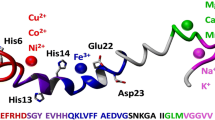
Abstract
An elevated concentration of copper ions in the brain of Alzheimer’s disease patients has been reported in many studies and might be associated with an increased aggregation of β-amyloid (Aβ) peptides. In the present work, the interaction with copper ions of a model β-amyloid peptide, Aβ(1–16), was investigated by electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (ESI–MS) at two pH values, 7.4 and 6.6, as well as at various peptide: copper ion ratios in the first minutes after components mixing and time intervals. Our results indicated that copper ions specifically bound to Aβ(1–16) peptide in solution and that the complex formation increased with time. Once formed in solution, Cu2+-Aβ(1–16) complexes could easily be detected in the gas phase by ESI–MS. The pH shift from 7.4 to 6.6 only slightly influenced the Cu2+ binding to Aβ(1–16). No oligomerization of Aβ(1–16) peptide was noticed in the first minutes of copper-peptide interaction.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali FE, Separovic F, Barrow CJ, Yao S, Barnham KJ (2006) Copper and zinc mediated oligomerisation of Aβ peptides. Int J Pept Res Ther 12:153–164
Alies B, Hureau C, Faller P (2013) The role of metal ions in amyloid formation: general principles from model peptides. Metallomics 5:183–192
Barnham KJ, Masters CL, Bush AI (2004) Neurodegenerative diseases and oxidative stress. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 3:205–214
Bush AI (2003) The metallobiology of Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Neurosci 26:207–214
Bush AI (2013) The metal theory of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 33:S277–S281
Bush AI, Tanzi RE (2008) Therapeutics for Alzheimer’s disease based on the metal hypothesis. Neurotherapeutics 5:421–432
Damante CA, Ősz K, Nagy Z, Pappalardo G, Grasso G, Impellizzeri G, Rizzarelli E, Sóvógó I (2009) Metal loading capacity of Aβ N-terminus: a combined potentiometric and spectroscopic study of zinc(II) complexes with Aβ(1-16), its short or mutated peptide fragments and its polyethylene glycol-ylated analogue. Inorg Chem 48:10405–10415
Drochioiu G, Damoc EN, Przybylski M (2006) Novel UV assay for protein determination and the characterization of copper-protein complexes by mass spectrometry. Talanta 69:556–564
Drochioiu G, Manea M, Dragusanu M, Murariu M, Dragan ES, Petre BA, Mezo G, Przybylski M (2009) Interaction of β-amyloid(1-40) peptide with pairs of metal ions: an electrospray ion trap mass spectrometric model study. Biophys Chem 144:9–20
Drochioiu G, Ion L, Ciobanu C, Habasescu L, Mangalagiu I (2013) Letter: mass spectrometric approach of high pH- and copper-induced glutathione oxidation. Eur J Mass Spectrom 19:71–75
Eskici G, Axelsen PH (2012) Copper and oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Biochemistry 51:6289–6311
Faller P, Hureau C, Dorlet P, Hellwig P, Coppel Y, Collin F, Alies B (2012) Methods and techniques to study the bioinorganic chemistry of metal-peptide complexes linked to neurodegenerative diseases. Coord Chem Rev 256:2381–2396
Gaggelli E, Kozlowski H, Valensin D, Valensin G (2006) Copper homeostasis and neurodegenerative disorders (Alzheimer’s, prion, and Parkinson’s diseases and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis). Chem Rev 106:1995–2044
Gradinaru R, Ionas A, Pui A, Zbancioc G, Drochioiu G (2011) Interaction of inorganic mercury with CoA-SH and acyl-CoAs. Biometals 24:1115–1121
Grasso G (2011) The use of mass spectrometry to study amyloid-β peptides. Mass Spectrom Rev 30:347–365
Minicozzi V, Stellato F, Comai M, Serra MD, Potrich C, Meyer-Klaucke W, Morante S (2008) Identifying the minimal copper- and zinc-binding site sequence in amyloid-{beta} peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 283:10784–10792
Murariu M (2013) Characterization of pH-dependent non-covalent copper-tetraglycine complexes by ESI-MS. Int J Mass Spectrom 351:12–22
Murariu M, Dragan ES, Drochioiu G (2007) Synthesis and mass spectrometric characterization of a metal-affinity decapeptide: copper-induced conformational alterations. Biomacromolecules 8:3836–3841
Murariu M, Dragan ES, Drochioiu G (2009) IR, MS and CD investigations on several conformationally-different peptides. Int J Pept Res Ther 15:303–311
Murariu M, Dragan ES, Drochioiu G (2010a) Model peptide-based system used for the investigation of metal ions binding to histidine-containing polypeptides. Biopolymers 93:497–508
Murariu M, Dragan ES, Drochioiu G (2010b) Electrospray ionization mass spectrometric approach of conformationally-induced metal binding to oligopeptides. Eur J Mass Spectrom 16:511–521
Pacheco-Quinto J, Eckman EA (2013) Endothelin-converting enzymes degrade intracellular β-amyloid produced within the endosomal/lysosomal pathway and autophagosomes. J Biol Chem 288:5606–5615
Schlosser G, Stefanescu R, Przybylski M, Murariu M, Hudecz F, Drochioiu G (2007) Copper-induced oligomerization of peptides: a model study. Eur J Mass Spectrom 13:331–337
Smith DP, Smith DG, Curtain CC, Boas JF, Pilbrow JR, Ciccotosto GD, Lau T-L, Tew DJ, Perez K, Wade JD, Bush AI, Drew SC, Separovic F, Masters CL, Cappai R, Barnham KJ (2006) Copper-mediated amyloid-beta toxicity is associated with an intermolecular histidine bridge. J Biol Chem 281:15145–15154
Syme CD, Nadal RC, Rigby SEJ, Viles JH (2004) Copper binding to the amyloid-β (Aβ) peptide associated with Alzheimer’s disease. J Biol Chem 279:18169–18177
Zecca L, Youdim MBH, Riederer P, Connor JR, Crichton RR (2004) Iron, brain ageing and neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:863–873
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by the Romanian Government (Contract CNCSIS IDEI 313/2011).
Conflict of interest
Marilena Manea, Gitta Schlosser, and Manuela Murariu declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manea, M., Schlosser, G. & Murariu, M. Time- and pH-Dependent Copper Binding to Aβ(1–16) Peptide: An Electrospray Ionization-Mass Spectrometric Approach. Int J Pept Res Ther 21, 125–131 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-014-9437-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-014-9437-5