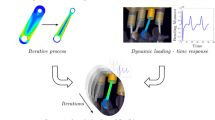
Abstract
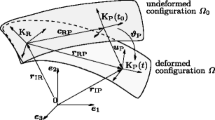
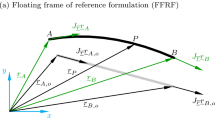
The paper concerns a detailed comparison between two optimization methods that are used to perform the structural optimization of flexible components within a multibody system (MBS) simulation. The dynamic analysis of flexible MBS is based on a nonlinear finite element formulation. The first method is a weakly coupled method, which reformulates the dynamic response optimization problem in a two-level approach. First, a rigid or flexible MBS simulation is performed, and second, each component is optimized independently using a quasi-static approach in which a series of equivalent static load (ESL) cases obtained from the MBS simulation are applied to the respective components. The second method, the fully coupled method, performs the dynamic response optimization using the time response obtained directly from the flexible MBS simulation. Here, an original procedure is proposed to evaluate the ESL from a nonlinear finite element simulation, contrasting with the floating reference frame formulation exploited in the standard ESL method. Several numerical examples are provided to support our position. It is shown that the fully coupled method is more general and accommodates all types of constraints at the price of a more complex optimization process.















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The difference is made between a multibody system and a structure since the latter is composed of only one body. This enables a simplification of the equations for this introductory section.
References
Arnold, M., Brüls, O.: Convergence of the generalized-\(\alpha\) scheme for constrained mechanical systems. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 18(2), 185–202 (2007)
Bendsøe, M., Sigmund, O.: Topology Optimization: Theory, Methods, and Applications. Springer, Berlin (2003)
Bestle, D., Seybold, J.: Sensitivity analysis of constrained multibody systems. Arch. Appl. Mech. 62, 181–190 (1992)
Brüls, O., Eberhard, P.: Sensitivity analysis for dynamic mechanical systems with finite rotations. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 74(13), 1897–1927 (2008)
Brüls, O., Lemaire, E., Duysinx, P., Eberhard, P.: Optimization of multibody systems and their structural components. In: Multibody Dynamics: Computational Methods and Applications, vol. 23, pp. 49–68. Springer, Berlin (2011)
Bruns, T., Tortorelli, D.: Computer-aided optimal design of flexible mechanisms. In: Proceedings of the Twelfth Conference of the Irish Manufacturing Commitee, IMC12, Competitive Manufacturing, University College Cork, Ireland (1995)
Cardona, A., Géradin, M.: Modelling of superelements in mechanism analysis. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 32(8), 1565–1593 (1991)
Choi, W., Park, G.: Structural optimization using equivalent static loads at all time intervals. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 191(19–20), 2105–2122 (2002)
Chung, J., Hulbert, G.: A time integration algorithm for structural dynamics with improved numerical dissipation: The generalized-\(\alpha\) method. J. Appl. Mech. 60, 371–375 (1993)
Deaton, J., Grandhi, R.: A survey of structural and multidisciplinary continuum topology optimization: Post 2000. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 49(1), 1–38 (2014)
Etman, L., Van Campen, D., Schoofs, A.: Design optimization of multibody systems by sequential approximation. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 2(4), 393–415 (1998)
Géradin, M., Cardona, A.: Flexible Multibody Dynamics: A Finite Element Approach. Wiley, New York (2001)
Häussler, P., Emmrich, D., Müller, O., Ilzhöfer, B., Nowicki, L., Albers, A.: Automated topology optimization of flexible components in hybrid finite element multibody systems using ADAMS/Flex and MSC.Construct. In: Proceedings of the 16th European ADAMS Users’ Conference (2001)
Häussler, P., Minx, J., Emmrich, D.: Topology optimization of dynamically loaded parts in mechanical systems: Coupling of MBS, FEM and structural optimization. In: Proceedings of NAFEMS Seminar Analysis of Multi-Body Systems Using FEM and MBS, Wiesbaden, Germany (2004)
Held, A.: On structural optimization of flexible multibody systems. Ph.D. thesis, Institut für Technische und Numerische Mechanik, Universität Stuttgart (2014)
Hong, E., You, B., Kim, C., Park, G.: Optimization of flexible components of multibody systems via equivalent static loads. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 40, 549–562 (2010)
The MathWorks, Inc.: MATLAB and Optimization Toolbox Release 2012b. Natick, Massachusetts, United States (2012)
Kang, B., Park, G., Arora, J.: Optimization of flexible multibody dynamic systems using the equivalent static load method. AIAA J. 43(4), 846–852 (2005)
Oral, S., Kemal Ider, S.: Optimum design of high-speed flexible robotic arms with dynamic behavior constraints. Comput. Struct. 65(2), 255–259 (1997)
Saravanos, D., Lamancusa, J.: Optimum structural design of robotic manipulators with fiber reinforced composite materials. Comput. Struct. 36, 119–132 (1990)
Seifried, R., Held, A.: Integrated design approaches for controlled flexible multibody systems. In: Proceedings of the ASME 2011 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences & Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, IDETC/CIE 2011, Washington DC, USA (2011)
Shabana, A.: Dynamics of Multibody Systems, 4th edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2013)
Sherif, K., Irschik, H.: Efficient topology optimization of large dynamic finite element systems using fatigue. AIAA J. 48(7), 1339–1347 (2010)
Sigmund, O., Maute, K.: Topology optimization approaches: A comparative review. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 48(6), 1031–1055 (2013)
Sohoni, V.N., Haug, E.J.: A state space technique for optimal design of mechanisms. J. Mech. Des. 104(4), 792–798 (1982)
Stolpe, M.: On the equivalent static loads approach for dynamic response structural optimization. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 50, 921–926 (2014)
Tobias, C., Fehr, J., Eberhard, P.: Durability-based structural optimization with reduced elastic multibody systems. In: Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Engineering Optimization, Lisbon, Portugal (2010)
Tromme, E., Brüls, O., Emonds-Alt, J., Bruyneel, M., Virlez, G., Duysinx, P.: Discussion on the optimization problem formulation of flexible components in multibody systems. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 48, 1189–1206 (2013)
Wasfy, T., Noor, A.: Computational strategies for flexible multibody systems. Appl. Mech. Rev. 56(6), 553–613 (2003)
Acknowledgements
Parts of this research have been supported by the LIGHTCAR Project sponsored by the pole of competitiveness “MecaTech” and the Walloon Region of Belgium (Contract RW-6500) and the CIMEDE 2 Project sponsored by the pole of competitiveness “GreenWin” and the Walloon Region of Belgium (Contract RW-7179).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tromme, E., Brüls, O. & Duysinx, P. Weakly and fully coupled methods for structural optimization of flexible mechanisms. Multibody Syst Dyn 38, 391–417 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11044-015-9493-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11044-015-9493-4