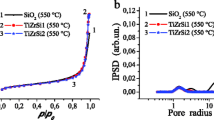
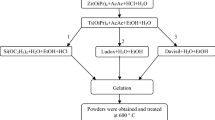
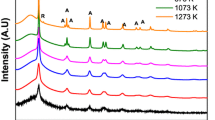
Abstract
Two depths of surface of three kinds of 10 % SiO2 Ti–Si binary oxide powder, prepared by three kinds of sol–gel processes and annealed at higher temperature, are comparatively studied by ARXPS, SEM and HRTEM. ARXPS shows that the two depths of surface for all samples enrich in Si about 38.2–63.2 % and are the mixture of TiO x (x ≤ 2), SiOy (y ≤ 2), Ti–O–Si, adsorbed O-containing species and C-containing species. With increasing depth, the change of Si/Ti ratio closely relates to the original structure formed in sol–gel. The surface contents of SiO2 and Ti–O–Si linkages increase in depth for all samples. The surface of silica-supported titania and intimately mixed silica–titania has more sub-valence Ti and Si than that of silica-coated titania, but the surface of silica-coated titania has higher concentration of Ti, O and C than that of the other two. ARXPS and SEM images consistently confirm that the surface of silica-coated titania is a porous structure. HRTEM verifies that nanocrystalline anatase TiO2 with many crystal defects has been produced in silica-coated titania.
Graphical Abstract
Three nanocomposite silica–titania binary oxide powders with three different structures were synthesized by three different sol–gel processes and analyzed by ARXPS, SEM and HRTEM. As it shows that the surface of silica-coated titania is a porous structure with more O and C, the surfaces of intimately mixed silica–titania and silica-supported titania, respectively, conglomerate and sinter with more suboxide Ti and Si.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fujishima A, Honda K (1972) Electrochemcal photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 238:37–38
Henderson MA (2011) A surface science perspective on TiO2 photocatalysis. Surf Sci Rep 66:185–297
Notari B, Willey RJ , Panizza M, Busca G (2006) Which sites are the active sites in TiO2–SiO2 mixed oxides? Catal Today 116:99–110
Debecker DP, Hulea V, Mutin PH (2013) Mesoporous mixed oxide catalysts via non-hydrolytic sol–gel: a review. Appl Catal A Gen 451:192–206
Mirabedini A, Mirabedini SM, Babalou AA, Pazokifard S (2011) Synthesis, Characterization and enhanced photocatalytic activity of TiO2/SiO2 nanocomposite in an aqueous solution and acrylic-based coatings. Prog Org Coat 72:453–460
Anpo M, Nakaya H, Kodama S et al (1986) Photocatalysis over binary metal oxides, Enhancement of the photocatalytic activity of titanium dioxide in titanium–silicon oxides. J Phys Chem 90:1633–1636
Seo HO, Sim CW, Kim KD, Kim YD, Limb DC (2012) Nanoporous TiO2/SiO2 prepared by atomic layer deposition as adsorbents of methylene blue in aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 183:381–386
Dong WY, Sun YJ, Ma QW, Zhu L, Hua W, Lu X, Zhuang G, Zhang S, Guo Z, Zhao D (2012) Excellent photocatalytic degradation activities of ordered mesoporous anatase TiO2–SiO2 nanocomposites to various organic contaminants. J Hazard Mater 229–230:307–320
Yang SG, Fu HB, Sun C, Gao ZQ (2009) Rapid photocatalytic destruction of pentachlorophenol in F–Si-comodified TiO2 suspensions under microwave irradiation. J Hazard Mater 161:1281–1287
Matosa J, Garcíaa A, Park SE (2011) Ti-containing mesoporous silica for methylene blue photodegradation. Appl Catal A Gen 393:359–366
Yamashita H, Kawasaki S, Ichihashi Y, Harada M, Takeuchi M, Anpo M (1998) Characterization of titanium–silicon binary oxide catalysts prepared by the Sol–Gel method and their photocatalytic reactivity for the liquid-phase oxidation of 1-octanol. J Phys Chem B 102:5870–5875
Kibombo HS, Peng R, Rasalingam S, Koodali RT (2012) Versatility of heterogeneous photocatalysis: synthetic methodologies epitomizing the role of silica support in TiO2 based mixed oxides. Catal Sci Technol 2(1):737–1766
Bui DN, Kang SZ, Li XQ, Mu J (2011) Effect of Si doping on the photocatalytic activity and photoelectrochemical property of TiO2 nanoparticles. Catal Commun 13:14–17
Zhang YJ, Li XF, Chen D, Ma NH, Hua XS, Wang HW (2009) Si doping effects on the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanotubes film prepared by an anodization process. Scr Mater 60:543–546
Pakdel E, Daoud WA, Wang X (2013) Self-cleaning and superhydrophilic wool by TiO2/SiO2 nanocomposite. Appl Surf Sci 275:397–402
Pandiyaraj KN, Deshmukh RR, Mahendira R, Su PG, Yassitepe E, Shah I, Perni S, Prokopovich P, Nadagoud MN (2014) Influence of operating parameters on surface properties of RF glow discharge oxygen plasma treated TiO2/PET film for biomedical application. Mater Sci Eng C 36:309–319
Park KH, Dhayal M (2009) High efficiency solar cell based on dye sensitized plasma treated nano-structured TiO2 films. Electrochem Commun 11:75–79
Rungjaroentawon N, Onsuratoom S, Chavade S (2012) Hydrogen production from water splitting under visible light irradiation using sensitized mesoporous-assembled TiO2 and SiO2 mixed oxide photocatalysts. Int J Hydrogen Energy 37:11061–11071
Zhang LW , Dillert R, Bahnemann D, Vormoor M (2012) Photo-induced hydrophilicity and self-cleaning: models and reality. Energy Environ Sci 5:7491–7505
Bet-moushoul E, Mansourpanah Y, Farhadi K, Tabatabaei M (2016) TiO2 nanocomposite based polymeric membranes: a review on performance improvement for various applications in chemical engineering processes. Chem Eng J 283:29–46
Ge XY, Xia YQ, Cao ZF (2015) Tribological properties and insulation effect of nanometer TiO2 and nanometer SiO2 as additives in grease. Tribol Int 92:454–461
Hsiung TL, Wang HP, Wang HC (2006) XANES studies of photocatalytic active species in nano TiO2–SiO2. Radiat Phys Chem 75:2042–2045
Methaapanon R, Bent SF (2010) Comparative study of titanium dioxide atomic layer deposition on silicon dioxide and hydrogen-terminated silicon. J Phys Chem C 114:10498–10504
Ren CJ, Qiu W, Chen YQ (2013) Physicchemical properties and photocatalytic activity of the TiO2/SiO2 prepared by precipitation method. Sep Purif Technol 107:264–272
van Grieken R, Aguado J, López-Muñoz MJ et al (2002) Synthesis of size-controlled silica-supported TiO2 photocatalysts. J Photoch Photobio A 148:315–322
Shao PH, Tian JY, Zhao ZW, Shi W, Gao S, Cui F (2015) Amorphous TiO2 doped with carbon for visible light photodegradation of rhodamine B and 4-chlorophenol. Appl Surf Sci 324:35–43
Lázár I, Kalmár J, Peter A, Szilágyi A, Győri E, Ditrói T, Fábián I (2015) Photocatalytic performance of highly amorphous titania–silica aerogels with mesopores: the adverse effect of the in situ adsorption of some organic substrates during photodegradation. Appl Surf Sci 356:521–531
Holtzinger C, Rapenne L, Chaudoue¨t P, Berthome G, Langlet M (2012) Thickness effects in naturally superhydrophilic TiO2–SiO2 nanocomposite films deposited via a multilayer sol–gel route. J Sol Gel Sci Technol 64:465–479
Wang LY, Sun YP, Xu BS (2007) Comparison study on the microstructure of nanocrystalline TiO2 in different Ti–Si binary oxides. J Mater Sci Technol 23:604–610
Zhuo ZJ (2013) The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and its applications. China Petrochemical Press, Bejing
Arranz A, Palacio C (2007) Nanoscale reactive ion beam mixing of Ti/Si and Si/Ti interfaces. Thin Solid Films 515:3426–3433
He CX, Tian BZ, Zhang JL (2010) Thermally stable SiO2-doped mesoporousanatase TiO2 with large surface area and excellent photocatalytic activity. J Colloid Interf Sci 344:382–389
Haapanen J, Aromaa M, Teisala H, Tuominen M, Stepien M, Saarinen JJ, Heikkilä M, Toivakkd M, Kuusipalo J, Makel JM (2015) Binary TiO2/SiO2 nanoparticle coating for controlling the wetting properties of materials of paperboard. Mater Chem Phys 149–150:230–237
Pulsipher DJV, Fisher ER (2009) O2 plasma treatment of mesoporous and compact TiO2 photovoltaic films: revealing and eliminating effects of Si incorporation. Surf Coat Tech 203:2236–2242
Kumar PM, Badrinarayanan S, Sastry M (2000) Nanocrystalline TiO2 studied by optical, FTIR and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy: correlation to presence of surface states. Thin Solid Films 358:122–130
Yamashita H, Honda M, Harada M, Ichihashi Y, Anpo M (1998) Preparation of titanium oxide photocatalysts anchored on porous silica glass by a metal ion-implantation method and their photocatalytic reactivities for the degradation of 2-propanol diluted in water. J Phys Chem B 102:10707–10711
Sun DH, Huang Y, Han B, Yang GY (2006) Ti–Si mixed oxides prepared by polymer in situ Sol–Gel chemistry with the aid of CO2. Langmuir 22:4793–4798
Iatsunskyi I, Kempiński M, Nowaczyk G, Jancelewicz M, Pavlenko M, Zaeski K, Jurga S (2015) Structural and XPS studies of PSi/TiO2 nanocomposites prepared by ALD and Ag-assisted chemical etching. Appl Surf Sci 347:777–783
Wang LY, Sun YP, Xu BS (2008) Surface chemical structure of titania–silica nanocomposite powder. Chin Sci Bull 53:2964–2972
Jiang ZL, Dai X, Middleton H (2011) Effect of silicon on corrosion resistance of Ti–Si alloys. Mat Sci Eng B 176:79–86
Leshuk T, Parviz R, Everett P, Krishnakumar H, Varin RA, Frank Gu (2013) Photocatalytic activity of hydrogenated TiO2. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:1892–1895
Permpoon S, Houmard M, Riassetto D, Rapenne L, Berthomé G, Baroux B, Joud JC, Langlet M (2008) Natural and persistent superhydrophilicity of SiO2/TiO2 and TiO2/SiO2 bi-layer films. Thin Solid Films 516:957–966
Biesinger MC, Lau LWM, Gerson AR, Smart RSC (2010) Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Sc, Ti, V, Cu and Zn. Appl Surf Sci 257:887–898
Chenakin SP, Melaet G, Szukiewicz R, Kruse N (2014) XPS study of the surface chemical state of a Pd/(SiO2 + TiO2) catalyst after methane oxidation and SO2 treatment. J Catal 312:1–11
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Langfang Municipal Project (201011027) and Key Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (21136001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Liu, J., Meng, L. et al. Comparison study on surface depth distribution of chemical species of different nanocomposite Ti–Si binary oxides. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 80, 142–151 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-4048-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-4048-6