Abstract
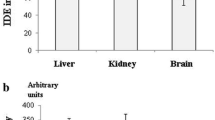
Time sequence study was performed to characterize the effects of diabetes mellitus type 1 on properties of the Na, K-ATPase in cerebral cortex derived from normal and streptozotocin (STZ)-diabetic rats of both genders. The samples were excised at varying time intervals of diabetes induced by STZ (65 mg kg−1) for 8 days, and 8 and 16 weeks. Expression of α1–3 isoforms of Na, K-ATPase was not altered in statistically significant level during all stages of diabetes neither in female nor in male rats as revealed from Western blot analysis. Studies of kinetic properties of the enzyme resulted in variations in active number of Na, K-ATPase molecules as well as its qualitative properties. Sixteen-week-old control male rats showed better affinity to substrate as indicated by 13 % decrease of K m value. The effect persisted also in males subjected to 8 days lasting diabetes; however, in males subjected to 8 weeks lasting diabetes, the effect was lost. In 25-week-old rats, the Na, K-ATPase revealed again altered properties in males and females but the mechanism of the variation was different. In females, the number of active molecules of Na, K-ATPase was higher by 32 % in controls and by 17 % in rats with chronic diabetes when comparing to respective male groups as suggested by increased value of V max. So the properties of Na, K-ATPase in cerebral cortex, playing crucial role in maintaining intracellular homeostasis of Na+ ions, depend on gender, age, and duration of diabetic insult.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frazon R, Chiarani F, Mendes RH, Bello-Klein A, Wyse AT (2005) Dietary soy prevents brain Na+, K+-ATPase reduction in streptozotocin diabetic rats. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 69:107–112. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2004.11.010
Brands AM, Henselmans JM, de Haan EH, Biessels GJ (2003) Diabetic encephalopathy: an underexposed complication of diabetes mellitus. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 147:11–14
Mijnhout GS, Scheltens P, Diamant M, Biessels GJ, Wessels AM, Simsek S, Snoek FJ, Heine RJ (2006) Diabetic encephalopathy: a concept in need of a definition. Diabetologia 49:1447–1448. doi:10.1007/s00125-006-0221-8
Brown PD, Davies SL, Speake T, Millar ID (2004) Molecular mechanisms of cerebrospinal fluid production. Neuroscience 129:957–970. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.07.003
Jorgensen PL, Pedersen PA (2001) Structure–function relationships of Na+, K+, ATP, or Mg2+ binding and energy transduction in Na, K-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1505:57–74
Pierce GN, Dhalla NS (1983) Sarcolemmal Na+–K+-ATPase activity in diabetic rat heart. Am J Physiol 245:C241–C247
Kato K, Lukas A, Chapman DC, Rupp H, Dhalla NS (2002) Differential effects of etomoxir treatment on cardiac Na+–K+ ATPase subunits in diabetic rats. Mol Cell Biochem 232:57–62
Liu X, Suzuki H, Sethi R, Tappia PS, Takeda N, Dhalla NS (2006) Blockade of the renin–angiotensin system attenuates sarcolemma and sarcoplasmic reticulum remodeling in chronic diabetes. Ann NY Acad Sci 1084:141–154. doi:10.1196/annals.1372.003
Vlkovicova J, Javorkova V, Stefek M, Kyselova Z, Gajdosikova A, Vrbjar N (2006) Effect of the pyridoindole antioxidant stobadine on the cardiac Na+, K+-ATPase in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Gen Physiol Biophys 25:111–124
Vér A, Szántó I, Bányász T, Csermely P, Végh E, Somogyi J (1997) Changes in the expression of Na+/K+-ATPase isoenzymes in the left ventricle of diabetic rat hearts: effect of insulin treatment. Diabetologia 40:1255–1262
Rosta K, Tulassay E, Enzsoly A, Ronai K, Szantho A, Pandics T, Fekete A, Mandl P, Ver A (2009) Insulin induced translocation of Na+/K+-ATPase is decreased in the heart of streptozotocin diabetic rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 30:1616–1624. doi:10.1038/aps.2009.162
Vér A, Szántó I, Csermely P, Kalff K, Végh E, Bányász T, Marcsek Z, Kovács T, Somogyi J (1995) Effect of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on kidney Na+/K(+)-ATPase. Acta Physiol Hung 83:323–332
Javorkova V, Mezesova L, Vlkovicova J, Vrbjar N (2009) Acute diabetes mellitus and its influence on renal Na, K-ATPase in both genders. Gen Physiol Biophys 28:39–46
Javorkova V, Mezesova L, Vlkovicova J, Vrbjar N (2010) Influence of sub-chronic diabetes mellitus on functional properties of renal Na+, K+-ATPase in both genders of rats. Gen Physiol Biophys 29:266–274. doi:10.4149/gpb_2010_03_266
Ver A, Csermely P, Banyasz T, Kovacs T, Somogyi J (1995) Alterations in the properties and isoform ratios of brain Na+/K+-ATPase in streptozotocin diabetic rats. Biochim Biophys Acta 1237:143–150
Sennoune S, Gerbi A, Duran MJ, Grillasca JP, Compe E, Pierre S, Planells R, Bourdeau M, Vague P, Pieroni G, Maixent JM (2000) Effect of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on rat liver Na+/K+-ATPase. Eur J Biochem 267:1–9
Kjeldsen K, Braendgaard H, Sidenius P, Larsen JS, Norgaard A (1987) Diabetes decreases Na+–K+ pump concentration in skeletal muscles, heart ventricular muscle, and peripheral nerves of rat. Diabetes 36:842–848
Zarros A, Liapi C, Galanopoulou P, Marinou K, Mellios Z, Skandali N, Al-Humadi H, Anifantaki F, Gkrouzman E, Tsakiris S (2009) Effects of adult-onset streptozotocin-induced diabetes on the rat brain antioxidant status and the activities of acetylcholinesterase, (Na+, K+)- and Mg2+-ATPase: modulation by l-cysteine. Metab Brain Dis 24:337–348. doi:10.1007/s11011-009-9133-x
Jorgensen PL (1974) Purification and characterization of (Na+, K+)-ATPase. III. Purification from the outer medulla of mammalian kidney after selective removal of membrane components by sodium dodecylsulphate. Biochim Biophys Acta 356:36–52
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Taussky HH, Shorr EE (1953) A microcolorimetric method for the determination of inorganic phosphorus. J Biol Chem 202:675–685
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Choi JW, Aseer KR, Chaudhari HN, Mukherjee R, Choi M, Yun JW (2013) Gender dimorphism in regulation of plasma proteins in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Proteomics 13:2482–2494. doi:10.1002/pmic.201200529
Seghieri G, Tesi F, Anichini R, De Bellis A, Fabbri G, Malagoli R, Franconi F (2007) Gender modulates the relationship between body weight and plasma glucose in overweight or obese subjects. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 80:134–138. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2007.10.025
Aaberg ML, Burch DM, Hud ZR, Zacharias MP (2008) Gender differences in the onset of diabetic neuropathy. J Diabetes Complicat 22:83–87. doi:10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2007.06.009
Booya F, Bandarian F, Larijani B, Pajouhi M, Nooraei M, Lotfi J (2005) Potential risk factors for diabetic neuropathy: a case control study. BMC Neurol 5:24. doi:10.1186/1471-2377-5-24
Vrbjar N, Strelková S, Stefek M, Kyselová Z, Gajdosíková A (2004) Effect of the pyridoindole antioxidant stobadine on sodium handling of renal Na, K-ATPase in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Acta Diabetol 41:172–178. doi:10.1007/s00592-004-0162-y
Vrbjar N, Strelková S, Javorková V, Vlkovicová J, Mézesová L, Stefek M, Kyselová Z, Gajdosíková A (2007) Effect of the pyridoindole antioxidant stobadine on ATP-utilisation by renal Na, K-ATPase in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Gen Physiol Biophys 26:207–213
Gick GG, Ismail-Beigi F, Edelman IS (1988) Hormonal regulation of Na, K-ATPase. Prog Clin Biol Res 268B:277–295
Oubaassine R, Weckering M, Kessler L, Breidert M, Roegel JC, Eftekhari P (2012) Insulin interacts directly with Na+/K+ATPase and protects from digoxin toxicity. Toxicology 299:1–9. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2012.04.013
Leong SF, Leung TK (1991) Diabetes induced by streptozotocin causes reduced Na–K ATPase in the brain. Neurochem Res 16:1161–1165
Oner P, Oztaş B, Koçak H (1997) Brain cortex Na+–K+ ATPase activities in streptozotocin-diabetic and pentylenetetrazol-epileptic rats. Pharmacol Res 36(1):69–72
Ahmed N, Zahra N (2011) Neurochemical correlates of alloxan diabetes: glucose and related brain metabolism in the rat. Neurochem Res 36:494–505. doi:10.1007/s11064-010-0369-y
Moreira PI, Santos MS, Moreno AM, Proença T, Seiça R, Oliveira CR (2004) Effect of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on rat brain mitochondria. J Neuroendocrinol 16:32–38
Sumbalová Z, Kucharská J, Kašparová S, Mlynárik V, Bystrický P, Božek P, Uličná O, Vančová O, Singh RB, Govzdjaková A (2005) Brain energy metabolism in experimental chronic diabetes: effect of long-term administration of coenzyme Q10 and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Biologia 60(Suppl. 17):105–108
Dzurba A, Ziegelhoffer A, Vrbjar N, Styk J, Slezak J (1997) Estradiol modulates the sodium pump in the heart sarcolemma. Mol Cell Biochem 176:113–118. doi:10.1023/A:1006835214312
Palacios J, Marusic ET, Lopez NC, Gonzalez M, Michea L (2004) Estradiol-induced expression of N(C)–K(C)-ATPase catalytic isoforms in rat arteries: gender differences in activity mediated by nitric oxide donors. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 286:H1793–H1800. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00990.2003
Sudar E, Velebit J, Gluvic Z, Zakula Z, Lazic E, Vuksanovic-Topic L, Putnikovic B, Neskovic A, Isenovic ER (2008) Hypothetical mechanism of sodium pump regulation by estradiol under primary hypertension. J Theor Biol 251:584–592. doi:10.1016/j.jtbi.2007.12.023
Obradovic M, Bjelogrlic P, Rizzo M, Katsiki N, Haidara M, Stewart AJ, Jovanovic A, Isenovic ER (2013) Effects of obesity and estradiol on Na+/K+-ATPase and their relevance to cardiovascular diseases. J Endocrinol 218:13–23. doi:10.1530/JOE-13-0144
Obradovic M, Stewart AJ, Pitt SJ, Labudovic-Borovic M, Sudar E, Petrovic V, Zafirovic S, Maravic-Stojkovic V, Vasic V, Isenovic ER (2014) In vivo effects of 17β-estradiol on cardiac Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase expression and activity in rat heart. Mol Cell Endocrinol 388:58–68. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2014.03.005
Dobretsov M, Stimers JR (2005) Neuronal function and alpha3 isoform of the Na/K-ATPase. Front Biosci 10:2373–2396
Azarias G, Kruusmägi M, Connor S, Akkuratov EE, Liu XL, Lyons D, Brismar H, Broberger C, Aperia A (2013) A specific and essential role for Na, K-ATPase α3 in neurons co-expressing α1 and α3. J Biol Chem 288:2734–2743. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.425785
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by Slovak Grant Agency: VEGA-2/0141/13. The authors thank to Mrs. Z. Hradecká for her careful technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaločayová, B., Mézešová, L., Barteková, M. et al. Effect of duration of diabetes mellitus type 1 on properties of Na, K-ATPase in cerebral cortex. Mol Cell Biochem 405, 41–52 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2394-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2394-2