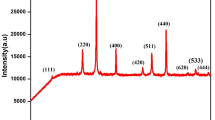
Abstract
CuO/CuFe2O4 nanocomposite was prepared by reverse co-precipitation method. The microstructure and magnetic properties of the synthesized powders were characterized by X-ray diffraction, thermo-gravimetric and differential thermal analysis, Fourier transmission infrared spectroscopy, Brunauer–Emmett–Teller surface area analysis, scanning electron microscope, transmission electron microscope, and vibrating sample magnetometer. Magnetic measurements revealed that the saturation magnetization of samples increases with increasing calcination temperature. The increase of magnetic property of calcined powders can be explained as the results of the two important factors: formation of CuFe2O4 phase and grain growth of the nanoparticles. The results showed that the precipitates calcined at 900 °C resulted in the formation of a crystalline CuO/CuFe2O4 nanocomposite with a maximum saturation magnetization of 21.2 emu g−1.
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Laokul P, Amornkitbamrung V, Seraphin S, Maensiri S (2011) Characterization and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline CuFe2O4, NiFe2O4, ZnFe2O4 powders prepared by the Aloe vera extract solution. Curr Appl Phys 11:101–108
Melo RS, Silva FC, Moura KRM, Menezes AS, Sinfrônio FSM (2015) Magnetic ferrites synthesised using the microwave-hydrothermal Method. J Magn Magn Mater 381:109–115
Foroughi F, Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi SA, Amighian J, Saffar-Teluri A (2015) A designed magnetic CoFe2O4–hydroxyapatite core–shell nanocomposite for Zn(II) removal with high efficiency. Ceram Int 41:6844–6850
Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi SA, Behbahanian S, Amighian J (2016) Synthesis and magnetic properties of NiFe2_xSmxO4 nanopowder. J Magn Magn Mater 410:242–247
Foroughi F, Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi SA, Bigham A (2016) In situ microemulsion synthesis of hydroxyapatite-MgFe2O4 nanocomposite as a magnetic drug delivery system. Mater Sci Eng C 68:774–779
Tao S, Gao F, Liu X, Toft Sørensen O (2000) Preparation and gas-sensing properties of CuFe2O4 at reduced temperature. Mater Sci Eng B 77:172–176
Desai M, Prasad S, Venkataramani N, Samajdar I, Nigam AK, Krishnan R (2002) Enhanced magnetization in sputter-deposited copper ferrite thin films. J Magn Magn Mater 246:266–269
Bomio M, Lavela P, Tirado JL (2008) Electrochemical evaluation of CuFe2O4 samples obtained by sol–gel methods used as anodes in lithium batteries. J Solid State Electrochem 12:729–737
Jing P, Li J, Pan L, Wang J, Sun X, Liu Q (2015) Efficient photocatalytic degradation of acid fuchsin in aqueous solution using separate porous tetragonal-CuFe2O4 nanotubes. J Hazard Mater 284:163–170
Feng J, Su L, Ma Y, Ren C, Guo Q, Chen X (2013) CuFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles: a simple and efficient catalyst for the reduction of nitrophenol. Chem Eng J 221:16–24
Nilmoung S, Sinprachim T, Kotuth I, Kidkhunthod P, Yimnirun R, Rujirawat S, Maensiri S (2016) Electrospun carbon/CuFe2O4 composite nanofibers with improved electrochemical energy storage performance. J Alloys Compd 688:1131–1140
Yao Y, Lu F, Chen H, Wei F, Liu X, Lian C, Wang S (2015) Magnetic core–shell CuFe2O4@C3N4 hybrids for visible light photocatalysis of Orange II. J Hazard Mater 297:224–233
Parka S, Kim S, Kheel H, Hyun SK, Jin C, Lee C (2015) Enhanced H2S gas sensing performance of networked CuO–ZnO composite nanoparticle sensor. Mater Res Bull 82:130–135
Cantalini C (2004) Cr2O3, WO3 single and Cr/W binary oxide prepared by physical methods for gas sensing applications. J Eur Ceram Soc 24:1421–1424
Chapelle A, El Younsi I, Vitale S, Thimont Y, Nelis T, Presmanes L, Barnabé A, Tailhades P (2014) Improved semiconducting CuO/CuFe2O4 nanostructured thin films for CO2 gas sensing. Sens Actuators B Chem 204:407–413
Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi SA, Motlagh MM, Salahshour S (2016) Synthesis of ZnO/CuO nanocomposite immobilized on γ-Al2O3 and application for removal of methyl orange. Appl Surf Sci 384:237–243
Alizadeh S, Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi SA (2015) MoO3 fibers and belts: molten salt synthesis, characterization and optical properties. Ceram Int 41:10839–10843
Foletto EL, Battiston S, Simoes JM, Bassaco MM, Pereira LSF, Flores EMM, Muller EI (2012) Synthesis of ZnAl2O4 nanoparticles by different routes and the effect of its pore size on the photocatalytic process. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 163:29–33
Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi SA, Taheri-Nassaj E (2010) Compressibility and sinterability of Al2O3–YAG nanocomposite powder synthesized by an aqueous sol–gel method. J Alloys Compd 506:640–644
Barnabé A, Chapelle A, Presmanes L, Tailhades P (2013) Copper and iron based thin film nanocomposites prepared by radio frequency sputtering. Part II: elaboration and characterization of oxide/oxide thin film nanocomposites using controlled ex-situ oxidation process. J Mater Sci 48:3304–3314
Rashad MM, Soltan S, Ramadan AA, Bekheet MF, Rayan DA (2015) Investigation of the structural, optical and magnetic properties of CuO/CuFe2O4 nanocomposites synthesized via simple microemulsion method. Ceram Int 41:12237–12245
Ramachandran K, Chidambaram S, Baskaran B, Muthukumarasamy A, Mohan Kumar G (2016) One pot polyol synthesis of CuO–CuFe2O4 nanocomposites and their structural, optical and electrical property studies. Mater Lett 175:106–109
Rashad MM, Rayan DA, Ramadan AA (2013) Optical and magnetic properties of CuO/CuFe2O4 nanocomposites. J Mater Sci 24:2742–2749
Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi SA, Taheri-Nassaj E (2011) Synthesis of high surface area Al2O3–CeO2 composite nanopowder via inverse co-precipitation method. Ceram Int 37:1251–1257
Aono H, Nagamachi T, Naohara T, Itagaki Y, Maehara T, Hirazawa H (2016) Synthesis conditions of nano-sized magnetite powder using reverse coprecipitation method for thermal coagulation therapy. J Ceram Soc Jpn 124:23–28
Aono H, Hirazawa H, Naohara T, Maehara T, Kikkawa H, Watanabe Y (2005) Synthesis of fine magnetite powder using reverse co-precipitation method and its heating properties by applying AC magnetic field. Mater Res Bull 40:1126–1135
Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi SA (2012) Synthesis and luminescence properties of YAG:Ce nanopowder prepared by the Pechini method. Adv Powder Technol 23:324–327
Shojaei S, Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi SA, Ghashang M (2014) Reverse microemulsion synthesis and characterization of CaSnO3 nanoparticles. Ceram Int 40:9609–9613
Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi SA (2015) Influences of Cr content and heat treatment on the optical property of the green mica-nano Cr2O3 pearlescent pigment. J Coat Technol Res 12(4):751–756
Anbia M, Neyzehdar M, Ghaffarinejad A (2014) Humidity sensitive behavior of Fe(NO3)3 loaded mesoporous silica MCM-41. Sens Actuators B 193:225–229
Motlagh MM, Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi SA, Saffar-Teluri A (2014) Influence of Mn2O3 content on the textural and catalytic properties of Mn2O3/Al2O3/SiO2 nanocatalyst. Ceram Int 40:16177–16181
Tavakoli H, Sarraf-Mamoory R, Zarei AR (2015) Solvothermal synthesis of copper nanoparticles loaded on multi-wall carbon nanotubes as catalyst for thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. J Adv Mater Process 3:3–10
Shaheen WM, Ali AA (2001) Thermal solid–solid interaction and physicochemical properties of CuO–FeO system. Int J Inorg Mater 3:1073–1081
Sun Z, Liu L, zeng Jia D, Pan W (2007) Simple synthesis of CuFe2O4 nanoparticles as gas-sensing materials. Sens Actuators B 125:144–148
Sing KSW, Everett DH, Haul RAW, Moscou L, Pierotti RA, Rouquerol J, Siemieniewska T (2005) Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure Appl Chem 57:603–619
Zhang J, Jiang D, Chen Z, Huang Z (2013) Synthesis of calcium phosphate fluoride hybrid hollow spheres. Mater Lett 91:35–38
Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi SA, Mazaheri M, Aminzare M, Sadrnezhaad SK (2010) Reverse precipitation synthesis and characterization of CeO2 nanopowder. J Alloys Compd 491:499–502
Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi SA, Taheri-Nassaj E (2008) Effects of milling and calcination temperature on the compressibility and sinterability of a nanocrystalline Al2O3–Y3Al5O12 composite powder. J Am Ceram Soc 91:3546–3551
Foroughi F, Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi SA, Amighian J (2015) Microemulsion synthesis and magnetic properties of hydroxyapatite-encapsulated nano CoFe2O4. J Magn Magn Mater 382:182–187
Harzali H, Saida F, Marzouki A, Megriche A, Baillon F, Espitalier F, Mgaidi A (2016) Structural and magnetic properties of nano-sized NiCuZn ferrites synthesized by co-precipitation method with ultrasound irradiation. J Magn Magn Mater 419:50–56
Masrour R, Hamedoun M, Benyoussef A, Hlil EK (2014) Magnetic properties of mixed Ni–Cu ferrites calculated using mean field approach. J Magn Magn Mater 363:1–5
Kodama RH, Berkowitz AE, Mcniff EJ, Foner S (1996) Surface spin disorder in NiFe2O4 nanoparticles. Phys Rev Lett 77:394
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karimi, M., Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi, S. & Saffar-Teluri, A. In situ reverse co-precipitation synthesis and magnetic properties of CuO/CuFe2O4 nanocomposite. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 83, 124–131 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4386-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4386-z