Abstract
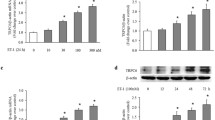
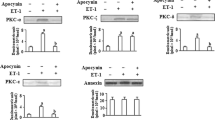
We investigated the mechanism by which TxA2 mimetic, U46619, activates proMMP-2 in bovine pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. Our study showed that treatment of the cells with U46619 caused an increase in the expression and subsequently activation of proMMP-2 in the cells. Pretreatment with p38MAPK inhibitor, SB203580; and NF-κB inhibitor, Bay11-7082 inhibited the expression and activation of proMMP-2 induced by U46619. U46619 also induced increase in MT1-MMP expression, which was inhibited upon pretreatment with SB203580 and Bay11-7082. U46619 treatment to the cells stimulated p38MAPK activity as well as NF-κB activation by IκB-α phosphorylation, translocation of NF-κBp65 subunit from cytosol to nucleus and subsequently, by increasing its DNA-binding activity. Induction of NF-κB activation seems to be mediated through IKK, as transfection of cells with either IKKα or IKKβ siRNA prevented U46619-induced phosphorylation of IκB-α and NF-κBp65 DNA-binding activity. U46619 treatment to the cells also downregulated the TIMP-2 level. Pretreatment of the cells with SB203580 and Bay11-7082 did not show any discernible change in TIMP-2 level by U46619. Overall, U46619-induced activation of proMMP-2 is mediated via involvement of p38MAPK-NFκB-MT1MMP signaling pathway with concomitant downregulation of TIMP-2 expression in bovine pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SMC:
-
Smooth muscle cell
- proMMP-2:
-
pro matrix metalloprotease 2
- MT1-MMP:
-
Membrane type 1 matrix metalloprotease
- TIMP-2:
-
Tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloprotease 2
- IKK:
-
Inhibitory κB kinase
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor κB, IκB-α, inhibitory κBα
References
Fitzgerald GA, Healy C, Daugherty J (1987) Thromboxane A2 biosynthesis in human disease. Fed Proc 46:154–158
Christman BW, McPherson CD, Newman JH, King GA, Bernard GR, Groves BM, Loyd JE (1992) An imbalance between the excretion of thromboxane and prostacyclin metabolites in pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med 327:70–75
Jankov RP, Belcastro R, Ovcina E, Lee J, Massaeli H, Lye SJ, Tanswell AK (2002) Thromboxane A2 receptors mediate pulmonary hypertension in 60 % oxygen-exposed newborn rats by a cyclooxygenase-independent mechanism. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 166:208–214
Hassoun PM (2005) Deciphering the “matrix” in pulmonary vascular remodelling. Eur Respir J 25:778–779
Cox TR, Erler JT (2011) Remodeling and homeostasis of the extracellular matrix: implications for fibrotic diseases and cancer. Dis Model Mech 4:165–178
Lu P, Takai K, Weaver VM, Werb Z (2011) Extracellular matrix degradation and remodeling in development and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a005058
Stamenkovic I (2003) Extracellular matrix remodelling: the role of matrix metalloproteinases. J Pathol 200:448–464
Woessner JF Jr (1991) Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in connective tissue remodeling. FASEB J 5:2145–2154
Lepetit H, Eddahibi S, Fadel E, Frisdal E, Munaut C, Noel A, Humbert M, Adnot S, d’Ortho MP, Lafuma C (2005) Smooth muscle cell matrix metalloproteinases in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Respir J 25:834–842
Sato H, Takino T, Kinoshita T, Imai K, Okada Y, Stetler Stevenson WG, Seiki M (1996) Cell surface binding and activation of gelatinase a induced by expression of membrane-type-1-matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP). FEBS Lett 385:238–240
Jo Y, Yeon J, Kim HJ, Lee ST (2000) Analysis of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 effect on pro-matrix metalloproteinase-2 activation by membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase using baculovirus/insect-cell expression system. Biochem J 345:511–519
Pons M, Cousins SW, Alcazar O, Striker GE, Marin-Castaño ME (2011) Angiotensin II-induced MMP-2 activity and MMP-14 and basigin protein expression are mediated via the angiotensin II receptor type 1-mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 pathway in retinal pigment epithelium: implications for age-related macular degeneration. Am J Pathol 178:2665–2681
Denkert C, Siegert A, Leclere A, Turzynski A, Hauptmann S (2002) An inhibitor of stress-activated MAP-kinases reduces invasion and MMP-2 expression of malignant melanoma cells. Clin Exp Metastasis 19:79–85
Melnikova VO, Mourad-Zeidan AA, Lev DC, Bar-Eli M (2006) Platelet-activating factor mediates MMP-2 expression and activation via phosphorylation of cAMP-response element-binding protein and contributes to melanoma metastasis. J Biol Chem 281:2911–2922
Carter AB, Knudtson KL, Monick MM, Hunninghake GW (1999) The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is required for NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression. The role of TATA-binding protein (TBP). J Biol Chem 274:30858–30863
Han YP, Tuan TL, Wu H, Hughes M, Garner WL (2001) TNF-alpha stimulates activation of pro-MMP2 in human skin through NF-(kappa) B mediated induction of MT1-MMP. J Cell Sci 114:131–139
Chen F, Castranova V, Shi X, Demers LM (1999) New insights into the role of nuclear factor-kappaB, a ubiquitous transcription factor in the initiation of diseases. Clin Chem 45:7–17
You R, Zheng M, McKeown-Longo PJ (2010) The first type III repeat in fibronectin activates an inflammatory pathway in dermal fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 285:36255–36259
Das S, Mandal M, Chakraborti T, Mandal A, Chakraborti S (2004) Isolation of MMP-2 from MMP-2/TIMP-2 complex: characterization of the complex and the free enzyme in pulmonary vascular smooth muscle plasma membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta 1674:158–174
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 76:4350–4354
Roy S, Samanta K, Chakraborti T, Chowdhury A, Chakraborti S (2011) Role of TGF-β1 and TNF-α in IL-1β mediated activation of proMMP-9 in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells: involvement of an aprotinin sensitive protease. Arch Biochem Biophys 513:61–69
Lafleur MA, Forsyth PA, Atkinson SJ, Murphy G, Edwards DR (2001) Perivascular cells regulate endothelial membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 282:463–473
Lenardo MJ, Kuang A, Gifford A, Baltimore D (1988) NF-kappa B protein purification from bovine spleen: nucleotide stimulation and binding site specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 85:8825–8829
Smith PK, Krohn RI, Hermanson GT, Mallia AK, Gartner FH, Provenzano MD, Fujimoto EK, Goeke NM, Olson BJ, Klenk DC (1985) Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem 150:76–85
Adli M, Merkhofer E, Cogswell P, Baldwin AS (2010) IKK alpha and IKK beta each function to regulate NF-kappaB activation in the TNF-induced/canonical pathway. PLoS One 5:e9428
Chakrabarti S, Patel KD (2005) Matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and MMP-9 in pulmonary pathology. Exp Lung Res 31:599–621
Bolla M, Matrougui K, Loufrani L, Maclouf J, Levy B, Levy-Toledano S, Habib A, Henrion D (2002) p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation is required for thromboxane- induced contraction in perfused and pressurized rat mesenteric resistance arteries. J Vasc Res 39:353–360
Ushio-Fukai M, Alexander RW, Akers M, Griendling KK (1998) p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase is a critical component of the redox-sensitive signaling pathways activated by angiotensin II. Role in vascular smooth muscle cell hypertrophy. J Biol Chem 273:15022–15029
Zheng YH, Tian C, Meng Y, Qin YW, Du YH, Du J, Li HH (2012) Osteopontin stimulates autophagy via integrin/CD44 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cell Physiol 227:127–135
Kim ES, Kim MS, Moon A (2004) TGF-beta-induced upregulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9 depends on p38 MAPK, but not ERK signaling in MCF10A human breast epithelial cells. Int J Oncol 25:1375–1382
Kwon CH, Moon HJ, Park HJ, Choi JH, Park do Y (2013) S100A8 and S100A9 promotes invasion and migration through p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent NF-κB activation in gastric cancer cells. Mol Cells 35:226–234
Juliana C, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Wu J, Datta P, Solorzano L, Yu JW, Meng R, Quong AA, Latz E, Scott CP, Alnemri ES (2010) Anti-inflammatory compounds parthenolide and Bay 11-7082 are direct inhibitors of the inflammasome. J Biol Chem 285:9792–9802
Lu KV, Jong KA, Rajasekaran AK, Cloughesy TF, Mischel PS (2004) Up regulation of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP)-2 promotes matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 activation and cell invasion in a human glioblastoma cell line. Lab Invest 84:8–20
Roy S, Chakraborti T, Chowdhury A, Chakraborti S (2013) Role of PKC-α in NF-κB-MT1-MMP-mediated activation of proMMP-2 by TNF-α in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. J Biochem 153:289–302
Park JM, Kim A, Oh JH, Chung AS (2007) Methylseleninic acid inhibits PMA-stimulated pro-MMP-2 activation mediated by MT1-MMP expression and further tumor invasion through suppression of NF-kappaB activation. Carcinogenesis 28:837–847
Eddahibi S, Morrell N, d’Ortho MP, Naeije R, Adnot S (2002) Pathobiology of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Respir J 20:1559–1572
Frisdal E, Gest V, Vieillard-Baron A, Levame M, Lepetit H, Eddahibi S, Lafuma C, Harf A, Adnot S, d’Ortho MP (2001) Gelatinase expression in pulmonary arteries during experimental pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J 18:838–845
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chowdhury, A., Roy, S., Chakraborti, T. et al. Activation of proMMP-2 by U46619 occurs via involvement of p38MAPK-NFκB-MT1MMP signaling pathway in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. Mol Cell Biochem 385, 53–68 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1814-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1814-4