Abstract
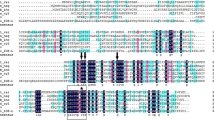
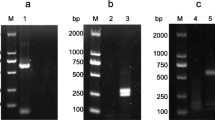
Previous studies have demonstrated that 14-3-3 proteins exist in all the eukaryotic organisms studied; however, studies on the 14-3-3 proteins have not been involved in the halotolerant, unicellular green alga Dunaliella salina so far. In the present study, a cDNA encoding 14-3-3 protein of D. salina was cloned and sequenced by PCR and rapid amplification of cDNA end (RACE) technique based on homologous sequences of the 14-3-3 proteins found in other organisms. The cloned cDNA of 1485 bp in length had a 29.2 kDa of molecular weight and contained a 774 bp of open reading frame encoding a polypeptide of 258 amino acids. Like the other 14-3-3 proteins, the deduced amino acid sequences of the D. salina 14-3-3 protein also contained two putative phosphorylation sites within the N-terminal region (positions 62 and 67). Furthermore, an EF hand motif characteristic for Ca2+-binding sites was located within the C-terminal part of this polypeptide (positions 208–219). Analysis of bioinformatics revealed that the 14-3-3 protein of D. salina shared homology with that of other organisms. Real-time quantitative PCR demonstrated that expression of the 14-3-3 protein gene is cell cycle-dependent.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- RACE:
-
Rapid amplification of cDNA ends
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction
References
Liebich I, Voigt J (1995) A Chlamydomonas homologue to the 14-3-3 proteins: cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence. Biochim Biophys Acta 1263:79–85
Voigt J, Frank R (2003) 14-3-3 proteins are constituents of the insoluble glycoprotein framework of the chlamydomonas cell wall. Plant Cell 15:1399–1413
Moore BW, Perez VJ (1967) Specific acid proteins in the nervous system. In: Carlson FD (ed) Physiological and biochemical aspects of nervous integration. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs Prentice Hall, New Jersey, pp 343–359
Aitken A, Colling DB, Van Heusden BPH, Isobe T, Roseboom PH, Rosenfeld G, Soll J (1992) 14–3-3 proteins: a highly conserved, widespread family of eukaryotic proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 17:498–501
Ichimura T, Sugano H, Kuwano R, Sunaya T, Okuyama T, Isobe T (1991) Widespread distribution of the 14-3-3 protein in vertebrate brains and bovine tissues: correlation with the distributions of calcium-dependent protein kinases. J Neurochem 56:1449–1451
Tang SJ, Suen TC, McInnes RR, Buchwald M (1998) Association of the TLX-2 homeodomain and 14-3-3 eta signaling proteins. J Biol Chem 273:25356–25363
Morrison D (1994) 14-3-3: modulators of signaling protein. Science 266:56–57
Wilker EW, van Vugt MA, Artim SA, Huang PH, Petersen CP, Reinhardt HC, Feng Y, Sharp PA, Sonenberg N, White FM, Yaffe MB (2007) 14-3-3 sigma controls mitotic translation to facilitate cytokinesis. Nature 446:329–332
Yang X, Lee WH, Sobott F, Papagrigoriou E, Robinson CV, Grossmann JG, Sundstrom M, Doyle DA, Elkins JM (2006) Structural basis for protein-protein interactions in the 14-3-3 protein family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:17237–17242
Aitken A, Howell S, Jones D, Madrazo J, Patel Y (1995) 14-3-3 alpha and delta are the phosphorylated forms of Raf-activating 14-3-3 beta and zeta. J Biol Chem 270:5706–5709
Piotrowski M, Oecking C (1998) Five new 14-3-3 isoforms from Nicotiana tabacum L.: implications for the phylogeny of plant 14-3-3 proteins. Planta 204:127–130
Wang W, Shakes DC (1996) Molecular evolution of the 14-3-3 protein family. J Mol Evol 43:384–398
Vasara T, Keranen S, Penttila M, Saloheimo M (2002) Characterization of two 14-3-3 genes from Trichoderma reesei: interactions with yeast secretory pathway components. Biochim Biophys Acta 1590:27–40
Aitken A (2006) 14-3-3 proteins: a historic overview. Semin Cancer Biol 16:162–172
Wu K, Rooney MF, Ferl RJ (1997) The Arabidopsis 14-3-3 multigene family. Plant Physiol 114:1421–1431
Daugherty CJ, Ronney MF, Miller PW, Ferl RJ (1996) Molecular organization and tissue-specific expression of an Arabidopsis 14-3-3 gene. Plant Cell 8:1239–1248
Voigt J, Stevanovic S, Schirle M, Fausel M, Maier J, Adam KH, Marquardt O (2004) A 14-3-3 protein of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii associated with the endoplasmic reticulum: nucleotide sequence of the cDNA and the corresponding gene and derived amino acid sequence. Biochim Biophys Acta 1679:180–194
Voigt J, Liebich I, Kiess M, Frank R (2001) Subcellular distribution of 14-3-3 proteins in the unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Eur J Biochem 268:6449–6457
Wang T, Xue L, Hou W, Yang B, Cha Y, Ji X, Wang Y (2007) Increased expression of transgene in stably transformed cells of Dunaliella salina by matrix attachment regions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76(3):651–657
Silflow CD, Youngblom J (1986) Chlamydomonas reinhardtii tubulin gene structure. Ann NY Acad Sci 466:18–30
Combet C, Blanchet C, Geourjon C, Deleage G (2000) Network protein sequence analysis. Trends Biochem Sci 25:147–150
Voigt J, Liebich I, Wöstemeyer J, Adam KH, Marquardt O (2000) Nucleotide sequence, genomic organization and cell-cycle-dependent expression of a Chlamydomonas 14-3-3 gene. Biochim Biophys Acta 1492(2–3):395–405
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.30470030), and carried out in Henan Key Laboratory for Molecular Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, T., Xue, L., Ji, X. et al. Cloning and characterization of the 14-3-3 protein gene from the halotolerant alga Dunaliella salina . Mol Biol Rep 36, 207–214 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-007-9168-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-007-9168-1