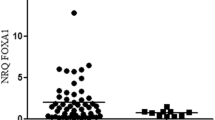
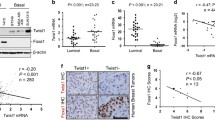
Abstract
Twist is a basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor family normally expressed during embryonic development and apparently activated in variety of tumours. Overexpression of twist is correlated with uncontrolled cell proliferation, differentiation, invasion and metastasis. Twist expression is associated with oestrogen receptor (ER); however, the molecular mechanism behind involvement of twist in progression of breast cancer is still unclear. Nitric oxide synthases (NOSs) which cause damage to the cellular DNA are also shown to be involved in cancer progression. The present study involves total number of n = 85 breast biopsies, which include 19 non-cancer and 66 cancerous lesions. We analysed twist, iNOS and ER expression pattern in human breast carcinomas by RT-PCR and also analysed twist cellular localisation by immunohistochemical analysis. iNOS expression pattern was correlated with different stages of breast carcinoma. Twist expression was significantly increased in cancer lesions when compared to the non-cancer. The breast cancer lesions positive to ER showed positivity to twist (72 %) as well. The higher stages of cancer lesions showed a significant expression of twist localised in cytoplasm of the cancer cells. Collectively these data indicate that up-regulation of twist is correlated with the ER presenting breast cancer, and iNOS expression was positively correlated with tumour-node metastasis (TNM) staging of breast cancer. These findings suggest that expression of twist and iNOS may have a functional role in cancer progression.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM (2010) Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: Globocan 2008. Int J Cancer 127(12):2893–2917
Asthana S, Chauhan S, Laban S (2014) Breast and cervical cancer risk in India: an update. Indian J Public Health 58(1):5–10
Russo IH, Russo J (1998) Role of hormones in mammary cancer initiated and progression. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 3(1):49–61
Snedekar SM, Diaugustine RP (1996) Hormonal and environmental factors affecting cell proliferation and neoplasia in the mammary gland. Prog Clin Biol Res 394:211–253
Murre C, Bain G, van Dijk MA, Engel I, Furnari BA, Massari ME et al (1994) Structure and function of helix-loop-helix proteins. Biochem Biophys Acta 1218(2):129–135
Yang J, Mani SA, Donaher JL, Ramaswamy S, Itzykson RA, Come C et al (2004) Twist, a master regulator of morphogenesis, plays an essential role in tumor metastasis. Cell 117(7):927–939
Thisse B, Messal M, Perrin-Schmitt F (1987) The twist gene: isolation of a Drosophila zygotic gene necessary for the establishment of dorsoventral pattern. Nucleic Acids Res 15(8):3439–3453
Leptin M (1991) Twist and snail as positive and negative regulators during Drosophila mesoderm development. Genes Dev 5(9):1568–1576
Hamamori Y, Sartorelli V, Ogryzko V, Puri PL, Wu HY et al (1999) Regulation of histone acetyltransferases p300 and PCAF by the bHLH protein twist and adenoviral oncoprotein E1A. Cell 96(3):405–413
Gong XQ, Li L (2002) Dermo-1, a multifunctional basic helix-loop-helix protein, represses MyoD transactivation via the HLH domain, MEF2 interaction, and chromatin deacetylation. J Biol Chem 277(14):12310–12317
Pan D, Fujimoto M, Lopes A, Wang YX (2009) Twist-1 is a PPARdelta-inducible, negative-feedback regulator of PGC-1alpha in brown fat metabolism. Cell 137(1):73–86
Li L, Cserjesi P, Olson EN (1995) Dermo-1: a novel twist-related bHLH protein expressed in the developing dermis. Dev Biol 172(1):280–292
Zhang Z, Xie D, Li X, Wong YC, Xin D, Guan XY, Chua CW, Leung SC, Na Y, Wang X (2007) Significance of TWIST expression and its association with E-cadherin in bladder cancer. Hum Pathol 38(4):598–606
Yoshida J, Horiuchi A, Kikuchi N, Hayashi A, Osada R, Ohira S, Shiozawa T, Konishi I (2009) Changes in the expression of E-cadherin repressors, Snail, Slug, SIP1, and Twist, in the development and progression of ovarian carcinoma: the important role of Snail in ovarian tumorigenesis and progression. Med Mol Morphol 42(2):82–91
Yuen HF, Chua CW, Chan YP, Wong YC, Wang X, Chan KW (2007) Significance of TWIST and E-cadherin expression in the metastatic progression of prostatic cancer. Histopathology 50(5):648–658
Yang MH, Chen CL, Chau GY, Chiou SH, Su CW, Chou TY, Peng WL, Wu JC (2009) Comprehensive analysis of the independent effect of twist and snail in promoting metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 50(5):1464–1474
Vesuna F, Lisok A, Kimble B, Domek J, Kato Y, van der Groep P, Artemov D, Kowalski J, Carraway H, van Diest H, Raman V (2011) Twist contributes to hormone resistance in breast cancer by down regulating oestrogen receptor alpha. Oncogene 31(27):3223–3234
Tschegguel W, Schneeberger C, Unfried G, Czerwenka K et al (1999) Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in human breast cancer depends on tumor grade. Breast Cancer Res Treat 56(2):145–151
Kostourou V, Cartwrignt JE, Johnstone AP, Boult JK et al (2011) The role of tumour-derived iNOS in tumour progression and angiogenesis. Br J Cancer 104(1):83–90
Janakiram NB, Rao CV (2012) iNOS-selective inhibitor for cancer prevention: promise and progress. Future Med Chem 4(17):2193–2204
Sergio G, Liu Y, Guevara ML, Blanco E et al (2015) Inhibition of iNOS as a novel effective targeted therapy against triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 17:25
Xu W, Liu L, Smith GC, Charles IG (2000) Nitric oxide upregulates expression of DNA-PKcs to protect cells from DNA-damaging anti-tumour agents. Nat Cell Biol 2(6):339–345
Wink DA, Ridnour LA, Hussain PS, Harris CC (2008) The reemergence of nitric oxide and cancer. Nitric Oxide 19(2):65–67
Nieto MA (2002) The snail superfamily of zinc-finger transcription factors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3(3):155–166
Yuen HF, Chan YP, Wong ML, Kwok WK et al (2007) Up-regulation of TWIST in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma is associated with neoplastic transformation and distant metastasis. J Clin Pathol 60(5):510–514
Elias MC, Tozer KR, Silber JR, Mikheeva S et al (2005) TWIST is expressed in human gliomas and promotes invasion. Neoplasia 7(9):824–837
Zhao M, Hu HG, Huang J, Zou Q et al (2013) Expression and correlation of Twist and gelatenase in breast cancer. Exp Ther Med 6(1):97–100
Vesuna F, Lisok A, Kimble B, Domek J et al (2012) Twist contributes to hormone resistance in breast cancer by down-regulating estrogen receptor alpha. Oncogene 31(27):3223–3234
Fu J, Zhang L, He T, Xiao X, Liu X, Wang L et al (2012) TWIST represses estrogen receptor-alpha expression by recruiting the NuRD protein complex in breast cancer cells. Int J of Biol Sci 8(4):522–532
Orucevic A, Bechberger J, Green AM, Shapiro RA, Billiar TR, Lala PK (1999) Nitric-oxide production by murine mammary adenocarcinoma cells promotes tumor-cell invasiveness. Int J Cancer 1(6):889–896
Jadeski LC, Hum KO, Chakraborty C, Lala PK (2000) Nitric oxide promotes murine mammary tumour growth and metastasis by stimulating tumour cell migration, invasiveness and angiogenesis. Int J Cancer 86(1):30–39
Zhang J, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Snyder SH (1994) Nitric oxide activation of poly (ADP-ribose) synthetase in neurotoxicity. Science 263(5147):687–689
Nathan C (1997) Inducible nitric oxide synthase: what difference does it make? J Clin Invest 100(10):2417–2423
Thomsen LL, Miles DW, Happerfield L, Bobrow LG, Knowles RG, Moncada S (1995) Nitric oxide synthase activity in human breast cancer. Br J Cancer 72(1):41–44
Reveneau S, Arnould L, Jolimoy G, Hilpert S, Lejeune P, Saint- Giorgio V, Belichard C, Jeannin JF (1999) Nitric oxide synthase in human breast cancer is associated with tumor grade, proliferation rate, and expression of progesterone receptors. Lab Invest 79(10):1215–1225
Ambs S, Merriam WG, Bennett WP, Felley-Bosco E et al (1998) Frequent nitric oxide synthase-2 expression in human colon adenomas: implication for tumor angiogenesis and colon cancer progression. Cancer Res 58(2):334–341
Chhatwal VJ, Ngoi SS, Chan ST, Chia YW, Moochhala SM (1994) Aberrant expression of nitric oxide synthase in human polyps, neoplastic colonic mucosa and surrounding peritumoral normal mucosa. Carcinogenesis 15(10):2081–2085
Glynn SA, Boersma BJ, Dorsey TH, Yi M et al (2010) Increased NOS2 predicts poor survival in estrogen receptor negative breast cancer patients. J Clin Invest 120(11):3843–3854
Dave B, Granados-principle S, Zhu R, Benz S et al (2014) Targeting RPL39 and LF2 reduces tumor initiation and metastasis in breast cancer by inhibiting nitric oxide synthase signalling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(24):8838–8843
Acknowledgments
The first author thanks University Grants Commission (UGC) and Council for Industrial and Scientific research (CSIR) for financial assistance in the form of Senior Research Fellowship (SRF). We thank Dr. N. T. Balasubramanian, Retd Proffessor, Kerala University, India, for statistical analysis. We also thank Dr. Lalith, Dr. Gunasekaran and Dr. Chithra, Department of Surgery, Madras Medical College, Chennai, for the kind help towards the collection of samples. We thank all the patients involved in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Ethical approval
All the procedures are performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional ethical committee and with the 1964 Heisinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranganathan, S., Krishnan, A. & Sivasithambaram, N.D. Significance of twist and iNOS expression in human breast carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem 412, 41–47 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2606-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2606-9