Abstract
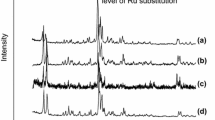
Monometallic catalysts containing Pt supported on dealuminated Y zeolite were prepared by impregnation with a solution containing H2PtCl6·6H2O cationic complexes. The catalysts were calcined and characterized by X-ray fluorescence (XRF), X-ray diffraction (XRD), simultaneous thermogravimetry/differential thermal analysis (TG/DTA), temperature programmed reduction, physisorption of nitrogen, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX). The XRD results showed that zeolite Y maintained its crystalline structure throughout the dealumination and metal incorporation processes. However, the relative crystallinity of the various samples was reduced upon impregnation. Furthermore, the XRD diffractograms, the SEM and TEM micrographs, and EDX spectra for the impregnated samples presented evidence for the presence of Pt oxides. The adsorption isotherms of the nitrogen physisorption showed the existence of micropores and mesopores within the Pt/Y zeolite. Temperature programmed reduction profiles suggest that the reduction temperature of Pt depends on the location of the metal within the zeolitic structure. The reduction peaks can be attributed to cations located in the large cavities, sodalite cages, or hexagonal prisms. The TG/DTA analyses showed the endothermic decomposition of the Pt complexes deposited on the zeolite during impregnation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Le Van Mao R, Saberi MA. Catalysts for the hydroisomerization of n-heptane, prepared according to the concept of ‘triangular’ site configuration (acid/metal/desorption-transfer promoting sites). Appl Catal A. 2000;199:99–107. doi:10.1016/S0926-860X(99)00557-8.
Park K, Ihm S. Comparison of Pt/zeolite catalysts for n-hexadecane hydroisomerization. Appl Catal A. 2000;203:201–9. doi:10.1016/S0926-860X(00)00490-7.
Thybaut J, Narasimhan CS, Denayer J, Baron G, Pierre J, Martens JA, Marin G. Acid–metal balance of a hydrocracking catalyst: ideal versus nonideal behavior. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2005;44:5159–69. doi:10.1021/ie049375.
Yasuda H, Yoshimura Y. Hydrogenation of tetralin over zeolite-supported Pd–Pt catalysts in the presence of dibenzothiophene. Catal Lett. 1997;46:43–8.
Jin WY, Yang OB, Woo SI. Decane reforming reaction over Pt, Ir, Pt–Ir and Pt–Ni bimetallic catalysts supported on y-zeolite. Korean J Chem Eng. 1996;13(4):351–5.
Sinfelt JH. Catalysis by alloys and bimetallic clusters. Acc Chem Res. 1977;10:15–20. doi:10.1021/ar50109a003.
Rahimpour M, Jafari M, Iranshahi D. Progress in catalytic naphtha reforming process: a review. Appl Energy. 2013;109:79–93.
Giannetto GP, Perot G, Guisnet M. Zeolites: synthesis structure, technology and application. Stud Surf Sci Catal. 1985;24:631–8.
Bushuev Y, Sastre G, Julian-Ortiz JV, Galvez J. Water-Hydrophobic zeolite systems. J Phys Chem C. 2012;116(47):24916–29.
Díaz U, Fornés V, Corma A. On the mechanism of zeolite growing: crystallization by seeding with delayered zeolites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006;90:73–80.
http://www.iza-structure.org/databases/. Accessed 09 Feb 2014.
Breck DW. Zeolite molecular sieves, structure, chemistry and use. New York, London, Sydney, Toronto: Wiley; 1974.
Borges L, Moura N, Costa A, Braga P, Dias J, Dias S, de Macedo J, Ghesti G. Investigation of biodiesel production by HUSY and Ce/HUSY zeolites: Influence of structural and acidity parameters. Appl Catal A. 2013;450:114–9.
Katikaneni SPR, Adjaye JD, Bakhshi NN. Studies on the catalytic conversion of canola oil to hydrocarbons: influence of hybrid catalysts and steam. Energy Fuels. 1995;9:599–609.
Corma A. Zeolites in oil refining and petrochemistry. Zeolite microporous solids: synthesis, structure and reactivity. NATO ASI Ser., Ser. C. 1992;352:373–436.
Dandik L, Aksoy HA, Erdem-Senatalar A. Catalytic conversion of used oil to hydrocarbon fuels in a fractionating pyrolysis reactor. Energy Fuels. 1998;12(6):1148.
Sternik D, Staszczuk P, Majdan M, Gladysz-Plaska A, Dlbrowska E, Bigda K. Studies of physico-chemical properties of mixed adsorbent in the Zeolite/SiO2 system. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2006;86(1):69–75.
Triantafillidis CS, Vlessidis AG, Nalbandian L, Evmiridis NP. Effect of the degree and type of the dealumination method on the structural, compositional and acidic characteristics of HZSM-5 Zeolites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2001;47:369–88.
Muller M, Harvey G, Prins R. Comparison of the dealumination of Zeolites Beta, Mordenite, ZSM-5 and Ferrierite by thermal treatment, leaching with oxalic acid and treatment with SiCl4 by 1H,29Si and 27Al MAS NMR. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2000;34:135–47.
Kooyman PJ, Van Der Waal P, Bekkum HV. Acid dealumination of ZSM-5. Zeolites. 1997;18:50–3.
Ward WJ. The nature of active sites on zeolites I. The decationated Y zeolite. J Catal. 1967;9:225–36. doi:10.1016/0021-9517(67)90248-5.
De la Puente G, Sedran U. Influence of dealumination on the micropore adsorption in FCC catalysts. Microporous Mater. 1997;12:251–60.
Groen CJ, Peffer L, Moulijn JA, Perez-Ramirez J. Mesoporosity development in ZSM-5 zeolite upon optimized desilication conditions in alkaline medium. Colloids Surf A. 2004;24:153–8.
You S, Park E. Effects of dealumination and desilication of H-ZSM-5 on xylose dehydration. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014;186:121–9.
Hanafi A, Gobara H, Elmelawy M, Abo-El-Enein A, Alkahlawy A. Catalytic behavior of Pt nanoparticles dealuminated Y-zeolite for some n-alkane hydroisomerization. Egypt J Pet. 2014;23:151–61. doi:10.1016/j.ejpe.2014.05.001.
Talebia G, Sohrabi M, Keiskib LR, Huuhtanenb M, Royaeea SJ, Maghsoudic S, Imamverdizadeha H. Synthesis and determination of the properties of the bifunctional beta zeolite catalysts for n-heptane hydroisomerization. J Chil Chem Soc. 2008;53(1):1424–30.
Alam N, Mokaya R. Characterisation and hydrogen storage of Pt doped carbons template by Pt exchanged zeolite Y. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011;142:716–24. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2011.01.024.
Denayer J, Ocakoglu R, Huybrechts W, Dejonckheere B, Jacobs P, Calero S, Krishna R, Smit B, Baron G, Martens J. High-pressure liquid phase hydroconversion of heptane/nonane mixtures on Pr/H-Y zeolite catalyst. J Catal. 2003;220(1):66–73. doi:10.1016/S0021-9517(03)00239-2.
Reyniers M, Marin G. Experimental and theoretical methods in kinetic studies of heterogeneously catalyzed reactions. Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng. 2014;5:563–94. doi:10.1146/annurev-chembioeng-060713-040032.
Primera-Pedrozo J, Torres-Cosme B, Clardy M, Rivera-Ramos M, Hernandez-Maldonado A. Titanium silicate porous materials for carbon dioxide adsorption: synthesis using a structure directing agent, detemplation and inclusion of alkaline earth metal cations. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2010;49:7515–23. doi:10.1021/ie100331q.
Ruey-Shin J, Hsiang-Chien K, Fong-Yi L. Ion exchange recovery of Ni(II) from simulated electroplating waste solutions containing anionic ligands. J Hazard Mater. 2006;B128:53–9.
Martins L, Toloni BR, Cardoso D. Ion exchange and catalytic properties of methylammonium FAU Zeolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2007;98:166–73.
Scherzer J. The preparation and characterization of aluminum-deficient zeolites. In: Whyte Jr, Dalla Betta TE, Derouane E, Baker RTK, editors. Catalytic materials: relationship between structure and reactivity. Washington, DC: ACS; 1984. doi:10.1021/bk-1984-0248.ch010.
Nováková J, Kubelková L, Habersberger K, Dolejsek Z. Catalytic activity of dealuminated Y and HZSM-5 zeolites measured by the temperature-programmed desorption of small amounts of preadsorbed methanol and by the low-pressure flow reaction of methanol. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans. 1984;80:1457–65. doi:10.1039/F1988001457.
Giannetto G, Alvarez F, Ribeiro FR, Pérot G, Guisnet M. Hydroisomerization and hydrocracking of alkanes. influence of the pore structure on the selectivity of Pt-zeolite. In: Barthomeuf D, Derouane E, Holderich W, editors. Guidelines for mastering the properties of molecular sieves. Relationship between the physicochemical properties of zeolytic systems and their low dimensionality. NATO ASI Series, vol. 221. New York: Plenum Publishing Corporation; 1990. p. 355–363. ISBN:978-1-4684-5789-6 (Print) 978-1-4684-5787-2 (Online).
Cavalcanti LC Jr, Silva M, Sousa-Aguiar EF, Sobrinho E. Diffusion of paraffins in dealuminated Y mesoporous molecular sieves. Adsorption. 2003;9:205–12.
Joyner R. Extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) studies of highly dispersed platinum catalysts. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans. 1980;1(76):357–61. doi:10.1039/F19807600357.
Weller S, Montagna A. O2 chemisorption at high temperatures on platinum-alumina and platinum-zeolite. J Catal. 1971;20:394–407. doi:10.1016/0021-9517(71)90102-3.
Lieske H, Lietz G, Spindler H, Volteri J. Reactions of platinum in oxygen- and hydrogen-treated Pt/ɤ-A1203 catalysts I. Temperature-programmed reduction, adsorption, and redispersion of platinum. J Catal. 1983;81(1):8–16. doi:10.1016/0021-9517(83)90142-2.
Barbier J, Bahloul D, Marecot P. Effect of chloride on sintering of Pt/Al2O3. Catal Lett. 1991;8:327–34.
Jordão M, Simões V, Cardoso D. Zeolite supported Pt-Ni catalysts in n-hexane isomerization. Appl Catal A. 2007;319:1–6. doi:10.1016/j.apcata.2006.09.039.
Wagstaff N, Prins R. Alloy formation and metal oxide segregation in Pt-Re/γ-Al2O3 catalysts as investigated by temperature-programmed reduction. J Catal. 1979;59(3):434–45. doi:10.1016/S0021-9517(79)80012-3.
Wagstaff N, Prins R. Reply to interpretation of temperature-programmed reduction (TPR) experiments of platinum–iridium catalysts. J Catal. 1981;67:255–6. doi:10.1016/0021-9517(81)90283-9.
Moretti G, Sachtler WMH. Geometric causes of the methylcyclopentane ring opening selectivity over Pt/NaY catalysts. J Catal. 1989;116:350.
Pedrosa AMG, Souza MJB, Melo DMA, Souza AG, Araújo AS. Determination of surface properties of nickel supported on HY zeolite by TG, DTA and TPR. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2005;79:439–43. doi:10.1007/s10973-005-0081-3.
Domine ME, Hernandez-Soto MC, Navarro MT, Perez Y. Pt and Pd nanoparticles supported on structured materials as catalysts for the selective reductive amination of carbonyl compounds. Catal Today. 2011;172:13–20. doi:10.1016/j.cattod.2011.05.013.
Hernandez J, Choren E. Thermal stability of some platinum complexes. Thermochim Acta. 1983;71:265–72. doi:10.1016/0040-6031(83)80059-8.
Pedrosa AMG, Souza MJB, Lima SH, Melo DMA, Araújo AS. Influence of the synthesis method on the DTG-TPR profiles of Pt/WOx–ZrO2 bifunctional catalysts. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2007;87(3):703–7. doi:10.1007/s10973-006-7777-x.
Sousa B, Brito K, Alves J, Rodrigues M, Yoshioka C, Cardoso D. n-Hexane isomerization on Pt/HMOR: effect of Platinum contente. React Kinet Mech Catal. 2011;102:473–85. doi:10.1007/s11144-010-0273-0.
Hurst NW, Gentry SJ, Jones A. Temperature programmed reduction. Catal Rev Sci Eng. 1982;24(2):233–309.
Makowski W, Mlekodaj KM. Characterization of acidic zeolite catalysts by thermodesorption and cracking of n-nonane. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013;166:137–43. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2012.04.034.
Verheyen E, Jo Ch, Kurttepeli M, Vanbutsele G, Gobechiya E, Korányi TI, Bals S, Tendeloo GV, Ryoo R, Kirschhock C, Martens JA. Molecular shape-selectivity of MFI zeolite nanosheets in n-decane isomerization and hydrocracking. J Catal. 2013;300:70–80. doi:10.1016/j.jcat.2012.12.017.
Aboul-Gheit A, Aboul-Fotouh Sameh M. Insight in cyclohexene hydroconversion process using catalysts containing 0.35 % Pt on amorphous and zeolite supports. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng. 2012;43:711–717. doi:10.1016/j.jtice.2012.03.007.
Brunauer S, Emmett PH, Teller E. Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J Am Chem Soc. 1938;60:309–19.
Janssen A, Koster A, Jong K. Three-dimensional transmission electron microscopic observations of mesopores in dealuminated zeolite Y. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2001;40(6):1102–4.
Jong K, Zecevic J, Friedrich H, Jongh P, Bulut M, Van Donk S, Kenmogne R, Finiels A, Hulea V, Fajula F. Zeolite Y crystals with trimodal porosity as ideal hydrocracking catalysts. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2010;122:10272–6. doi:10.1002/anie.201004360.
Jeanjean J, Aouali L, Delafosse D, Dereigne A. Crystal structure of different dealuminated Y-type zeolites determination of framework vacancies and non-framework species. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans. 1989;1F(85):2771–83. doi:10.1039/F19898502771.
Acknowledgements
Programa Nacional de Cooperação Acadêmica—Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior 083/2009, Auxilio Financeiro a Projeto de Pesquisa 762/2010, Rede de Catálises Norte/Nordeste III, Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico, OAS Partnership Program for Education and Training PAEC-GCUB for the financial support to carry out this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vieira dos Santos, B.R., Montoya Urbina, M., Souza, M.J.B. et al. Preparation and characterization of Pt-dealuminated Y zeolite by TG/DTA and TPR. J Therm Anal Calorim 119, 391–399 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-4183-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-4183-7