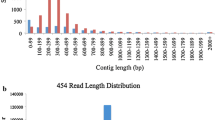
Abstract
The general approach to discovering single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) requires locus-specific PCR amplification. To enhance the efficiency of SNP discovery in soybean, we used in silico analysis prior to re-sequencing as it is both rapid and inexpensive. In silico analysis was performed to detect putative SNPs in expressed sequence tag (EST) contigs assembled using publicly available ESTs from 18 different soybean genotypes. SNP validation by direct sequencing of six soybean cultivars and a wild soybean genotype was performed with PCR primers designed from EST contigs aligned with at least 5 out of 18 soybean genotypes. The efficiency of SNP discovery among the confirmation genotypes was 81.2%. Furthermore, the efficiency of SNP discovery between Pureunkong and Jinpumkong 2 genotypes was 47.4%, a great improvement on our previous finding based on direct sequencing (22.3%). Using SNPs between Pureunkong and Jinpumkong 2 in EST contigs, which were linked to target traits, we were able to genotype 90 recombinant inbred lines by high-resolution melting (HRM) analysis. These SNPs were mapped onto the expected locations near quantitative trait loci for water-logging tolerance and seed pectin concentration. Thus, our protocol for HRM analysis can be applied successfully not only to genetic diversity studies, but also to marker-assisted selection (MAS). Our study suggests that a combination of in silico analysis and HRM can reduce the cost and labor involved in developing SNP markers and genotyping SNPs. The markers developed in this study can also easily be applied to MAS if the markers are associated with the target traits.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbazuk WB, Emrich SJ, Chen HD, Li L, Schnable PS (2007) SNP discovery via 454 transcriptome sequencing. Plant J 51:910–918. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03193.x
Cai CM, Van K, Kim MY, Jun TH, Shin JH, Cho SY, Lee YS, Lee SH (2008) SNP discovery, linkage analysis and microsynteny in tentative consensus sequences derived from roots cDNA in a supernodulating soybean mutant. Euphytica 164:189–197. doi:10.1007/s10681-008-9702-9
Chantarangsu S, Cressey T, Mahasirimongkol S, Tawon Y, Ngo-Giang-Huong N, Jourdain G, Lallemant M, Chantratita W (2007) Comparison of the TaqMan and LightCycler systems in evaluation of CYP2B6 516G > T polymorphism. Mol Cell Probes 21:408–411. doi:10.1016/j.mcp.2007.06.008
Choi IY, Hyten DL, Lakshmi KM, Qijian S, Julian MC, Charles VQ, Kevin C, Lark KG, Robert SR, Mun SY, Eun YH, Seung IY, Nevin DY, Randy CS, Curtis PVT, James ES, Cregan PB (2007) A soybean transcript map: gene distribution, haplotype and SNP analysis. Genetics 176:685–696. doi:10.1534/genetics.107.070821
Cogan NOI, Dratyton MC, Ponting RC, Vecchies AC, Bannan NR, Sawbridge TI, Smit KF, Spangenberg GC, Forster JW (2007) Validation of in silico-predicted genic SNPs in white clover (Trifolium repens L.), an outbreeding allopolyploid species. Mol Genet Genomics 277:413–425. doi:10.1007/s00438-006-0198-5
Cornelious B, Chen P, Chen Y, de Leon N, Shannon JG, Wang D (2005) Identification of QTLs underlying water-logging tolerance in soybean. Mol Breed 16:103–112. doi:10.1007/s11032-005-5911-2
Croxford AE, Rogers T, Caligari PDS, Wilkinson MJ (2008) High-resolution melt analysis to identify and map sequence-tagged site anchor points onto linkage maps: a white lupin (Lupinus albus) map as an exemplar. New Phytol 180:594–607. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02588.x
Dantec LL, Chagne D, Pot D, Cantin O, Garnier GP, Bedon F, Frigerio J, Chaumeil P, Leger P, Garcia V, Laigret F, Daruvar A, Plomion C (2004) Automated SNP detection in expressed sequence tags: statistical considerations and application to maritime pine sequences. Plant Mol Biol 54:461–470. doi:10.1023/B:PLAN.0000036376.11710.6f
Dreher K, Khairallah M, Ribaut J, Morris M (2003) Money matters (I): costs of field and laboratory procedures associated with conventional and marker-assisted maize breeding at CIMMYT. Mol Breed 11:221–234. doi:10.1023/A:1022820520673
Garritano S, Gemignani F, Voegele F, Dumont TN, Kelm FLC, Silva DD, Lesueur F, Landi S, Tavtigian SV (2009) Determining the effectiveness of High Resolution Melting analysis for SNP genotyping and mutation scanning at the TP53 locus. BMC Genetics 10:5. doi:10.1186/1471-2156-10-5
Grivet L, Glaszmann JC, Vincentz M, Silva F, Arruda P (2003) ESTs as a source for sequence polymorphism discovery in sugarcane: example of the Adh genes. Theor Appl Genet 106:190–197. doi:10.1007/s00122-002-1075-1
Gupta PK, Roy JK, Prasad M (2001) Single nucleotide polymorphisms: a new paradigm for molecular marker technology and DNA polymorphism detection with emphasis on their use in plants. Curr Sci 80:524–535
Ha BK, Hussey RS, Boerma HR (2007) Development of SNP assays for marker-assisted selection of two Southern Root-Knot Nematode resistance QTL in soybean. Crop Sci 47:S73–S82. doi:10.2135/cropsci2006.10.0660tpg
Kim MY, Ha BK, Jun TW, Hwang EY, Van KJ, Kuk YI, Lee SH (2004) Single nucleotide polymorphism discovery and linkage mapping of lipoxygenase-2 gene (Lx2) in soybean. Euphytica 135:169–177. doi:10.1023/B:EUPH.0000014909.40136.20
Kim KD, Shin JH, Van K, Kim DH, Lee SH (2009) Dynamic rearrangements determine genome organization and useful traits in soybean. Plant Physiol 151:1066–1067. doi/10.1104/pp.109.141739
Kota R, Rudd S, Facius A, Kolesov G, Thiel T, Zhang H, Stein N, Mayer K, Graner A (2003) Snipping polymorphisms from large EST collections in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Mol Gen Genomics 270:24–33. doi:10.1007/s00438-003-0891-6
Kristensen LS, Dobrovic A (2008) Direct genotyping of single nucleotide polymorphisms in methyl metabolism genes using probe-free high-resolution melting analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 17:1240–1247. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-07-2531
Labate JA, Baldo AM (2005) Tomato SNP discovery by EST mining and resequencing. Mol Breed 16:343–349. doi:10.1007/s11032-005-1911-5
Laurie AD, George PM (2009) Evaluation of high-resolution melting analysis for screening the LDL receptor gene. Clin Biochem 42:528–535. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2008.11.015
Lee SH, Walker DR, Cregan PB, Boerma HR (2004) Comparison of four flow cytometric SNP detection assays and their use in plant improvement. Theor Appl Genet 110:167–174. doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1827-1
Lehmensiek A, Sutherland MW, McNamara RB (2008) The use of high resolution melting (HRM) to map single nucleotide polymorphism markers linked to a covered smut resistance gene in barley. Theor Appl Genet 117:721–728. doi:10.1007/s00122-008-0813-4
Liew M, Pryor R, Palais R, Meadows C, Erall M, Lyon E, Wittwer C (2004) Genotyping of single-nucleotide polymorphisms by high-resolution melting of small amplicons. Clin Chem 50:1156–1164. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2004.032136
Marth GT, Korf I, Yandell MD, Yeh RT, Gu Z, Zakeri H, Stitziel NO, Hillier LD, Kwok PY, Gish WR (1999) A general approach to single-nucleotide polymorphism discovery. Nat Genet 23:453–456. doi:10.1038/70570
Matukumalli LK, Grefenstette JJ, Hyten DL, Choi IY, Cregan PB, Tassell CPV (2006) Application of machine learning in SNP discovery. BMC Bioinformatics 7:4. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-7-4
Pavy N, Parsons L, Paule C, MacKay J, Bousquet J (2006) Automated SNP detection from a large collection of white spruce expressed sequences: contributing factors and approaches for the categorization of SNPs. BMC Genomics 7:174. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-7-174
Pertea G, Huang X, Liang F, Antonescu V, Sultana R, Karamycheva S, Lee Y, White J, Cheung F, Parvizi B, Tsai J, Quackenbush J (2003) TIGR Gene Indices clustering tools (TGICL): a software system for fast clustering of large EST datasets. Bioinformatics 19:651–652. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btg034
Picoult NL, Ideker TE, Pohl MG, Taylor DL, Donaldson MA, Nickerson DA, Boyce JM (1999) Mining SNPs from EST database. Genome Res 9:167–174
Rafalski A (2002) Applications of single nucleotide polymorphisms in crop genetics. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:94–100. doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(02)00240-6
Romo S, Labrador E, Dopico B (2001) Water stress-regulated gene expression in Cicer arietinum seedlings and plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 39:1017–1026
Schmid KJ, Sorensen TR, Stracke R, Torjek O, Altmann T, Mitchell OT, Weisshaar B (2003) Large-scale identification and analysis of genome-wide single-nucleotide polymorphisms for mapping in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genome Res 13:1250–1257. doi:10.1101/gr.728603
Sémon M, Wolfe KH (2008) Preferential subfunctionalization of slow-evolving genes after allopolyploidization in Xenopus laevis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:8333–8338. doi:10.1073/pnas.0708705105
Shin JH, Van K, Kim DH, Kim KD, Jang YE, Choi BS, Kim MY, Lee SH (2008) The lipoxygenase gene family: a genomic fossil of shared polyploidy between Glycine max and Medicago truncatula. BMC Plant Biol 8:133. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-8-133
Shure M, Wessler S, Fedoreff N (1983) Molecular identification and isolation of waxy locus in maize. Cell 35:225–233
Stombaugh SK, Orf JH, Jung HG, Chase K, Lark KG, Somers DA (2004) Quantitative trait loci associated with cell wall polysaccharides in soybean seed. Crop Sci 44:2101–2106
Studer B, Jensen LB, Fiil A, Asp T (2009) “Blind” mapping of genic DNA sequence polymorphisms in Lolium perenne L. by high resolution melting curve analysis. Mol Breed 24:191–199. doi:10.1007/s11032-009-9291-x
Thornsberry JM, Goodman MM, Doebley J, Kresovich S, Nielsen D, Buckler ES (2001) Dwarf8 polymorphisms associate with variation in flowering time. Nat Genet 28:286–289
Van K, Hwang EY, Kim MY, Kim YH, Cho YI, Cregan PB, Lee SH (2004) Discovery of single nucleotide polymorphisms in soybean using primers designed from ESTs. Euphytica 139:147–157. doi:10.1007/s10681-004-2561-0
Van K, Hwang EY, Kim MY, Park HJ, Lee SH, Cregan PB (2005) Discovery of SNPs in soybean genotypes frequently used as the parents of mapping populations in the United States and Korea. J Hered 96:529–535. doi:10.1093/jhered/esi069
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78
Wu SB, Wirthensohn MG, Hunt P, Gibson JP, Sedgley M (2008) High resolution melting analysis of almond SNPs derived from ESTs. Theor Appl Genet 118:1–14. doi:10.1007/s00122-008-0870-8
Yang K, Moon J-K, Jeong N, Back K, Kim HM, Jeong S-C (2008) Genome structure in soybean revealed by a genomewide genetic map constructed from a single population. Genomics 92:52–59
Zenglu L, Nelson RL (2002) RAPD marker diversity among cultivated and wild soybean accessions from four Chinese provinces. Crop Sci 42:1737–1744
Zhu YL, Song QJ, Hyten DL, Tassell CPV, Matukumalli LK, Grimm DR, Hyatt SM, Fickus EW, Young ND, Cregan PB (2003) Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in soybean. Genetics 163:1123–1134
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant (no. CG3121) from the Crop Functional Genomics Center of the 21st Century Frontier Research Program funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, the Republic of Korea, and also supported by the Korea Rural Development Administration, BioGreen 21 Project 20080401034010, the Republic of Korea. We also thank the National Instrumentation Center for Environmental Management at Seoul National University in Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaisan, T., Van, K., Kim, M.Y. et al. In silico single nucleotide polymorphism discovery and application to marker-assisted selection in soybean. Mol Breeding 29, 221–233 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-010-9541-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-010-9541-y