Abstract
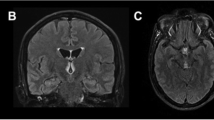
Wernicke’s encephalopathy (WE) is a thiamine deficiency-related condition, in which lesions are usually present in the periventricular and subcortical areas of the brain. However, lesions have also been found in atypical areas, such as the cerebral cortex. The present study summarizes the clinical outcomes and radiological features of WE with cortical impairment. We report two cases of cortical involvement in patients with WE, and review 22 similar cases from other reports. Among all 24 cases, 4 patients had a confirmed history of chronic daily alcohol abuse, and 19 of them had an identified causes of thiamine deficiency. 17 cases reported specific clinical information, among which 11 patients had symptoms of cortical impairment. 23 cases reported prognostic information at the end of treatment or at follow-up. The mortality rate was 26.1 % in our review. All patients had abnormal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) signals or pathological findings in the bilateral cortex. Among patients with available MRI, 89.0 % had banding-like signs along the para-central sulcus. 13 cases underwent follow-up MRI examinations and 76.9 % displayed normal images. We suggest that WE with bilateral cortical involvement may have an acceptable prognosis, but that the mortality rate is higher than that among typical cases, especially if patients are not treated promptly and correctly. We identified the frontal and parietal lobes, especially around the central sulcus, to be the most susceptible areas, and suggest that the banding signs may be characteristic of WE. Persistent hyper-intensity on T2-weighted–fluid-attenuated inversion recovery, or gadolinium enhancement, may predict poor outcome.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberti N, Bocquet J, Molinier S et al (2012) Wernicke’s encephalopathy with atypical cortical damage. Diagn Interv Imaging 93(10):804–807
Blanco-Munez O, Suarez-Gauthier A, Martin-Garcia H et al (2006) Unusual cortical compromise in a case of Wernicke’s encephalopathy. Rev Neurol 42(10):596–599
Chu K, Kang DW, Kim HJ et al (2002) Diffusion-weighted imaging abnormalities in Wernicke encephalopathy: reversible cytotoxic edema? Arch Neurol 59(1):123–127
Cui HW, Zhang BA, Peng T et al (2012) Wernicke’s encephalopathy in a patient with acute pancreatitis: unusual cortical involvement and marvelous prognosis. Neurol Sci 33(3):615–618
D’Aprile P, Tarantino A, Santoro N et al (2000) Wernicke’s encephalopathy induced by total parenteral nutrition in patient with acute leukaemia: unusual involvement of caudate nuclei and cerebral cortex on MRI. Neuroradiology 42(10):781–783
Doss A, Mahad D, Romanowski CA (2003) Wernicke encephalopathy: unusual findings in nonalcoholic patients. J Comput Assist Tomogr 27(2):235–240
Fei GQ, Zhong C, Jin L et al (2008) Clinical characteristics and MR imaging features of nonalcoholic Wernicke encephalopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29(1):164–169
Gascon-Bayarri J, Campdelacreu J, Garcia-Carreira MC et al (2011) Wernicke’s encephalopathy in non-alcoholic patients: a series of 8 cases. Neurologia 26(9):540–547
Kinoshita Y, Inoue Y, Tsuru E et al (2001) Unusual MR findings of Wernicke encephalopathy with cortical involvement. Brain Nerve 53(1):65–68
Kuhn J, Friedel V, Knitelius HO et al (2004) Iatrogenic Wernicke-Korsakow syndrome with unusual neurological deficits and MRI lesions. Nervenarzt 75(8):795–800
Liu YT, Fuh JL, Lirng JF et al (2006) Correlation of magnetic resonance images with neuropathology in acute Wernicke’s encephalopathy. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 108(7):682–687
Luigetti M, De Paulis S, Spinelli P et al (2009) Teaching NeuroImages: the full-blown neuroimaging of Wernicke encephalopathy. Neurology 72(22):e115
Machado A, Ribeiro M, Soares-Fernandes J et al (2010) Cortical linear lesions in Wernicke’s encephalopathy: can diffusion-weighted imaging herald prognostic information? J Neuropsychiatr Clin Neurosci 22(1):123–124
Manzo G, De Gennaro A, Cozzolino A et al (2014) MR imaging findings in alcoholic and nonalcoholic acute Wernicke’s encephalopathy: a review. Biomed Res Int 2014:503596
Nolli M, Barbieri A, Pinna C et al (2005) Wernicke’s encephalopathy in a malnourished surgical patient: clinical features and magnetic resonance imaging. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 49(10):1566–1570
Pereira DB, Pereira ML, Gasparetto EL (2011) Nonalcoholic Wernicke encephalopathy with extensive cortical involvement: cortical laminar necrosis and hemorrhage demonstrated with susceptibility-weighted MR phase images. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32(2):E37–E38
Sakurai K, Sasaki S, Hara M et al (2009) Wernicke’s encephalopathy with cortical abnormalities: clinicoradiological features: report of 3 new cases and review of the literature. Eur Neurol 62(5):274–280
Victor M, Adams RD, Collins GH (1971) The Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome. A clinical and pathological study of 245 patients, 82 with post-mortem examinations. Jama thes 7(3):389–389
Yamashita M, Yamamoto T (1995) Wernicke encephalopathy with symmetric pericentral involvement: MR findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr 19(2):306–308
Zhong C, Jin L, Fei G (2005) MR imaging of nonalcoholic Wernicke encephalopathy: a follow-up study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26(9):2301–2305
Zuccoli G, Pipitone N (2009) Neuroimaging findings in acute Wernicke’s encephalopathy: review of the literature. AJR Am J Roentgenol 192(2):501–508
Zuccoli G, Santa CD, Bertolini M et al (2009) MR imaging findings in 56 patients with Wernicke encephalopathy: nonalcoholics may differ from alcoholics. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30(1):171–176
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from the two Cases included in the study.
Additional information
Lei Wu and Di Jin contributed to the work equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, L., Jin, D., Sun, X. et al. Cortical damage in Wernicke’s encephalopathy with good prognosis: a report of two cases and literature review. Metab Brain Dis 32, 377–384 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-016-9920-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-016-9920-0