Abstract
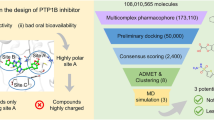
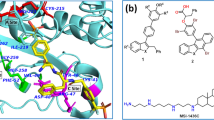
Current clinical studies have revealed that diabetic complications are multifactorial disorders that target two or more pathways. The majority of drugs in clinical trial target aldose reductase and protein kinase C (\(\text {PKC}{\upbeta }\)), while recent studies disclosed a significant role played by poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1). In light of this, the current study was aimed to identify novel dual inhibitors of \(\text {PKC}{\upbeta }\) and PARP-1 using a pharmaco-informatics methodology. Pharmacophore-based 3D QSAR models for these two targets were generated using HypoGen and used to screen three commercially available chemical databases to identify dual inhibitors of \(\text {PKC}{\upbeta }\) and PARP-1. Overall, 18 hits were obtained from the screening process; the hits were filtered based on their drug-like properties and predicted binding affinities (docking analysis). Important amino acid residues were predicted by developing a fingerprint of the active site using alanine-scanning mutagenesis and molecular dynamics. The stability of the complexes (18 hits with both proteins) and their final binding orientations were investigated using molecular dynamics simulations. Thus, novel hits have been predicted to have good binding affinities for \(\text {PKC}{\upbeta }\) and PARP-1 proteins, which could be further investigated for in vitro/in vivo activity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fowler MJ (2008) Microvascular and macrovascular complications of diabetes. Clin Diabetes 26:77–82. doi:10.2337/diaclin.26.2.77
Chung SS1, Ho EC, Lam KS, Chung SK (2003) Contribution of polyol pathway to diabetes-induced oxidative stress. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:S233–S236. doi:10.1097/01.ASN.0000077408.15865.06
Giardino I, Edelstein D, Brownlee M (1994) Nonenzymatic glycosylation in vitro and in bovine endothelial cells alters basic fibroblast growth factor activity. A model for intracellular glycosylation in diabetes. J Clin Invest 94:110. doi:10.1172/JCI117296
Horie K, Miyata T, Maeda K, Miyata S, Sugiyama S, Sakai H, van Ypersole de Strihou C, Monnier VM, Witztum JL, Kurokawa K (1997) Immunohistochemical colocalization of glycoxidation products and lipid peroxidation products in diabetic renal glomerular lesions. Implication for glycoxidative stress in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. J Clin Invest 100:2995–3004. doi:10.1172/JCI119853
Xia P, Kramer RM, King GL (1995) Identification of the mechanism for the inhibition of Na+, K (+)-adenosine triphosphatase by hyperglycemia involving activation of protein kinase C and cytosolic phospholipase A2. J Clin Invest 96:733. doi:10.1172/JCI118117
Sayeski PP, Kudlow JE (1996) Glucose metabolism to glucosamine is necessary for glucose stimulation of transforming growth factor-\({\upalpha }\) gene transcription. J Biol Chem 271:15237–15243. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.25.15237
Brownlee M (2005) The pathobiology of diabetic complications a unifying mechanism. Diabetes 54:1615–1625. doi:10.2337/diabetes.54.6.1615
Clarke M, Dodson PM (2007) PKC inhibition and diabetic microvascular complications. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 21:573–586. doi:10.1016/j.beem.2007.09.007
Faul MM, Gillig JR, Jirousek MR, Ballas LM, Schotten T, Kahl A, Mohr M (2003) Acyclic N-(azacycloalkyl)bisindolylmaleimides: isozyme selective inhibitors of \(\text{ PKC }{\upbeta }\). Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13:1857–1859. doi:10.1016/S0960-894X(03)00286-5
Hu H, Mendoza JS, Lowden CT, Ballas LM, Janzen WP (1997) Synthesis and protein kinase C inhibitory activities of balanol analogues with modification of 4-hydroxybenzamido moiety. Bioorg Med Chem 5:1873–1882. doi:10.1016/S0968-0896(97)00125-9
Li H, Hong Y, Nukui S, Lou J, Johnson S, Scales S, Botrous I, Tompkins E, Yin C, Zhou R, He M, Jensen J, Bouzida D, Alton G, Lafontaine J, Grant S (2011) Identification of novel pyrrolopyrazoles as protein kinase C \({\upbeta }\) II inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21:584–587. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.10.032
Mohammad G, Siddiquei MM, Abu El-Asrar AM (2013) Poly (ADP-Ribose) polymerase mediates diabetes-induced retinal neuropathy. Mediators Inflamm 2013:510451. doi:10.1155/2013/510451
Li H, Sutter J, Hoffmann R (2000) HypoGen: an automated system for generating predictive 3D pharmacophore models. In: Güner OF (ed) Pharmacophore perception, development, and use in drug design. International University Line, La Jolla, CA, pp 173–189
Asinex Gold Platinum database. http://www.asinex.com/. Accessed Sep 2015
Chembridge database. http://www.chembridge.com/index.php. Accessed Aug 2015
Maybridge database. http://www.maybridge.com/. Accessed Aug 2015
Discovery Studio version 4.1, (2015) Accelrys Inc., San Diego, CA. www.accelrys.com
Wu G, Robertson DH, Brooks CL, Vieth M (2003) Detailed analysis of grid-based molecular docking: a case study of CDOCKER-A CHARMm-based MD docking algorithm. J Comput Chem 24:1549–1562. doi:10.1002/jcc.10306
Bowers KJ, Chow E, Xu H, Dror RO, Eastwood MP, Gregersen B, Klepeis JL, Kolossvary I, Moraes MA, Sacerdoti FD, Salmon JK, Shan Y, Shaw DE (2006) Scalable algorithms for molecular dynamics simulations on commodity clusters. SC 2006 Conference, Proceedings of the ACM/IEEEed. IEEE 84: 43-43. doi:10.1145/1188455.1188544
Guo Z, Mohanty U, Noehre J, Sawyer TK, Sherman W, Krilov G (2010) Probing the \({\upalpha }\)-helical structural stability of stapled p53 peptides: molecular dynamics simulations and analysis. Chem Biol Drug Des 75:348–359. doi:10.1111/j.1747-0285.2010.00951.x
Shivakumar D, Williams J, Wu Y, Damm W, Shelley J, Sherman W (2010) Prediction of absolute solvation free energies using molecular dynamics free energy perturbation and the OPLS force field. J Chem Theory Comput 6:1509–1519. doi:10.1021/ct900587b
Leonard TA, Różycki B, Saidi LF, Hummer G, Hurley JH (2011) Crystal structure and allosteric activation of protein kinase C \({\upbeta }\)II. Cell 144:55–66. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.12.013
Aoyagi-Scharber M, Gardberg AS, Yip BK, Wang B, Shen Y, Fitzpatrick PA (2014) Structural basis for the inhibition of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerases 1 and 2 by BMN 673, a potent inhibitor derived from dihydropyridophthalazinone. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun 70:1143–1149. doi:10.1107/S2053230X14015088
Gangloff AR, Brown J, De Jong R, Dougan DR, Grimshaw CE, Hixon M, Jennings A, Kamran R, Kiryanov A, O’Connell S, Taylor E, Vu P (2013) Discovery of novel benzo [b][1, 4] oxazin-3 (4H)-ones as poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23:4501–4505. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.06.055
Ye N, Chen C-H, Chen T, Song Z, He JX, Huan XJ, Song SS, Liu Q, Chen Y, Ding J, Xu Y, Miao ZH, Zhang A (2013) Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of a series of benzo [de][1, 7] naphthyridin-7 (8 H)-ones bearing a functionalized longer chain appendage as novel PARP1 inhibitors. J Med Chem 56:2885–2903. doi:10.1021/jm301825t
Penning TD, Zhu G-D, Gong J, Thomas S, Gandhi VB, Liu X, Shi Y, Klinghofer V, Johnson EF, Park CH, Fry EH, Donawho CK, Frost DJ, Buchanan FG, Bukofzer GT, Rodriguez LE, Bontcheva-Diaz V, Bouska JJ, Osterling DJ, Olson AM, Marsh KC, Luo Y, Giranda VL (2010) Optimization of phenyl-substituted benzimidazole carboxamide poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors: identification of (S)-2-(2-fluoro-4-(pyrrolidin-2-yl) phenyl)-1 H-benzimidazole-4-carboxamide (A-966492), a highly potent and efficacious inhibitor. J Med Chem 53:3142–3153. doi:10.1021/jm901775y
http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=3gn7. Accessed April 2015
Miyashiro J, Woods KW, Park CH, Liu X, Shi Y, Johnson EF, Bouska JJ, Olson AM, Luo Y, Fry EH, Giranda VL, Penning TD (2009) Synthesis and SAR of novel tricyclic quinoxalinone inhibitors of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1). Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19(15):4050–4054. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.06.016
http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=2rd6. Accessed April 2015
Ferraris D, Ficco RP, Pahutski T, Lautar S, Huang S, Zhang J, Kalish V (2003) Design and synthesis of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) inhibitors. Part 3: in vitro evaluation of 1, 3, 4, 5-tetrahydro-benzo [c][1, 6]-and [c][1, 7]-naphthyridin-6-ones. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13(15):2513–2518. doi:10.1016/S0960-894X(03)00465-7
Jagtap PG, Southan GJ, Baloglu E, Ram S, Mabley JG, Marton A, Salzman A, Szabó C (2004) The discovery and synthesis of novel adenosine substituted 2, 3-dihydro-1H-isoindol-1-ones: potent inhibitors of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1). Bioorg Med Chem Lett 14:81–85. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2003.10.007
Ishida J, Hattori K, Yamamoto H, Iwashita A, Mihara K, Matsuoka N (2005) 4-Phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine, an excellent fragment to improve the potency of PARP-1 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15:4221–4225. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2005.06.094
Ishida J, Yamamoto H, Kido Y, Kamijo K, Murano K, Miyake H, Ohkubo M, Kinoshita T, Warizaya M, Iwashita A, Mihara K, Matsuoka N, Hattori K (2006) Discovery of potent and selective PARP-1 and PARP-2 inhibitors: SBDD analysis via a combination of X-ray structural study and homology modeling. Bioorg Med Chem 14:1378–1390. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2005.09.061
Chen J, Peng H, He J, Huan X, Miao Z, Yang C (2014) Synthesis of isoquinolinone-based tricycles as novel poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 24:2669–2673. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.04.061
Hattori K, Kido Y, Yamamoto H, Ishida J, Kamijo K, Murano K, Ohkubo M, Kinoshita T, Iwashita A, Mihara K, Yamazaki S, Matsuoka N, Teramura Y, Miyake H (2004) Rational approaches to discovery of orally active and brain-penetrable quinazolinone inhibitors of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase. J Med Chem 47:4151–4154. doi:10.1021/jm0499256
Jones P, Altamura S, Boueres J, Ferrigno F, Fonsi M, Giomini C, Lamartina S, Monteagudo E, Ontoria JM, Orsale MV, Palumbi MC, Pesci S, Roscilli G, Scarpelli R, Schultz-Fademrecht C, Toniatti C, Rowley M (2009) Discovery of 2-4-[(3 S)-Piperidin-3-yl] phenyl-2 H-indazole-7-carboxamide (MK-4827): a novel oral poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) Inhibitor efficacious in BRCA-1 and-2 mutant tumors. J Med Chem 52:7170–7185. doi:10.1021/jm901188v
Lord A-M, Mahon MF, Lloyd MD, Threadgill MD (2008) Design, synthesis, and evaluation in vitro of quinoline-8-carboxamides, a new class of poly (adenosine-diphosphate-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) inhibitor. J Med Chem 52:868–877. doi:10.1021/jm8013629
Menear KA, Adcock C, Boulter R, X-l Cockcroft, Copsey L, Cranston A, Dillon KJ, Drzewiecki J, Garman S, Gomez S, Javaid H, Kerrigan F, Knights C, Lau A, Loh VM Jr, Matthews IT, Moore S, O’Connor MJ, Smith GC, Martin NM (2008) 4-[3-(4-cyclopropanecarbonylpiperazine-1-carbonyl)-4-fluorobenzyl]-2 H-phthalazin-1-one: a novel bioavailable inhibitor of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1. J Med Chem 51:6581–6591. doi:10.1021/jm8001263
Orvieto F, Branca D, Giomini C, Jones P, Koch U, Ontoria JM, Palumbi MC, Rowley M, Toniatti C, Muraglia E (2009) Identification of substituted pyrazolo [1, 5-a] quinazolin-5 (4H)-one as potent poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19:4196–4200. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.05.113
Scarpelli R, Boueres JK, Cerretani M, Ferrigno F, Ontoria JM, Rowley M, Schultz-Fademrecht C, Toniatti C, Jones P (2010) Synthesis and biological evaluation of substituted 2-phenyl-2H-indazole-7-carboxamides as potent poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20:488–492. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.11.127
Sunderland PT, Woon EC, Dhami A, Bergin AB, Mahon MF, Wood PJ, Jones LA, Tully SR, Lloyd MD, Thompson AS, Javaid H, Martin NM, Threadgill MD (2011) 5-Benzamidoisoquinolin-1-ones and 5-(\({\upomega }\)-carboxyalkyl) isoquinolin-1-ones as isoform-selective inhibitors of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 2 (PARP-2). J Med Chem 54:2049–2059. doi:10.1021/jm1010918
Jasuja H, Chadha N, Kaur M, Silakari O (2014) Dual inhibitors of Janus kinase 2 and 3 (JAK2/3): designing by pharmacophore-and docking-based virtual screening approach. Mol Divers 18:253–267. doi:10.1007/s11030-013-9497-z
Egan WJ, Lauri G (2002) Prediction of intestinal permeability. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 54:273–289. doi:10.1016/S0169-409X(02)00004-2
Egan WJ, Merz KM, Baldwin JJ (2000) Prediction of drug absorption using multivariate statistics. J Med Chem 43:3867–3877. doi:10.1021/jm000292e
Cheng A, Merz KM (2003) Prediction of aqueous solubility of a diverse set of compounds using quantitative structure-property relationships. J Med Chem 46:3572–3580. doi:10.1021/ci9501507
Susnow RG, Dixon SL (2003) Use of robust classification techniques for the prediction of human cytochrome P450 2D6 inhibition. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 43:1308–1315. doi:10.1021/ci030283p
Xia X, Maliski EG, Gallant P, Rogers D (2004) Classification of kinase inhibitors using a Bayesian model. J Med Chem 47:4463–4470. doi:10.1021/jm0303195
Cheng A, Dixon SL (2003) In silico models for the prediction of dose-dependent human hepatotoxicity. J Comput Aid Mol Des 17:811–823. doi:10.1023/B:JCAM.0000021834.50768.c6
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi for providing the financial support (No. 02(0111)/12/EMR-II).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chadha, N., Silakari, O. Active site fingerprinting and pharmacophore screening strategies for the identification of dual inhibitors of protein kinase C \((\hbox {PKC}{\upbeta })\) and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1). Mol Divers 20, 747–761 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-016-9676-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-016-9676-9