Abstract
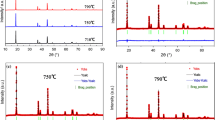
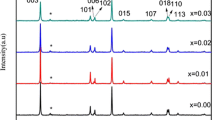
Acetates of lithium (LiC2H3O2) and nickel (NiC2H3O2) together with ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (NH4)H2PO4 were used as starting materials to prepare LiNiPO4 cathode materials via sol–gel technique. This simple and effective method of using distilled water as main solvent was assisted by small amount of oxalic acid. Final product was obtained after sintering process at temperatures of 500 °C, 600 °C, 700 °C, and 800 °C for 3 h. The peaks in X-ray diffraction patterns reveal ordered olivine structure of LiNiPO4 under Pnma space group. The surface morphologies as in field emission scanning electron microscopy images clearly showed complete formation of LiNiPO4 with uniform size distribution. Charge–discharge tests recorded initial discharge capacities of 97.3 mAh g−1 and 91.1 mAh g−1 for LiNiPO4 obtained at sintering temperatures of 700 and 800 °C respectively in the voltage range 2.5–4.5 V. Insitu carbon coating during synthesis improved electrochemical performances of LiNiPO4. Sintering temperature 700 °C produced smaller LiNiPO4 particles compared to 800 °C, which enables good capacity retention.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rui X, Zhao X, Lu Z, Tan H, Sim D, Hng HH et al. (2013) Olivine-Type Nanosheets for Lithium Ion Battery Cathodes, ACS Nano 7(6):5637–5646
Alyoshin VA, Pleshakov EA, Ehrenberg H, Mikhailova D (2014) Platelike LiMPO4 (M=Fe, Mn, Co, Ni) for Possible Application in Rechargeable Li Ion Batteries: beyond Nanosize. J Phys Chem C 4:17426–17435
Minakshi M, Singh P, Appadoo D, Martin DE (2011) Synthesis and characterization of olivine LiNiPO4 for aqueous rechargeable battery. Electrochim Acta 56:4356–4360
Chen H, Chen M, Du C, Cui Y, Zuo P (2016) Synthesis and electrochemical performance of hierarchical nanocomposite of carbon coated LiCoPO4 crosslinked by graphene. Mater Chem Phys 171:6–10
Gong C, Xue Z, Wen S, Ye Y, Xie X (2016) Advanced carbon materials/olivine LiFePO4 composites cathode for lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 318:93–112
Zhang SM, Zhang JX, Xu SJ, Yuan XJ, He BC (2013) Li ion diffusivity and electrochemical properties of FePO4 nanoparticles acted directly as cathode materials in lithium ion rechargeable batteries. Electrochim Acta 88:287–293
Zhang Y, Huo Q, Du P, Wang L, Zhang A, Song Y et al. (2012) Advances in new cathode material LiFePO4 for lithium-ion batteries. Synth Met 162:1315–1326
Huang Q, Wu Z, Su J, Long Y, Lv X, Wen Y (2016) Synthesis and electrochemical performance of Ti – Fe co-doped LiMnPO4/C as cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. Ceram Int 42:11348–11354
Xiong J, Wang Y, Wang Y, Zhang J (2016) PVP-assisted solvothermal synthesis of LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C cathode material for lithium ion batteries. Ceram Int 42:9018–9024
Ding J, Su Z, Tian H (2016) Synthesis of high rate performance LiFe1- xMnxPO4/C composites for lithium-ion batteries. Ceram Int 42:12435–12440
Karthickprabhu S, Hirankumar G, Maheswaran A, Bella RSD, Sanjeeviraja C (2014) Structural and electrical studies on Zn2+ doped LiCoPO4. J Electrostat 72:181–186
Li H, Wang Y, Yang X, Liu L, Chen L, Wei J (2014) Improved electrochemical performance of 5 V LiCoPO4 cathode materials via yttrium doping. Solid State Ionics 255:84–88
Doan TNL, Taniguchi I (2012) Effect of spray pyrolysis temperature on physical and electrochemical properties of LiCoPO4/C nanocomposites. Powder Technol 217:574–580
Truong QD, Devaraju MK, Honma I (2014) LiMPO4 nanoplates by a supercritical ethanol. J Mater Chem A Mater Energy Sustain 2:17400–17407
Karthickprabhu S, Hirankumar G, Maheswaran A, Sanjeeviraja C, Bella RSD (2013) Structural and conductivity studies on LiNiPO4 synthesized by the polyol method. J Alloys Compd 548:65–69
Örnek A, Kazancioglu MZ (2016) A novel and effective strategy for producing core-shell LiNiPO4/C cathode material for excellent electrochemical stability using a long-time and low-level microwave approach. Scr Mater 122:45–49
Devaraju MK, Truong QD, Honma I (2015) One pot synthesis of in situ Au decorated LiNiPO4 nanoplates for Li-ion batteries, Applied Materialstoday 1:95–99
Hamamoto K, Fukushima M, Mamiya M, Yoshizawa Y, Akimoto J, Suzuki T et al. (2012) Morphology control and electrochemical properties of LiFePO4/C composite cathode for lithium ion batteries. Solid State Ionics 225:560–563
Yoshida J, Stark M, Holzbock J, Hüsing N, Nakanishi S, Iba H et al. (2013) Analysis of the size effect of LiMnPO4 particles on the battery properties by using STEM-EELS. J Power Sources 226:122–126
Zhao RR, Hung IM, Li YT, Chen HY, Lin CP (2012) Synthesis and properties of Co-doped LiFePO 4 as cathode material via a hydrothermal route for lithium-ion batteries. J Alloys Compd 513:282–288
Fang H, Yi H, Hu C, Yang B, Yao Y, Ma W (2012) Effect of Zn doping on the performance of LiMnPO4 cathode for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 71:266–269
Hu C, Yi H, Fang H, Yang B, Yao Y, Ma W et al. (2010) Improving the electrochemical activity of LiMnPO4 via Mn-site co-substitution with Fe and Mg. Electrochem commun 12:1784–1787
Rajammal K, Sivakumar D, Duraisamy N, Ramesh K, Ramesh S (2016) Structural and electrochemical characterizations of LiMn1-xAl0.5xCu0.5xPO4 (x=0.0, 0.1, 0.2) cathode materials for lithium ion batteries. Mater Lett 173:131–135
Lee J, Kumar P, Lee J, Moudgil BM, Singh RK (2013) ZnO incorporated LiFePO4 for high rate electrochemical performance in lithium ion rechargeable batteries. J Alloys Compd 550:536–544
Li Y-D, Zhao S-X, Nan C-W, Li B-H (2011) Electrochemical performance of SiO2-coated LiFePO4 cathode materials for lithium ion battery. J Alloys Compd 509:957–960
Rajammal K, Sivakumar D, Duraisamy N, Ramesh K, Ramesh S, (2016) Enhanced electrochemical properties of ZnO-coated LiMnPO4 cathode materials for lithium ion batteries, Ionics (Kiel) 22:1551–1556
Zhao D, Feng Y, Wang Y, Xia Y (2013) Electrochemical performance comparison of LiFePO4 supported by various carbon materials. Electrochim Acta 88:632–638
Cheng G, Zuo P, Wang L, Shi W, Ma Y, Du C, Cheng X, Gao Y, Yin G (2015) High-performance carbon-coated LiMnPO4 nanocomposites by facile two-step solid-state synthesis for lithium-ion battery, J Solid State Electr 19:281–288
Zhou X, Xie Y, Deng Y, Qin X, Chen G (2015) The enhanced rate performance of LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4/C cathode material via synergistic strategies of surfactant-assisted solid state method and carbon coating. Mater Chem A 3:996–1004
Xie G, Zhu HJ, Liu XM, Yang H (2013) A core-shell LiFePO4/C nanocomposite prepared via a sol-gel method assisted by citric acid. J Alloys Compd 574:155–160
Bechir MBEN, Rhaiem ABEN, Guidara K (2014) A. C. conductivity and dielectric study of LiNiPO4 synthesized by solid-state method. Bull Mater Sci 37:1–8
Prabu M, Selvasekarapandian S (2012) Dielectric and modulus studies of LiNiPO4. Mater Chem Phys 134:366–370
Rommel SM, Rothballer J, Schall N, Brünig C, Weihrich R (2015) Characterization of the carbon-coated LiNi1−yCoyPO4 solid solution synthesized by a non-aqueous sol-gel route. Ionics 325–333
Nucleus T, Umtaz MM, Yaqub A, Bahat SSA, Mujtaba A (2014) Electrocatalytic activity of LiNiPO4 and the copper doped analogues towards oxygen reduction. Nucleus 1:109–115
Dimesso L, Spanheimer C, Jaegermann W (2013) Effect of the Mg-substitution on the graphitic carbon foams—LiNi1- yMgyPO4 composites as possible cathodes materials for 5 V applications. Mater Res Bull 48:559–565
Örnek A, Bulut E, Can M (2015) Influence of gradual cobalt substitution on lithium nickel phosphate nano-scale composites for high voltage applications. Mater Charact 106:152–162
Zhao X, Baek D, Manuel J, Heo M, Yang R, Keun J et al. (2012) Electrochemical properties of magnesium doped LiFePO4 cathode material prepared by sol – gel method. Mater Res Bull 47:2819–2822
Jiang T, Pan W, Wang J, Bie X, Du F, Wei Y et al. (2010) Carbon coated Li3V2(PO4)3 cathode material prepared by a PVA assisted sol—gel method. Electrochim Acta 55:3864–3869
Sheng-kui Z, You W, Jie-qun LIU, Jian W (2012) Synthesis of LiMnPO4/C composite material for lithium ion batteries by sol gel method. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 22:2535–2540
Manikandan P, Periasamy P, Jagannathan R (2013) Sol-gel synthesis and impedance characteristics of networked nanocrystalline olivine cathode for Li-ion full cells. J Mater Chem A 1:15397–15405
Jugović D, Mitrić M, Kuzmanović M, Cvjetićanin N, Škapin S, Cekić B et al. (2011) Preparation of LiFePO4/C composites by co-precipitation in molten stearic acid. J Power Sources 196:4613–4618
Kim K, Cho Y, Kam D, Kim H, Lee J (2010) Effects of organic acids as reducing agents in the synthesis of LiFePO4. J Alloys Compd 504:166–170
Jian XM, Wenren HQ, Huang S, Shi SJ, Wang XL, Gu CD et al. (2014) Oxalic acid-assisted combustion synthesized LiVO3 cathode material for lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 246:417–422
Kabi S, Ghosh A (2013) Microstructure of Li (Mn1/3Ni1/3Co1/3)O2 cathode material for lithium ion battery: Dependence of crystal structure on calcination and heat-treatment temperature. Mater Res Bull 48:3405–3410
Lu J, Zhou Y, Jiang T, Tian X, Tu X, Wang P (2016) Synthesis and optimization of three-dimensional lamellar LiFePO4 and nanocarbon composite cathode materials by polyol process. Ceram Int 42:1281–1292
Han B, Meng X, Ma L, Nan J (2016) Nitrogen-doped carbon decorated LiFePO4 composite synthesized via a microwave heating route using polydopamine as carbon—nitrogen precursor. Ceram Int 42:2789–2797
Ben Bechir M, Ben Rhaiem A, Guidara K (2014) A. C. conductivity and dielectric study of LiNiPO4 synthesized by solid-state method. Bull Mater Sci 37:1–8
Wang L, Zhou X, Guo Y (2010) Synthesis and performance of carbon-coated Li3V2(PO4)3 cathode materials by a low temperature solid-state reaction. J Power Sources 195:2844–2850
Wei C, He W, Zhang X, Xu F, Liu Q, Sun C et al. (2015) Effects of morphology on the electrochemical performances of Li3V2(PO4)3 cathode material for lithium ion batteries. RSC Adv 5:54225–54245
Wang D, Cao L, Huang J, Wu J (2013) Effects of different chelating agents on the composition, morphology and electrochemical properties of LiV3O8 crystallites synthesized via sol – gel method. Ceram Int 39:3759–3764
Muruganantham R, Sivakumar M, Subadevi R (2015) Enhanced rate performance of multiwalled carbon nanotube encrusted olivine type composite cathode material using polyol technique. J Power Sources 300:496–506
Kwon SN, Song J, Mumm DR (2011) Effects of cathode fabrication conditions and cycling on the electrochemical performance of LiNiO2 synthesized by combustion and calcination. Ceram Int 37:1543–1548
Zuo R, Liang X, Liu Z (2014) Synthesis and characterization of LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 material for rechargeable lithium batteries by polyacrylic acid-assisted sol – gel method, J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 69:303–310
Rommel SM, Schall N, Brünig C, Weihrich R (2014) Challenges in the synthesis of high voltage electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries: a review on LiNiPO4. Monatsh Chem 145:385–404
Xiao L, Guo Y, Qu D, Deng B, Liu H, Tang D (2013) Influence of particle sizes and morphologies on the electrochemical performances of spinel LiMn2O4 cathode materials. J Power Sources 225:286–292
Zhu C, Nobuta A, Saito G, Nakatsugawa I, Akiyama T (2014) Solution combustion synthesis of LiMn2O4 fine powders for lithium ion batteries. Adv Powder Technol 25:342–347
Cai Y, Huang Y, Wang X, Jia D, Pang W, Guo Z et al. (2015) Facile synthesis of LiMn2O4 octahedral nanoparticles as cathode materials for high capacity lithium ion batteries with long cycle life. J Power Sources 278:574–581
Liu J, Chen H, Xie J, Sun Z, Wu N, Wu B (2014) Electrochemical performance studies of Li-rich cathode materials with different primary particle sizes. J Power Sources 251:208–214
Wang X, Cheng K, Zhang J, Yu L, Yang J (2013) Advanced powder technology effect of carbon content and calcination temperature on the electrochemical performance of lithium iron phosphate/carbon composites as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Adv Powder Technol 24:593–598
Rajammal K, Sivakumar D, Duraisamy N, Ramesh K, Ramesh S (2016) Effect of sintering temperature on structural properties of LiMnPO4 cathode materials obtained by sol – gel method. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 80:514–522
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank financial support from the University of Malaya for the PPP grant PG 099—2014B and Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FP012-2015A), from Ministry of Education, Malaysia. One of the author Dr. Navaneethan Duraisamy acknowledges UGC-Dr. D.S. Kothari Postdoctoral Fellowship (Ref no: No.F.4-2/2006 (BSR)/EN/15-16/0031)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajammal, K., Sivakumar, D., Duraisamy, N. et al. Influences of sintering temperatures and crystallite sizes on electrochemical properties of LiNiPO4 as cathode materials via sol–gel route for lithium ion batteries. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 83, 12–18 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4372-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4372-5