Cladosporium cladosporioides: A Rare Case Report and Review of Published Literatures. Mycopathologia 181, 567–573 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-016-9995-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-016-9995-5