Abstract
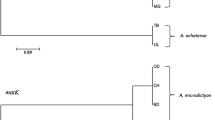
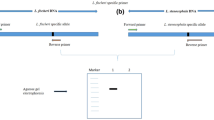
Tetrastigma hemsleyanum is a rare and endangered herb, which is commercialized as the resource of anti-cancer drugs. Wild T. hemsleyanum plants are on the verge of extinction recently, there are increasing numbers of counterfeits on the market. In the present study, inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR), Cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence (CAPS), and the internal transcribed spacer region II (ITS2) barcode were used for the first time for the authentication of T. hemsleyanum from its commonly counterfeits. ISSR analysis suggested that it was a useful method for distinguishing T. hemsleyanum from its adulterants of different genus. However, it was insufficient to distinguish T. hemsleyanum from those adulterants of the same genus. ITS2 of T. hemsleyanum and the commonly counterfeits were amplified and sequenced. The Neighbor-Joining tree constructed from the ITS2 sequences showed that T. hemsleyanum was clearly differentiated from all counterfeits samples. A mutation site in the ITS2 region of T. hemsleyanum had been found which could be recognized by the restriction endonuclease NcoI. T. hemsleyanum could be readily distinguished from counterfeits as the PCR products from T. hemsleyanum could be digested sufficiently by NcoI, while the PCR products from counterfeits could not be digested. The results indicated that CAPS and ITS2 barcode methods provided effective and accurate identification of T. hemsleyanum from all its adulterants, while ISSR could only distinguish T. hemsleyanum from its adulterants of different genus. The CAPS method developed in the present study will serve as a reliable tool for safe and effective use of T. hemsleyanum in the clinic application. It will also play an important role for the identification, management and conservation of this endangered species.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vijayan D, Cheethaparambil A, Pillai GS, Balachandran I (2014) Molecular authentication of Cissampelos pareira L. var. hirsuta (Buch.-Ham. ex DC.) Forman, the genuine source plant of ayurvedic raw drug ‘Patha’, and its other source plants by ISSR markers. 3. Biotechnology 4:559–562
Moon BC, Ji Y, Lee YM, Kang YM, Kim HK (2015) Authentication of Akebia quinata DECNE from its common adulterant medicinal plant species based on the RAPD-derived SCAR markers and multiplex-PCR. Genes Genom 37:23–32
Mukherjee P, Varshney A, Johnson TS, Jha TB (2011) Jatropha curcas: a review on biotechnological status and challenges. Plant Biotechnol Rep 5:197–215
Long Y, Cheng J, Mei ZQ, Zhao L, Wei C, Fu S, Khan MA, Fu JJ (2015) Genetic analysis of litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.) in southern China by improved random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) and inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR). Mol Biol Rep 42:159–166
Lee JW, Bang KH, Kim YC, Seo AY, Jo IH, Lee JH, Kim OT, Hyun DY, Cha SW (2012) CAPS markers using mitochondrial consensus primers for molecular identification of Panax species and Korean ginseng cultivars (Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer). Mol Biol Rep 39:729–736
Van Dan N, Ramchiary N, Choi SR, Uhm TS, Yang TJ, Ahn IO, Lim YP (2010) Development and characterization of new microsatellite markers in Panax ginseng (C.A. Meyer) from BAC end sequences. Conserv Genet 11:1223–1225
Ganopoulos I, Madesis P, Tsaftaris A (2012) Universal ITS2 barcoding DNA region coupled with high- resolution melting (HRM) analysis for seed authentication and adulteration testing in leguminous forage and pasture species. Plant Mol Biol Rep 30:1322–1328
Fišer ŽP, Buzan EV (2014) 20 years since the introduction of DNA barcoding: from theory to application. J Appl Genet 55:43–52
Kshirsagar P, Umdale S, Chavan J, Gaikwad N (2015) Molecular authentication of medicinal plant, Swertia chirayita and its adulterant species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. doi:10.1007/s40011-015-0556-3
Peng X, Ji QY, Fan SW, Zhang YJ, Zhang JJ (2015) Genetic diversity in populations of the endangered medicinal plant Tetrastigma hemsleyanum revealed by ISSR and SRAP markers: implications for conservation. Genet Resour Crop Ev 62:1069–1078
He FG (2010) Research progress in anticancer effect of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg and its mechanism. J Oncol 16:75–77 (in Chinese)
Peng X, Zhang YY, Wang J (2015) Ethylacetate extract from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum induces apoptosis via the mitochondrial-caspase-dependent intrinsic pathway in HepG2 cells. Tumor Biol. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-3579-8
Peng X, Zhang TT, Zhang J (2015) Effect of subculture times on genetic fidelity, endogenous hormone level and pharmaceutical potential of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum callus. Plant Cell Tissue Org 122:67–77
Rohlf FJ (2001) NTSYS-pc numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system. Exeter Software, New York
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F (1997) The CLUSTAL X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Guo WL, Gong L, Ding ZF, Li YD, Li FX, Zhao SP, Liu B (2006) Genomic instability in phenotypically normal regenerants of medicinal plant Codonosis lanceolata Benth.et Hook.f., as revealed by ISSR and RAPD markers. Plant Cell Rep 25:896–906
Shilpha J, Silambarasan T, Pandian SK, Ramesh M (2013) Assessment of genetic diversity in Solanum trilobatum L., an important medicinal plant from south India using RAPD and ISSR markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 60:807–818
Su HY, Wang L, Liu LD, Chi XY, Zhang YX (2008) Use of inter-simple sequence repeat markers to develop strain-specific SCAR markers for Flammulina velutipes. J Appl Genet 49:233–235
Touhata K, Namikoshi A, Suzuki T, Iguchi J, Mizusawa N, Hara T, Imamura S, Yabu T, Yamashita Y, Yamashita M (2013) Origin identification of dried seaweed product “nori” by PCR–RFLP analysis of Pyropia yezoensis in the internal transcribed spacer ITS-1 region. Fish Sci 79:865–875
Ma SH, Burchi G, Suh JK, Roh MS, Joung YH (2014) Identification of Ligustrum seedlings based on sequence analysis of an internal transcribed spacer. Hort Environ Biotechnol 55(5):423–427
Rinthong P, Zhu S, Komatsu K, Chanama S, De-Eknamkul W (2011) Genetic variation of Croton stellatopilosus ohba based on non-coding DNA sequences of ITS, trnK and trnL-F regions. J Nat Med 65:641–645
Wang CZ, Li P, Ding JY, Fishbein A, Yuan CS (2007) Discrimination of Lonicera japonica thunb. from different geographical origins using restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. Biol Pharm Bull 30:779–782
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the public welfare technology research projects of Zhejiang province (Grant No. 2013C32103), the Science and Technology Innovation Team Project of Ningbo Science and Technology Bureau, China (2015C110027), the agricultural research projects of Ningbo city (Grant No. 2014C10031), and the traditional Chinese Medical Science Technology Research Projects of Zhejiang province (Grant No. 2013ZA119).
Author Contribution
Xin Peng—Sequence alignment and analysis; Write the manuscript, Xiurong Wu—ISSR fingerprinting and statistical analysis, Qingyong Ji—Plant material sampling and pre-process, Ruikang Yang—DNA extraction and PCR amplification, Yulan Li—Restriction enzyme site analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, X., Wu, X., Ji, Q. et al. Molecular authentication of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum from its adulterant species using ISSR, CAPS, and ITS2 barcode. Mol Biol Rep 43, 785–794 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-016-4023-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-016-4023-x