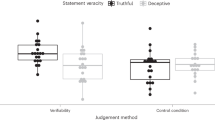
Abstract
We examined whether individuals’ ability to detect deception remained stable over time. In two sessions, held one week apart, university students viewed video clips of individuals and attempted to differentiate between the lie-tellers and truth-tellers. Overall, participants had difficulty detecting all types of deception. When viewing children answering yes–no questions about a transgression (Experiments 1 and 5), participants’ performance was highly reliable. However, rating adults who provided truthful or fabricated accounts did not produce a significant alternate forms correlation (Experiment 2). This lack of reliability was not due to the types of deceivers (i.e., children versus adults) or interviews (i.e., closed-ended questions versus extended accounts) (Experiment 3). Finally, the type of deceptive scenario (naturalistic vs. experimentally-manipulated) could not account for differences in reliability (Experiment 4). Theoretical and legal implications are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akehurst, L., Köhnken, G., Vrij, A., & Bull, R. (1996). Lay persons’ and police officers’ beliefs regarding deceptive behavior. Applied Cognitive Psychology, 10, 461–471. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-0720(199612)10:6<461::AID-ACP413>3.0.CO;2-2.
Anderson, D. E., DePaulo, B. M., & Ansfield, M. E. (2002). The development of deception detection skill: A longitudinal study of same-sex friends. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 28, 536–545. doi:10.1177/0146167202287010.
Anderson, D. E., DePaulo, B. M., Ansfield, M. E., Tickle, J. J., & Green, E. (1999). Beliefs about cues to deception: Mindless stereotypes or untapped wisdom? Journal of Nonverbal Behavior, 23, 67–89. doi:10.1023/A:1021387326192.
Bala, N., Ramakrishnan, K., Lindsay, R. C. L., & Lee, K. (2005). Judicial assessment of the credibility of child witnesses. Alberta Law Review, 42, 995–1017.
Bond, G. D. (in press). Deception detection expertise. Law and Human Behaviour.
Bond, C. F., Jr., & DePaulo, B. M. (2006). Accuracy of deception judgments. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 10, 214–234. doi:10.1207/s15327957pspr1003_2.
Bond, C. F., Jr., & DePaulo, (in press). Individual differences in judging deception: Accuracy and bias. Psychological Bulletin.
Bond, C. F., Jr., & Uysal, A. (2007). On lie detection “Wizards”. Law and Human Behavior, 31, 109–115. doi:10.1007/s10979-006-9016-1.
Bruck, M., Ceci, S. J., & Hembrooke, H. (1998). Reliability and credibility of young children’s reports: From research to policy and practice. American Psychologist, 53, 136–151. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.53.2.136.
Canada Customs and Revenue Agency. (1998). Student customs officer training program handbook – air. Rigaud, QC: Author.
Ceci, S. J., & Bruck, M. (1995). Jeopardy in the courtroom: A scientific analysis of children’s testimony. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Davis, M., Markus, K. A., & Walters, S. B. (2006). Judging the credibility of criminal suspect statements: Does mode of presentation matter? Journal of Nonverbal Behavior, 30, 181–198. doi:10.1007/s10919-006-0016-0.
DePaulo, B. M., & Kirkendol, S. E. (1989). The motivational impairment effects in the communication of deception. In J. Yuille (Ed.), Credibility assessment. Belgium: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
DePaulo, B. M., Lindsay, J. J., Malone, B. E., Muhlenbruck, L., Charlton, K., & Cooper, H. (2003). Cues to deception. Psychological Bulletin, 129, 74–118. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.129.1.74.
DePaulo, B. M., & Pfeifer, R. L. (1986). On-the-job experience and skill at detecting deception. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 16, 249–267. doi:10.1111/j.1559-1816.1986.tb01138.x.
DePaulo, B. M., & Tang, J. (1994). Social anxiety and social judgment: The example of detecting deception. Journal of Research in Personality, 28, 142–153. doi:10.1006/jrpe.1994.1012.
Edelstein, R. S., Luten, T., Ekman, P., & Goodman, G. S. (2006). Detecting lies in children and adults. Law and Human Behavior, 30, 1–10. doi:10.1007/s10979-006-9031-2.
Ekman, P., & O’Sullivan, M. (1991). Who can catch a liar? American Psychologist, 9, 913–920. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.46.9.913.
Ekman, P., O’Sullivan, M., & Frank, M. G. (1999). A few can catch liars. Psychological Science, 10, 263–266.
Etcoff, N. L., Ekman, P., Magee, J. J., & Frank, M. G. (2000). Lie detection and language comprehension. Nature, 405, 139.
Feldman, R. S., Jerkins, L, & Popoola, O. (1979). Detection of deception in adults and children via facial expressions. Child Development, 50, 350–355. doi:10.2307/1129409.
Feldman, R. S., & White, J. B. (1980). Detecting deception in children. Journal of Communication, 30, 121–128. doi:10.1111/j.1460-2466.1980.tb01974.x.
Frank, F. G., & Ekman, P. (1997). The ability to detect deceit generalizes across different types of high-stakes lies. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 72, 1429–1439. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.72.6.1429.
Fritzley, V. H., & Lee, K. (2003). Do children always say yes to yes-no questions? A metadevelopmental study of the affirmation bias. Child Development, 74, 1297–1313. doi:10.1111/1467-8624.00608.
Garrido, E., Masip, J., & Herrero, C. (2004). Police officer’s credibility judgments: Accuracy and estimated ability. International Journal of Psychology, 39, 254–275. doi:10.1080/00207590344000411.
Granhag, P. A., & Strömwall, L. A. (2001). Deception detection based on repeated interrogations. Legal and Criminological Psychology, 6, 85–101. doi:10.1348/135532501168217.
Inbau, F. E., Reid, J. E., Buckley, J. P., & Jayne, B. C. (2001). Criminal interrogation and confessions (4th ed.). Gaithersburg, MD: Aspen.
Kassin, S. M., & Fong, C. T. (1999). “I’m innocent!”: Effects of training on judgments of truth and deception in the interrogation room. Law and Human Behavior, 23, 499–516. doi:10.1023/A:1022330011811.
Kassin, S. M., Leo, R. A., Meissner, C. A., Richman, K. D., Colwell, L. H., Leach, A.-M., & LaFon, D. (2007). Police interviewing and interrogation: A self-report survey of police practices and beliefs. Law and Human Behavior, 31, 381–400. doi:10.1007/s10979–006-9073-5.
Kraut, R. E., & Poe, D. (1980). Behavioral roots of person perception: The deception judgments of customs inspectors and laypersons. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 39, 784–798. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.39.5.784.
Köhnken, G. (1987). Training police officers to detect deceptive eyewitness statements: does it work? Social Behavior, 2, 1–17.
Lane, J. D., & DePaulo, B. M. (1999). Completing Coyne’s cycle: Dysphorics’ ability to detect deception. Journal of Research in Personality, 33, 311–329. doi:10.1006/jrpe.1999.2253.
Leach, A.-M., Talwar, V., Lee, K., Bala, N. C., & Lindsay, R. C. L. (2004). “Intuitive” lie detection of children’s deception by law enforcement officials and university students. Law and Human Behavior, 28, 661–685. doi:10.1007/s10979-004-0793-0.
Lewis, M., Stanger, C., & Sullivan, M. W. (1989). Deception in 3-year-olds. Developmental Psychology, 25, 439–443. doi:10.1037/0012-1649.25.3.439.
Mann, S., & Vrij, A. (2006). Police officers’ judgements of veracity, tenseness, cognitive load and attempted behavioural control in real-life police interviews. Psychology, Crime, & Law, 12, 307–319.
Mann, S., Vrij, A., & Bull, R. (2004). Detecting true lies: Police officers’ ability to detect suspects’ lies. Journal of Applied Psychology, 89, 137–149. doi:10.1037/0021-9010.89.1.137.
Meissner, C. A., & Kassin, S. M. (2002). “He’s guilty!”: Investigator bias in judgments of truth and deception. Law and Human Behavior, 26, 469–480. doi:10.1023/A:1020278620751.
O’Sullivan, M. (2005). Emotional intelligence and deception detection: Why most people can’t “read” others, but a few can. In R. E. Riggio & R. S. Feldman (Eds.), Applications of nonverbal communication (pp. 215–253). Mahwah, NJ, US: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
O’Sullivan, M. (2007). Unicorns or Tiger Woods: Are lie detection experts myths or rarities? A response to On lie detection “Wizards” by Bond and Ulysal. Law and Human Behavior, 31, 117–123. doi:10.1007/s10979-006-9058-4.
O’Sullivan, M., & Ekman, P. (2004). The wizards of deception detection. In P. A. Granhag & L. A. Strömwall (Eds.), Deception detection in forensic contexts (pp. 269–286). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Porter, S., Campbell, M. A., Stapleton, J., & Birt, A. R. (2002). The influence of judge, target, and stimulus characteristics on the accuracy of detecting deceit. Canadian Journal of Behavioural Science, 34, 172–185.
Rosenthal, R. (1991). Meta-analytic procedures for social research. London: Sage.
Saarni, C., & Salisch, M. V. (1993). The socialization of emotional dissemblance. In M. Lewis & C. Saarni (Eds.), Lying and deception in everyday life (pp. 106–125). New York: The Guilford Press.
Sporer, S. (1997). The less travelled road to truth: Verbal cues in deception detection accounts of fabricated and self-experienced events. Applied Cognitive Psychology, 11, 373–397.
Talwar, V., & Lee, K. (2002). Development of lying to conceal a transgression: Children’s control of expressive behaviour during verbal deception. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 26, 436–444.
Talwar, V., Lee, K., Bala, N., & Lindsay, R. C. L. (2006). Adults’ judgments of child witness credibility and veracity. Law and Human Behavior, 30, 561–570.
Vrij, A. (2005). Criteria-based content analysis: A qualitative review of the first 37 years. Psychology, Public Policy, and Law, 11, 3–41.
Vrij, A., Akehurst, L., Brown, L., & Mann, S. (2006). Detecting lies in young children, adolescents, and adults. Applies Cognitive Psychology, 20, 1225–1237.
Vrij, A., & Baxter, M. (1999). Accuracy and confidence in detecting truths and lies in elaborations and denials: Truth bias, lie bias and individual differences. Expert Evidence, 7, 25–36.
Vrij, A., Edward, K., & Bull, R. (2001). People’s insight into their own behaviour and speech content while lying. British Journal of Psychology, 92, 373–389.
Vrij, A., Edward, K., Roberts, K. P., & Bull, R. (2000). Detecting deceit via analysis of verbal and nonverbal behavior. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior, 24, 239–263.
Vrij, A., & Graham, S. (1997). Individual differences between liars and the ability to detect lies. Expert Evidence, 5, 144–148.
Vrij, A., & Mann, S. (2001a). Telling and detecting lies in a high-stake situation: The case of a convicted murderer. Applied Cognitive Psychology, 15, 187–203.
Vrij, A., & Mann, S. (2001b). Who killed my relative? Police officers’ ability to detect real-life high-stake lies. Psychology, Crime, & Law, 7, 119–132.
Vrij, A., & Mann, S. (2004). Detecting deception: The benefit of looking at a combination of behavioral, auditory and speech content related cues in a systematic manner. Group Decision and Negotiation, 13, 61–79.
Vrij, A., Mann, S., Robbins, E., & Robinson, M. (2006). Police officers’ ability to detect deception in high stakes situations and in repeated lie detection tests. Applied Cognitive Psychology, 20, 741–755.
Vrij, A., & Semin, G. R. (1996). Lie experts’ beliefs about nonverbal indicators of deception. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior, 20, 65–80.
Wells, G. L., & Windshitl, P. D. (1999). Stimulus sampling in social psychological experimentation. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 25, 1115–1125.
Zuckerman, M., DePaulo, B. M., & Rosenthal, R. (1981). Verbal and nonverbal communication of deception. In L. Berkowitz (Ed.), Advances in experimental social psychology (Vol. 14, pp. 1–59). New York: Academic Press.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by grants to the authors (Leach, Lindsay, Bala, & Lee) from the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Leach, AM., Lindsay, R.C.L., Koehler, R. et al. The Reliability of Lie Detection Performance. Law Hum Behav 33, 96–109 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10979-008-9137-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10979-008-9137-9