Abstract
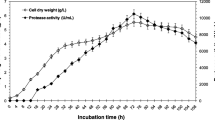
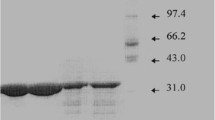
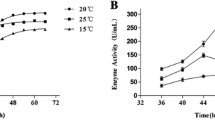
An extracellular cold-active alkaline serine protease from Penicillium chrysogenum FS010 has been purified. The purification procedure involved: ammonium sulfate precipitation, DEAE ion-exchange chromatography and sephadex G-100 gel chromatography. SDS–PAGE of the purified enzyme indicated a molecular weight of 41,000 ± 1,000 Da. The protease is stable in a pH range of 7.0–9.0 and has a maximum activity at pH 9.0. Compared with other industrial proteases, the enzyme shows a high hydrolytic activities at lower temperatures and a high sensitivity at a temperature over 50°C. The isoelectric point of the enzyme is approximate to 6.0. Enzymatic activity is enhanced by the addition of divalent cations such as Mg2+ and Ca2+ and inhibited by addition of Cu2+and Co2+. PMSF and DFP are its specific inhibitors. The application of the cold-active alkaline protease is extremely extensive, and widely used in detergents, feed, food, leather and many other industries.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nicholas JR (2000) Toward a molecular understanding of cold activity of enzymes from psychrophiles. Extremophiles 4:83–90
Hanna-Kirsti SL, Nils PW, Ame OS (2000) Structural comparison of psychrophilic and mesophilic trypsins. Eur J Biochem 267(4):1039–1049
Gerday C, Aittuleb M, Bentahir M et al (2000) Cold-adapted enzymes: from foundamentals to biotechnology. Tibtech 18:103–107
König GM, Wright AD (1997) Meeresorganismen-Produzenten pharmakologisch aktiver Sekundärstoffe. Pharm Unserer Zeit 26:281–288
Chen XL, Sun CY, Zhang YZ, Gao PJ (2002) Efects of different buffers on the thermostability and autolysis of a cold-adapted protease MCP-01. J Protein Chem 21(8):523–527
LAEMMLI UK (1970) Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Anja IP, Berne LJ, Marja-L et al (2002) Purification and properties of an alkaline proteinase of Fusarium culmorum. Eur J Biochem 269:798–807
Rashbehari T, Binita S, Rintu B (2003) Purification and characterization of a protease from solid state cultures of Aspergillus parasiticus. Process Biochem 38:1553–1558
María J, Mar R, Félix N et al (2002) Purification and Characterization of an Extracellular Protease from Penicillium chrysogenum Pg222 Active against Meat Proteins. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3532–3536
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ren Hongwei and Sun Caiyun (The State Key Laboratory of Microbial Technology, Shandong University, Jinan, and People’s Republic of China) for experimental assistances.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, HY., Tian, Y., Hou, YH. et al. Purification and characterization of the cold-active alkaline protease from marine cold-adaptive Penicillium chrysogenum FS010. Mol Biol Rep 36, 2169–2174 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-008-9431-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-008-9431-0