Abstract
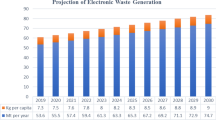
The disposal of waste from electrical and electronic equipment is an actual problem of industrialized countries. In the present work, thermal decomposition of different materials has been studied in a thermobalance at different heating rates. Kinetic models are proposed for the pyrolysis, gasification and combustion of crushed wood pellets (CWP), halogen-free electrical wires (EWs) and printed circuit boards (PCBs). Three different heating rates were used at each atmosphere condition. One set of parameters can explain all the experiments at the different atmospheres and at the three different heating rates used. In the case of CWP, a model considering three independent first-order reactions gave very good correlations all the heating rates tested both in inert and oxidant atmosphere. The decomposition of synthetic materials (EW and PCB) is modeled by using nth order kinetics. On the other hand, mixtures of these three materials have been prepared and tested for decomposition behavior. A weighted sum of the curves simulated using kinetics of the materials separately gives a good concordance with the experimental curve in the case of PCBs, indicating that there is not chemical interaction between CWP and PCBs when heated and decomposed. This would indicate that the production of pollutants in the decomposition will not be affected by the presence of the other material. Nevertheless, a strong interaction is found with the mixtures between biomass and EW.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldé CP, Wang, F., Kuehr, R., Huisman, J. The global e-waste monitor—2014. United Nations University, IAS—SCYCLE. 2015.
Conesa JA, Egea S, Moltó J, Ortuño N, Font R. Decomposition of two types of electric wires considering the effect of the metal in the production of pollutants. Chemosphere. 2013;91(2):118–23. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.11.014.
Goosey M, Kellner R. Recycling technologies for the treatment of end of life printed circuit boards (PCBs). Circuit World. 2003;29(3):33–7. doi:10.1108/03056120310460801.
Kantarelis E, Donaj P, Yang W, Zabaniotou A. Sustainable valorization of plastic wastes for energy with environmental safety via high-temperature pyrolysis (HTP) and high-temperature steam gasification (HTSG). J Hazard Mater. 2009;167(1–3):675–84.
Conesa JA, Moltó J, Font R, Egea S. Polyvinyl chloride and halogen-free electric wires thermal decomposition. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2010;49(22):11841–7. doi:10.1021/ie101265e.
Grønli MG, Várhegyi G, Di Blasi C. Thermogravimetric analysis and devolatilization kinetics of wood. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2002;41(17):4201–8.
Ortuño N, Moltó J, Egea S, Font R, Conesa JA. Thermogravimetric study of the decomposition of printed circuit boards from mobile phones. J Anal Appl Pyrol. 2013;103:189–200.
Brebu M, Vasile C, Rovana Antonie S, Chiriac M, Precup M, Yang J, et al. Study of the natural ageing of PVC insulation for electrical cables. Polym Degrad Stab. 2000;67(2):209–21.
Bene M, Plaek V, Matuschek G, Kettrup AA, Gyryov K, Emmerich WD, et al. Lifetime simulation and thermal characterization of PVC cable insulation materials. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2005;82(3):761–8.
Dong C, Yang Y, Jin B, Horio M. The pyrolysis of sawdust and polyethylene in TG and U-shape tube reactor. Waste Manag. 2007;27(11):1557–61. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2006.10.021.
Kim MR, Buonomo EL, Bonelli PR, Cukierman AL. The thermochemical processing of municipal solid wastes: Thermal events and the kinetics of pyrolysis. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util Environ Eff. 2010;32(13):1207–14. doi:10.1080/15567030802665992.
Ortuño N, Moltó J, Conesa JA, Font R. Formation of brominated pollutants during the pyrolysis and combustion of tetrabromobisphenol A at different temperatures. Environ Pollut. 2014;191:31–7.
Várhegyi G, Grønli MG, Di Blasi C. Effects of sample origin, extraction, and hot-water washing on the devolatilization kinetics of chestnut wood. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2004;43(10):2356–67.
Bach QV, Tran KQ, Skreiberg O, Khalil RA, Phan AN. Effects of wet torrefaction on reactivity and kinetics of wood under air combustion conditions. Fuel. 2014;137:375–83. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2014.08.011.
Caballero JA, Conesa JA. Mathematical considerations for nonisothermal kinetics in thermal decomposition. J Anal Appl Pyrol. 2005;73(1):85–100.
Martín-Gullón I, Gómez-Rico MF, Fullana A, Font R. Interrelation between the kinetic constant and the reaction order in pyrolysis. J Anal Appl Pyrol. 2003;68–69:645–55. doi:10.1016/s0165-2370(03)00032-9.
Conesa JA, Rey L. Thermogravimetric and kinetic analysis of the decomposition of solid recovered fuel from municipal solid waste. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;120(2):1233. doi:10.1007/s10973-015-4396-4.
Conesa JA, Domene A. Biomasses pyrolysis and combustion kinetics through n-th order parallel reactions. Thermochim Acta. 2011;523(1–2):176–81. doi:10.1016/j.tca.2011.05.021.
Acknowledgements
Support for this work was provided Spanish Ministry of Culture and Sport and by the CTQ2013-41006-R project from the Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (Spain) and the PROMETEOII/2014/007 project from the Valencian Community Government (Spain).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Conesa, J.A., Soler, A. Decomposition kinetics of materials combining biomass and electronic waste. J Therm Anal Calorim 128, 225–233 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5900-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5900-1