Abstract
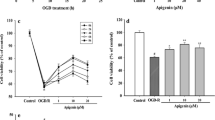
Ischemia stroke is the major cause of mortality and permanent neurological disability with little definitive therapeutic options. This cerebral ischemic injury leads to the oxidative stress and eventually cell death. We hypothesized that treatment of this condition with the trans-cinnamaldehyde(TC) could protect cells from ischemic and reperfusion injury. Oxygen and glucose deprivation/reperfusion (OGD/R) was used as an in vitro model of hypoxic ischemic injury in present study. MTT was used to evaluate the protective effects of TC. Next, we tested whether TC reduced the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Besides, experiments were performed to determine whether or not the mitochondrial membrane potential was affected. Furthermore, the inhibiters of NO and PI3 K were used to determine the initial mechanisms. TC treatment improved cell viability, reduced intracellular ROS, and increased MMP. Further, the inhibition of NO or PI3 K significantly reduced TC’s protective effects. These findings suggest that TC might be a promising agent for ischemic stroke.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao J, Zhang X, Li L et al (2015) Cinnamaldehyde inhibits inflammation and brain damage in a mouse model of permanent cerebral ischaemia. British J Pharmacol 172(20):5009–5023
Kianpour Rad S, Kanthimathi M, Abd Malek S, Lee G, Looi C, Wong W (2015) Cinnamomum cassia Suppresses Caspase-9 through Stimulation of AKT1 in MCF-7 Cells but Not in MDA-MB-231 Cells. Plos One 10(12):e0145216
Trinh N, Dumas E, Oulahal N et al (2015) Effect of a Vietnamese Cinnamomum cassia essential oil and its major component trans-cinnamaldehyde on the cell viability, membrane integrity, membrane fluidity, and proton motive force of Listeria innocua. Canadian J Microbiol 61(4):263–271
Roberta L, Marilia F, Thais A, de Moita WC, Isabella M, Maria Iz, Carlos F, Monica M (2016) Chitosan coating with trans-cinnamaldehyde improves structural integrity and antioxidant metabolism of fresh-cut melon. Postharvest Biol Technol 113:29–39
Rajamani K, Lin Y, Chiou T et al (2015) The antisenescence effect of trans-cinnamaldehyde on adipose-derived stem cells. Cell Transplant 24(3):493–507
Chen YF, Wang YW, Huang WS et al (2016) Trans-Cinnamaldehyde, An Essential Oil in Cinnamon Powder, Ameliorates Cerebral Ischemia-Induced Brain Injury via Inhibition of Neuroinflammation Through Attenuation of iNOS, COX-2 Expression and NFκ-B Signaling Pathway. Neuromol Med 10:1–12
Ballabeni V, Tognolini M, Giorgio C, Bertoni S, Bruni R, Barocelli E (2010) Ocotea quixos Lam. essential oil: in vitro and in vivo investigation on its anti-inflammatory properties. Fitoterapia 81(4):289–295
Cheung C, Hotchkiss S, Pease C (2003) Cinnamic compound metabolism in human skin and the role metabolism may play in determining relative sensitisation potency. J Dermatol Sci 31(1):9–19
Sun K et al (2010) Cerebralcare Granule, a Chinese herb compound preparation, improves cerebral microcirculatory disorder and hippocampal CA1 neuron injury in gerbils after ischemia-reperfusion. J Ethnopharmacol 130(2):398–406
Zhang P, Hou J, Fu J, Li D, Zhang C, Liu J (2013) Baicalin protects rat brain microvascular endothelial cells injured by oxygen-glucose deprivation via anti-inflammation. Brain Res Bullet 97:8–15
Rui C, Yuxiang L, Jianqiang Y et al (2012) Protective effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on neonatal rat primary cultured hippocampal neurons injured by oxygen-glucose deprivation and reperfusion. J Mol Histol 43(5):535–542
Lee J, Lee H, Kang S, Choi H, Ryu J, Yune T (2014) Fluoxetine inhibits transient global ischemia-induced hippocampal neuronal death and memory impairment by preventing blood-brain barrier disruption. Neuropharmacology 79:161–171
Broughton B, Reutens D, Sobey C (2009) Apoptotic mechanisms after cerebralischemia. Stroke 40(5):e331–e339
Ma N, Zhou R, Li Y et al (2015) Protective effects of aloperine on neonatal rat primary cultured hippocampal neurons injured by oxygen-glucose deprivation and reperfusion. J Nat Med 69(4):575–583
Doyle K, Simon R, Stenzel-Poore M (2008) Mechanisms of ischemic brain damage. Neuropharmacology 55(3):310–318
Xu Y, Long L, Wang Q et al (2013) Simvastatin induces neuroprotection in 6-OHDA-lesioned PC12 via the PI3K/AKT/caspase 3 pathway and anti-inflammatory responses. CNS Neurosci & Ther 19(3):170–177
Vahabzadeh G, Rahbar-Roshandel N, Ebrahimi S, Mahmoudian M (2016) Neuroprotective effect of noscapine on cerebral oxygen-glucose deprivation injury. Pharmacolog Rep 67(2):281–288
Bele S, Proescholdt M, Brawanski A et al (2015) Continuous intra-arterial nimodipine infusion in patients with severe refractory cerebral vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a feasibility study and outcome results. Acta Neurochirurgica 157(12):2041–2050
Kim S, Kim K, Cho J, Kim Y (2015) Clinical Variables Correlated with Numbers of Intra-arterial Nimodipine Infusion in Patients with Medically Refractory Cerebral Vasospasm. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg 17(3):157–165
Monzani D, Genovese E, Presutti L et al (2015) Nimodipine in otolaryngology: from past evidence to clinical perspectives. Acta Otorhinolaryngologica Italica: Organo Ufficiale Della Società Italiana Di Otorinolaringologia E Chirurgia 35(3):135–145
Agrawal M, Kumar V, Pant A et al (2013) Trans-Resveratrol protects ischemic PC12 Cells by inhibiting the hypoxia associated transcription factors and increasing the levels of antioxidant defense enzymes. ACS Chem Neurosci 4(2):285–294
Kang B, Kim M, Shin H et al (2015) Anti-Neuroinflammatory Effects of Uncaria sinensis in LPS-Stimulated BV2 Microglia Cells and Focal Cerebral Ischemic Mice. Am J Chin Med 43(6):1099–1115
Zeng K, Yu Q, Tu P et al (2015) Deoxysappanone B, a homoisoflavone from the Chinese medicinal plant Caesalpinia sappan L., protects neurons from microglia-mediated inflammatory injuries via inhibition of IκB kinase (IKK)-NF-κB and p38/ERK MAPK pathways. European J Pharmacol 748:18–29
Hwang C, Yun H, Hong J et al (2015) Reducing effect of IL-32α in the development of stroke through blocking of NF-κB, but enhancement of STAT3 pathways. Mol Neurobiol 51(2):648–660
Ryu S, Park H, Seol G, Choi I (2014) 1,8-Cineole ameliorates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced ischaemic injury by reducing oxidative stress in rat cortical neuron/glia. J Pharm Pharmacol 66(12):1818–1826
Wu J, Li M, Wang G et al (2015) Protease Omi cleaving Hax-1 protein contributes to OGD/R-induced mitochondrial damage in neuroblastoma N2a cells and cerebral injury in MCAO mice. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 36(9):1043–1052
Chang R, Zhou R, Yu J et al (2016) Protective effects of aloin on oxygen and glucose deprivation-induced injury in PC12 cells. Brain Res Bullet 121:75–83
Wang L, Zhang Y, Dong Q et al (2015) Neuroprotective effect of neuroserpin in oxygen-glucose deprivation- and reoxygenation-treated rat astrocytes in vitro. Plos One 10(4):e0123932
Mo Z, Fang Y, He Y, Zhang S (2012) β-Asarone protects PC12 cells against OGD/R-induced injury via attenuating Beclin-1-dependent autophagy. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 33(6):737–742
Ji H, Wang D, Chen N et al (2014) IMM-H004, a novel courmarin derivative, protects against oxygen-and glucose-deprivation/restoration-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. European J Pharmacol 723:259–266
Wang Y, Ma W, Jia A, Guo Q (2015) Parecoxib Protects Mouse Cortical Neurons Against OGD/R Induced Neurotoxicity by Up-Regulating Bcl-2. Neurochem Res 40(6):1294–1302
Zhao P, Zhou R, Yu J et al (2015) Matrine attenuates focal cerebral ischemic injury by improving antioxidant activity and inhibiting apoptosis in mice. Intl J Mol Med 36(3):633–644
Le X, Nguyet Pham H, Matsumoto K et al (2015) Protective effects of Bacopa monnieri on ischemia-induced cognitive deficits in mice: the possible contribution of bacopaside I and underlying mechanism. J Ethnopharmacol 164:37–45
Madineni A, Alhadidi Q, Shah Z (2016) Cofilin Inhibition Restores Neuronal Cell Death in Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation Model of Ischemia. Mol Neurobiol 53(2):867–878
Chen T, Liu W, Fei Z et al (2011) Neuroprotective effect of osthole against oxygen and glucose deprivation in rat cortical neurons: involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Neuroscience 183:203–211
Kang X, Chen J, Xu Z, Li H, Wang B (2007) Protective effects of Ginkgo biloba extract on paraquat-induced apoptosis of PC12 cells. Toxicol In Vitro 21(6):1003–1009
Chiu B, Chang C, Lin M et al (2014) Beneficial effect of astragalosides on stroke condition using PC12 cells under oxygen glucose deprivation and reperfusion. Cell Mol Neurobiol 34(6):825–837
Duong C, Kim J (2016) Exposure to electromagnetic field attenuates oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced microglial cell death by reducing intracellular Ca(2+) and ROS. Intl J Radiat Biol 92(4):195–201
Hwang C, Yun H, Hong J et al (2015) Reducing effect of IL-32α in the development of stroke through blocking of NF-κB, but enhancement of STAT3 pathways. Mol Neurobiol 51(2):648–660
Bak S, Choi H, Koh S et al (2015) Neuroprotective Effects of Acetyl-L-Carnitine Against Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation-Induced Neural Stem Cell Death. Mol Neurobiol. doi:10.1007/s12035-015-9563-x
Luo Y, Yang X, Wu J et al (2013) Hydrogen sulfide prevents OGD/R-induced apoptosis via improving mitochondrial dysfunction and suppressing an ROS-mediated caspase-3 pathway in cortical neurons. Neurochem Intl 63(8):826–831
Zeng K, Yu Q, Tu P et al (2015) Deoxysappanone B, a homoisoflavone from the Chinese medicinal plant Caesalpinia sappan L., protects neurons from microglia-mediated inflammatory injuries via inhibition of IκB kinase (IKK)-NF-κB and p38/ERK MAPK pathways. European J Pharmacol 748:18–29
Suematsu Y, Miura S, Saku K et al (2016) A novel inducible cholesterol efflux peptide, FAMP, protects against myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury through a nitric oxide pathway. Intl J Cardiol 202:810–816
Zheng L, Ding J, Wang J, Zhou C, Zhang W (2016) Effects and Mechanism of Action of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase on Apoptosis in a Rat Model of Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Anat Rec 299(2):246–255
Li Y, Liu K, Kang Z, Sun X, Liu W, Mao Y (2016) Helium preconditioning protects against neonatal hypoxia-ischemia via nitric oxide mediated up-regulation of antioxidases in a rat model. Behav Brain Res 300:31–37
Takata K, Imaizumi S, Saku K et al (2016) The ApoA-I mimetic peptide FAMP promotes recovery from hindlimb ischemia through a nitric oxide (NO)-related pathway. Intl J Cardiol 207:317–325
Chao X, Ma Y, Qu Y et al (2013) Up-regulation of heme oxygenase-1 attenuates brain damage after cerebral a) ischemia via simultaneous inhibition of superoxide production and preservation of NO bioavailability. Exp Neurol 239:163–169
Arabian M, Aboutaleb N, Soleimani M, Mehrjerdi F, Ajami M, Pazoki-Toroudi H (2015) Role of morphine preconditioning and nitric oxide following brain ischemia reperfusion injury in mice. Iranian J Basic Med Sci 18(1):14–21
Willcox J, Summerlee A (2014) Relaxin protects astrocytes from hypoxia in vitro. Plos One 9(3):e90864
Cheng Y, Xia Z, Han Y, Rong J (2016) Plant Natural Product Formononetin Protects Rat Cardiomyocyte H9c2 Cells against Oxygen Glucose Deprivation and Reoxygenation via Inhibiting ROS Formation and Promoting GSK-3β Phosphorylation. Oxid Med Cell Longev. doi:10.1155/2016/2060874
Ke Z, Liu J, Xu P, Gao A, Wang L, Ji L (2015) The Cardioprotective Effect of Icariin on Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Isolated Rat Heart: Potential Involvement of the PI3K-Akt Signaling Pathway. Cardiovasc Ther 33(3):134–140
Hu X, Xie C, He S, Zhang Y, Li Y, Jiang L (2013) Remifentanil postconditioning improves global cerebral ischemia-induced spatial learning and memory deficit in rats via inhibition of neuronal apoptosis through the PI3K signaling pathway. Neurolog Sci 34(11):1955–1962
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Science and Technology Key Program: The research on the material basis and modern preparations in the treatment of stroke with Hui Ethnic Herbal Fragrant Remedy (2013BAI11B07) and Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Science and Technology Support Program: The novel drug development for Hui Ethnic Herbal Specific Remedy (2015BAK45B01) (2012 [17]).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Xue Qi and Ru Zhou have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, X., Zhou, R., Liu, Y. et al. Trans-cinnamaldehyde protected PC12 cells against oxygen and glucose deprivation/reperfusion (OGD/R)-induced injury via anti-apoptosis and anti-oxidative stress. Mol Cell Biochem 421, 67–74 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-016-2785-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-016-2785-z