Abstract
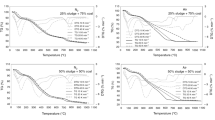
Mixing of sewage sludge with classical biomass, such as pine sawdust, can compensate the weaknesses of one fuel by another. The pyrolytic characteristics of sewage sludge (SS), pine sawdust (PS), and their blends were investigated under nitrogen atmosphere by dynamic thermogravimetric analysis at three heating rates of 10, 20, and 30 K min−1. Three thermal stages (dehydration, devolatilization, further carbonization) were identified during the pyrolysis of single materials, as well as the blends. Blending of PS with SS can improve the devolatilizaion properties of SS, whereas the initial decomposition temperature increases with the increase in proportion of PS. It has been found that the pyrolytic characteristics of the blends can be estimated from those of parent fuels, suggesting that no significant synergistic effect existed during thermal degradation of PS/SS blends. The dependence of apparent activation energy on conversion obtained by Friedman method and distributed activation energy model (DAEM) revealed that the blends can be considered as multistage process. The results indicated that the DAEM can provide reasonable fits to the experimental data.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Manara P, Zabaniotou A. Towards sewage sludge based biofuels via thermochemical conversion–a review. Renew Sust Energy Rev. 2012;16:2566–82.
Werle S, Wilk RK. A review of methods for the thermal utilization of sewage sludge: the Polish perspective. Renew Energy. 2010;35:1914–9.
Di Blasi C. Modeling chemical and physical processes of wood and biomass pyrolysis. Prog Energ Combust. 2008;34:47–90.
Rulkens W. Sewage sludge as a biomass resource for the production of energy: overview and assessment of the various options. Energy Fuel. 2007;22:9–15.
Pinto F, André RN, Lopes H, Dias M, Gulyurtlu I, Cabrita I. Effect of experimental conditions on gas quality and solids produced by sewage sludge cogasification. 2. Sewage sludge mixed with biomass. Energy Fuel. 2008;22:2314–25.
Várhegyi G. Aims and methods in non-isothermal reaction kinetics. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2007;79:278–88.
Vyazovkin S. Two types of uncertainty in the values of activation energy. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2001;64:829–35.
Burnham AK, Dinh L. A comparison of isoconversional and model-fitting approaches to kinetic parameter estimation and application predictions. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2007;89:479–90.
Vyazovkin S, Burnham AK, Criado JM, Pérez-Maqueda LA, Popescu C, Sbirrazzuoli N. ICTAC kinetics committee recommendations for performing kinetic computations on thermal analysis data. Thermochim Acta. 2011;520:1–19.
Várhegyi G, Szabó P, Antal MJ. Kinetics of charcoal devolatilization. Energy Fuel. 2002;16:724–31.
Zhao HY, Cao Y, Sit SP, Lineberry Q, Pan WP. Thermal characteristics of bitumen pyrolysis. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;107:541–7.
Li C, Suzuki K. Kinetic analyses of biomass tar pyrolysis using the distributed activation energy model by TG/DTA technique. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;98:261–6.
Li L, Wang G, Wang S, Qin S. Thermogravimetric and kinetic analysis of energy crop Jerusalem artichoke using the distributed activation energy model. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;114:1183–9.
Herce C, de Caprariis B, Stendardo S, Verdone N, De Filippis P. Comparison of global models of sub-bituminous coal devolatilization by means of thermogravimetric analysis. J Therm Calorim. 2014;117:507–16.
Please C, McGuinness M, McElwain D. Approximations to the distributed activation energy model for the pyrolysis of coal. Combust Flame. 2003;133:107–17.
Cai J, Ji L. Pattern search method for determination of DAEM kinetic parameters from nonisothermal TGA data of biomass. J Math Chem. 2007;42:547–53.
Miura K, Maki T. A simple method for estimating f (E) and k 0 (E) in the distributed activation energy model. Energy Fuel. 1998;12:864–9.
Soria-Verdugo A, Garcia-Hernando N, Garcia-Gutierrez L, Ruiz-Rivas U. Analysis of biomass and sewage sludge devolatilization using the distributed activation energy model. Energy Convers Manag. 2013;65:239–44.
Yang H, Yan R, Chen H, Lee DH, Zheng C. Characteristics of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin pyrolysis. Fuel. 2007;86:1781–8.
Whitely N, Ozao R, Cao Y, Pan W-P. Multi-utilization of chicken litter as a biomass source. Part II. Pyrolysis. Energy Fuel. 2006;20:2666–71.
Biagini E, Lippi F, Petarca L, Tognotti L. Devolatilization rate of biomasses and coal–biomass blends: an experimental investigation. Fuel. 2002;81:1041–50.
Francioso O, Rodriguez-Estrada MT, Montecchio D, Salomoni C, Caputo A, Palenzona D. Chemical characterization of municipal wastewater sludges produced by two-phase anaerobic digestion for biogas production. J Hazard Mater. 2010;175:740–6.
Ghetti P, Ricca L, Angelini L. Thermal analysis of biomass and corresponding pyrolysis products. Fuel. 1996;75:565–73.
Shuang-quan Z, Xiao-ming Y, Zhi-yuan Y, Ting-ting P, Ming-jian D, Tian-yu S. Study of the co-pyrolysis behavior of sewage-sludge/rice-straw and the kinetics. Procedia Earth Planet Sci. 2009;1:661–6.
Morgan TJ, Kandiyoti R. Pyrolysis of coals and biomass: analysis of thermal breakdown and its products. Chem Rev. 2013;114:1547–607.
Maiti S, Purakayastha S, Ghosh B. Thermal characterization of mustard straw and stalk in nitrogen at different heating rates. Fuel. 2007;86:1513–8.
Caballero J, Front R, Marcilla A, Conesa J. Characterization of sewage sludges by primary and secondary pyrolysis. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 1997;40:433–50.
Jeguirim M, Trouvé G. Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of Arundo donax using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour Technol. 2009;100:4026–31.
Luangkiattikhun P, Tangsathitkulchai C, Tangsathitkulchai M. Non-isothermal thermogravimetric analysis of oil-palm solid wastes. Bioresour Technol. 2008;99:986–97.
Di Nola G, De Jong W, Spliethoff H. TG-FTIR characterization of coal and biomass single fuels and blends under slow heating rate conditions: partitioning of the fuel-bound nitrogen. Fuel Process Technol. 2010;91:103–15.
Fiori L, Valbusa M, Lorenzi D, Fambri L. Modeling of the devolatilization kinetics during pyrolysis of grape residues. Bioresour Technol. 2012;103:389–97.
Biagini E, Fantei A, Tognotti L. Effect of the heating rate on the devolatilization of biomass residues. Thermochim Acta. 2008;472:55–63.
Aboyade AO, Hugo TJ, Carrier M, Meyer EL, Stahl R, Knoetze JH, et al. Non-isothermal kinetic analysis of the devolatilization of corn cobs and sugar cane bagasse in an inert atmosphere. Thermochim Acta. 2011;517:81–9.
Šimon P, Thomas P, Dubaj T, Cibulková Z, Peller A, Veverka M. The mathematical incorrectness of the integral isoconversional methods in case of variable activation energy and the consequences. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;115:853–9.
Sichone K. Pyrolysis of sawdust. PhD thesis. University of Waikato. 2013.
Acknowledgements
The work described in this paper was financially supported by SRF for ROCS, SEM, China, Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2013TS070, Cxy13q030.cx14-011.cx14-012.01-09-070098), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21276100), and Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China (No. 2014CFB441). The authors are also grateful to Cai Junmeng (Shanghai Jiao Tong University) who provided valuable comments and suggestions to the pyrolysis kinetic analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, X., Chen, Z., Xiao, B. et al. Co-pyrolysis behaviors and kinetics of sewage sludge and pine sawdust blends under non-isothermal conditions. J Therm Anal Calorim 119, 2269–2279 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-4321-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-4321-2