Abstract
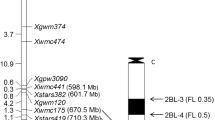
Since it was commercialized in 2008, Liangxing 66 is one of the most widely grown cultivars of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in winter and facultative wheat-producing regions in northern China. This cultivar displays broad-spectrum resistance to isolates of powdery mildew. To identify the powdery mildew resistance gene in Liangxing 66, genetic analysis and molecular mapping were conducted using the F2 populations and F2:3 families derived from the reciprocal crosses of Liangxing 66 and the susceptible cultivar Jingshuang 16. A single dominant gene, tentatively designated PmLX66, conferred resistance in Liangxing 66 to the powdery mildew isolate E09. The results of molecular mapping indicated that this gene was located on the short arm of chromosome 5D and flanked by SCAR203 and Xcfd81 at genetic distances of 0.4 and 2.8 cM, respectively, which is similar to the position of locus Pm2. However, PmLX66 and Pm2 showed different reactions to five of the 42 isolates of powdery mildew tested. Together, these results indicated that PmLX66 was most likely an allele of Pm2. Based on its superior yield and agronomic performance, in combination with powdery mildew resistance, Liangxing 66 is useful as a promising parent for control of powdery mildew and for the development of new disease-resistant cultivars.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam MA, Xue F, Wang CY, Ji WQ (2011) Powdery mildew resistance genes in wheat: identification and genetic analysis. J Mol Biol Res 1:20–39
Chen XM, Luo YH, Xia XC, Xia LQ, Chen X, Ren ZL, He ZH, Jia JZ (2005) Chromosomal location of powdery mildew resistance gene Pm16 in wheat using SSR marker analysis. Plant Breed 124:225–228
Duan XY, Sheng BQ, Zhou YL, Xiang QJ (1998) Monitoring of the virulence population of Erysiphe graminis f. sp. tritici. Acta Phytophylactica Sin 25:31–36
Duan SK, Xu YB, Wu XY (2002) Research progress of pathogen virulence, resistance genes and resistance breeding of wheat powdery mildew. J Triticeae Crops 22:83–86
Hao YF, Liu AF, Wang YH, Feng DS, Gao JR, Li XF, Liu SB, Wang HG (2008) Pm23: a new allele of Pm4 located on chromosome 2AL in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 117:1205–1212
He RL, Chang ZJ, Yang ZJ, Yuan ZY, Zhan HX, Zhang XJ, Liu JX (2009) Inheritance and mapping of powdery mildew resistance gene Pm43 introgressed from Thinopyrum intermedium into wheat. Theor Appl Genet 118:1173–1180
Hsam S, Huang X, Ernst F, Hartl L, Zeller F (1998) Chromosomal location of genes for resistance to powdery mildew in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L. em Thell.). 5. Alleles at the Pm1 locus. Theor Appl Genet 96:1129–1134
Huang XQ, Hsam SLK, Zeller FJ (1997) Identification of powdery mildew resistance genes in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L. em Thell.). 9. Cultivars, land races and breeding lines grown in China. Plant Breed 116:233–238
Huang XQ, Hsam SLK, Mohler V, Röder MS, Zeller FJ (2004) Genetic mapping of three alleles at the Pm3 locus conferring powdery mildew resistance in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Genome 47:1130–1136
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Li GP, Chen PD, Zhang SZ, Wang XE, He ZH, Zhang Y, Zhao H, Huang HY, Zhou XC (2007) Effect of the 6VS.6AL translocation on agronomic traits and dough properties of wheat. Euphytica 155:305–313
Li GQ, Fang TL, Zhu J, Gao LL, Li S, Xie CJ, Yang ZM, Sun QX, Liu ZY (2009) Molecular identification of a powdery mildew resistance gene from common wheat cultivar Brock. Acta Agron Sin 35:1613–1619
Li HJ, Wang XM, Song FJ, Wu CP, Wu XF, Zhang N, Zhou Y, Zhang XY (2011) Response to powdery mildew and detection of resistance genes in wheat cultivars from China. Acta Agron Sin 37:943–954
Lincoln SE, Daly MJ, Lander ES (1993) Constructing linkage maps with MAPMAKER/Exp version 3.0. A tutorial reference manual, 3rd edn. Whitehead Institute for Medical Research, Cambridge
Liu J, Liu D, Tao W, Li W, Wang S, Chen P, Cheng S, Gao D (2000) Molecular marker-facilitated pyramiding of different genes for powdery mildew resistance in wheat. Plant Breed 119:21–24
Liu ZY, Sun QX, Ni ZF, Nevo E, Yang TM (2002) Molecular characterization of a novel powdery mildew resistance gene Pm30 in wheat originating from wild emmer. Euphytica 123:21–29
Lutz J, Limpert E, Bartos P, Zeller FJ (1992) Identification of powdery mildew resistance genes in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L). Plant Breed 108:33–39
Lutz J, Hsam SLK, Limpert E, Zeller FJ (1995) Chromosomal location of powdery mildew resistance genes in Triticum aestivum L. (common wheat). 2. Genes Pm2 and Pm19 from Aegilops squarrosa L. Heredity 74:152–156
Ma HQ, Kong ZX, Fu BS, Li N, Zhang LX, Jia HY, Ma ZQ (2011) Identification and mapping of a new powdery mildew resistance gene on chromosome 6D of common wheat. Theor Appl Genet 123:1099–1106
McIntosh RA, Baker EP (1970) Cytogenetical studies in wheat. 4. Chromosome location and linkage studies involving Pm2 locus for powdery mildew resistance. Euphytica 19:71–77
McIntosh RA, Yamazaki Y, Dubcovsky J, Rogers J, Morris C, Somers DJ, Appels R, Devos KM (2008) Catalogue of gene symbols for wheat. In: Proceedings of the 11th international wheat genetic symposium. University of Sydney Press, Sydney
McIntosh RA, Dubcovsky J, Rogers WJ, Morris C, Appels R, Xia XC (2011) Catalogue of gene symbols for wheat: 2011 supplement. http://www.shigen.nig.ac.jp/wheat/komugi/genes/symbolClassList.jsp
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease–resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9828–9832
Miranda LM, Murphy JP, Marshall D, Leath S (2006) Pm34: a new powdery mildew resistance gene transferred from Aegilops tauschii Coss. to common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 113:1497–1504
Miranda LM, Murphy JP, Marshall D, Cowger C, Leath S (2007) Chromosomal location of Pm35, a novel Aegilops tauschii derived powdery mildew resistance gene introgressed into common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 114:1451–1456
Pugsley AT, Carter MV (1953) The resistance of twelve varieties of Triticum vulgare to Erysiphe graminis tritici. Aust J Biol Sci 6:335–346
Qiu YC, Sun XL, Zhou RH, Kong XY, Zhang SS, Jia JZ (2006) Identification of microsatellite markers linked to powdery mildew resistance gene Pm2 in wheat. Cereal Res Commun 34:1267–1273
Rohlf FJ (2000) NTSYS-pc: numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system. Version 2.1 Manual. Exeter Software, Setauket
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KM, Jorgensen RA, Allard RW (1984) Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: Mendelian inheritance, chromosomal locations and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:8014–8018
Santos FR, Pena SDJ, Epplen JT (1993) Genetic and population study of a Y-linked tetranucleotide repeat DNA polymorphism with a simple non-isotopic technique. Hum Genet 90:655–656
Wang LM, Zhu YL, Li XF, Wang HG (2011) Screening for SSR markers linked to wheat powdery mildew resistance gene Pm2. Acta Phytophylactica Sin 38:216–220
Wu XH, Luo PG, Yan BJ, Ren ZL (2006) Researches on powdery mildew resistance genes and its breeding in wheat. Chin Agric Sci Bull 22:346–351
Xu HX, Yao GQ, Xiong L, Yang LL, Jiang YM, Fu BS, Zhao WF, Zhang ZZ, Zhang CQ, Ma ZQ (2008) Identification and mapping of pm2026: a recessive powdery mildew resistance gene in an einkorn (Triticum monococcum L.) accession. Theor Appl Genet 117:471–477
Xu WG, Li CX, Hu L, Zhang L, Zhang JZ, Dong HB, Wang GS (2010) Molecular mapping of powdery mildew resistance gene PmHNK in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivar Zhoumai 22. Mol Breed 26:31–38
Zhang HT, Guan HY, Li JT, Zhu J, Xie CJ, Zhou YL, Duan XY, Yang TM, Sun QX, Liu ZY (2010) Genetic and comparative genomics mapping reveals that a powdery mildew resistance gene Ml3D232 originating from wild emmer co-segregates with an NBS-LRR analog in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 121:1613–1621
Zhuang QS (2003) Wheat improvement and pedigree analysis in China. China Agriculture Press (in Chinese), Beijing
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Dr. Y. L. Zhou for providing the powdery mildew isolates E03, E05, E09, E11, E16, E18, E20, E21, and E22. This study was financially supported by the Core Research Budget of Nonprofit Governmental Research Institution (20105), the earmarked fund for Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System (CARS-3-1), the National Program for Developing New Transgenic Varieties in China (2009ZX08002-006B), and the National High-Tech Research and Development Program of China (2011AA100103).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, J., Zhao, Z., Song, F. et al. Molecular detection of a gene effective against powdery mildew in the wheat cultivar Liangxing 66. Mol Breeding 30, 1737–1745 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-012-9757-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-012-9757-0