Abstract
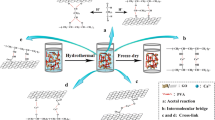
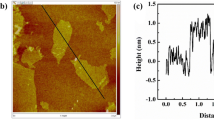
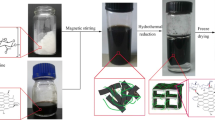
Ultra-low-density graphene nanosheet (GNS)/carbon composite aerogels (CAs) were prepared via GO (graphene oxide)/RF (resorcinol–formaldehyde) aerogel composite, supercritical fluid drying, and carbonization. Graphene oxide was found to act as an efficient anti-shrinkage additive in the carbonization process, making the linear shrinkage ratios decrease from 78 % to only 10 % (25 % GO content). The density of the aerogels thus decreases from 115 to 24.4 mg cm−3. 25 % GO-composited aerogel exhibits over two times modulus increase and over 11 times specific modulus increase in comparison with pure carbon aerogel. The microstructure results show that GO is fully cross-linked with RF polymers, makes the reaction more sufficient and ultimately strengthens the nanostructure to withstand the damage of carbonization. The resultant composite carbon aerogels exhibited super high specific surface area (as high as 2899 m2 g−1), good mechanical property, and high adsorption capacity of 403 mg g−1 for methylene blue.
Graphical Abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Du A, Zhou B, Zhang Z, Shen J (2013) A special material or a new state of matter: a review and reconsideration of the aerogel. Materials 6(3):941–968
Lu X, Arduini-Schuster M, Kuhn J, Nilsson O, Fricke J, Pekala R (1992) Thermal conductivity of monolithic organic aerogels. Science 255(5047):971–972
Pröbstle H, Wiener M, Fricke J (2003) Carbon aerogels for electrochemical double layer capacitors. J Porous Mater 10(4):213–222
Moreno-Castilla C, Maldonado-Hódar F (2005) Carbon aerogels for catalysis applications: an overview. Carbon 43(3):455–465
Pekala R, Coronado P, Calef D (1994) Carbon aerogels for hydrogen storage. Lawrence Livermore National Lab, CA
Yang W, Wu D, Fu R (2008) Effect of surface chemistry on the adsorption of basic dyes on carbon aerogels. Colloids Surf A 312(2):118–124
Wu X, Wu D, Fu R (2007) Studies on the adsorption of reactive brilliant red X-3B dye on organic and carbon aerogels. J Hazard Mater 147(3):1028–1036
Pekala RW, Alviso CT (1992) Carbon aerogels and xerogels. Lawrence Livermore National Lab, CA
Al-Muhtaseb SA, Ritter JA (2003) Preparation and properties of resorcinol–formaldehyde organic and carbon gels. Adv Mater 15(2):101–114
Mulik S, Sotiriou-Leventis C, Leventis N (2007) Time-efficient acid-catalyzed synthesis of resorcinol—formaldehyde aerogels. Chem Mater 19(25):6138–6144
Hanzawa Y, Kaneko K, Yoshizawa N, Pekala R, Dresselhaus M (1998) The pore structure determination of carbon aerogels. Adsorption 4(3–4):187–195
Feng J, Zhang C, Feng J, Jiang Y, Zhao N (2011) Carbon aerogel composites prepared by ambient drying and using oxidized polyacrylonitrile fibers as reinforcements. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3(12):4796–4803
Fu R, Zheng B, Liu J, Weiss S, Ying JY, Dresselhaus MS, Dresselhaus G, Satcher JH, Baumann TF (2003) Fabrication of activated carbon fibers/carbon aerogels composites by gelation and supercritical drying in isopropanol. J Mater Res 18(12):2765–2773
Liang J, Huang Y, Zhang L, Wang Y, Ma Y, Guo T, Chen Y (2009) Molecular-level dispersion of graphene into poly (vinyl alcohol) and effective reinforcement of their nanocomposites. Adv Funct Mater 19(14):2297–2302
Podsiadlo P, Kaushik AK, Arruda EM, Waas AM, Shim BS, Xu J, Nandivada H, Pumplin BG, Lahann J, Ramamoorthy A (2007) Ultrastrong and stiff layered polymer nanocomposites. Science 318(5847):80–83
Stankovich S, Dikin DA, Piner RD, Kohlhaas KA, Kleinhammes A, Jia Y, Wu Y, Nguyen ST, Ruoff RS (2007) Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. Carbon 45(7):1558–1565
Fukushima H, Drzal L Graphite nanoplatelets as reinforcements for polymers: structural and electrical properties. In: Proceedings of the 17th annual conference of the american society for composites, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, 2002
Geim AK (2009) Graphene: status and prospects. Science 324(5934):1530–1534
Park H, Seo J, Hwang S, Rhym Y-M, Baeck SH, Shim SE (2014) Influence of graphene nanoplatelets content on the structure and properties of macroporous carbon foams prepared by organic colloidal templates. J Mater Sci 49(5):2063–2069
Guo K, Song H, Chen X, Du X, Zhong L (2014) Graphene oxide as an anti-shrinkage additive for resorcinol–formaldehyde composite aerogels. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16(23):11603–11608
Guo K, Hu Z, Song H, Du X, Zhong L, Chen X (2015) Low-density graphene/carbon composite aerogels prepared at ambient pressure with high mechanical strength and low thermal conductivity. RSC Adv 5(7):5197–5204
Hummers WS Jr, Offeman RE (1958) Preparation of graphitic oxide. J Am Chem Soc 80(6):1339
Paredes J, Villar-Rodil S, Martinez-Alonso A, Tascon J (2008) Graphene oxide dispersions in organic solvents. Langmuir 24(19):10560–10564
Marcano DC, Kosynkin DV, Berlin JM, Sinitskii A, Sun Z, Slesarev A, Alemany LB, Lu W, Tour JM (2010) Improved synthesis of graphene oxide. ACS Nano 4(8):4806–4814
Hontoria-Lucas C, Lopez-Peinado A, López-González JdD, Rojas-Cervantes M, Martin-Aranda R (1995) Study of oxygen-containing groups in a series of graphite oxides: physical and chemical characterization. Carbon 33(11):1585–1592
Xu Y, Bai H, Lu G, Li C, Shi G (2008) Flexible graphene films via the filtration of water-soluble noncovalent functionalized graphene sheets. J Am Chem Soc 130(18):5856–5857
Xiao G-N, Man S-Q (2007) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering of methylene blue adsorbed on cap-shaped silver nanoparticles. Chem Phys Lett 447(4):305–309
Zhang J, Cao Y, Feng J, Wu P (2012) Graphene-oxide-sheet-induced gelation of cellulose and promoted mechanical properties of composite aerogels. J Phys Chem C 116(14):8063–8068
Lerf A, He H, Riedl T, Forster M, Klinowski J (1997) 13 C and 1 H MAS NMR studies of graphite oxide and its chemically modified derivatives. Solid State Ion 101:857–862
Hwang S-W, Hyun S-H (2004) Capacitance control of carbon aerogel electrodes. J Non-Cryst Solids 347(1):238–245
Sadezky A, Muckenhuber H, Grothe H, Niessner R, Pöschl U (2005) Raman microspectroscopy of soot and related carbonaceous materials: spectral analysis and structural information. Carbon 43(8):1731–1742
Zhu Y, Murali S, Cai W, Li X, Suk JW, Potts JR, Ruoff RS (2010) Graphene and graphene oxide: synthesis, properties, and applications. Adv Mater 22(35):3906–3924
Hu H, Wang X, Wang J, Wan L, Liu F, Zheng H, Chen R, Xu C (2010) Preparation and properties of graphene nanosheets–polystyrene nanocomposites via in situ emulsion polymerization. Chem Phys Lett 484(4):247–253
Zhou J, Song H, Ma L, Chen X (2011) Magnetite/graphene nanosheet composites: interfacial interaction and its impact on the durable high-rate performance in lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv 1(5):782–791
Pekala R, Schaefer D (1993) Structure of organic aerogels. 1. morphology and scaling. Macromolecules 26(20):5487–5493
Brunauer S, Deming LS, Deming WE, Teller E (1940) On a theory of the van der Waals adsorption of gases. J Am Chem Soc 62(7):1723–1732
Bi Y, Ren H, Chen B, Chen G, Mei Y, Zhang L (2012) Synthesis monolithic copper-based aerogel with polyacrylic acid as template. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 63(1):140–145
Gibson LJ, Ashby MF (1997) Cellular solids: structure and properties. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Hayase G, Kanamori K, Fukuchi M, Kaji H, Nakanishi K (2013) Facile synthesis of marshmallow-like macroporous gels usable under harsh conditions for the separation of oil and water. Angew Chem Int Ed 52(7):1986–1989
Guo Y, Yang S, Fu W, Qi J, Li R, Wang Z, Xu H (2003) Adsorption of malachite green on micro-and mesoporous rice husk-based active carbon. Dyes Pigm 56(3):219–229
Namasivayam C, Kavitha D (2002) Removal of Congo Red from water by adsorption onto activated carbon prepared from coir pith, an agricultural solid waste. Dyes Pigm 54(1):47–58
Malik PK (2003) Use of activated carbons prepared from sawdust and rice-husk for adsorption of acid dyes: a case study of Acid Yellow 36. Dyes Pigm 56(3):239–249
Dubinin M, Stoeckli H (1980) Homogeneous and heterogeneous micropore structures in carbonaceous adsorbents. J Colloid Interface Sci 75(1):34–42
Avom J, Mbadcam JK, Noubactep C, Germain P (1997) Adsorption of methylene blue from an aqueous solution on to activated carbons from palm-tree cobs. Carbon 35(3):365–369
Cousins HJ, Gardner PJ, Matthews SJ (1992) Microcalorimetric studies of solution adsorption by activated carbons. Carbon 30(1):17–20
Hang PT, Brindley G (1970) Methylene blue absorption by clay minerals. Determination of surface areas and cation exchange capacities (clay-organic studies XVIII). Clays Clay Miner 18(4):203–212
Lin Y-R, Teng H (2002) Mesoporous carbons from waste tire char and their application in wastewater discoloration. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 54(1):167–174
Yang N, Zhu S, Zhang D, Xu S (2008) Synthesis and properties of magnetic Fe 3 O 4-activated carbon nanocomposite particles for dye removal. Mater Lett 62(4):645–647
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51172163), National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (2013AA031801), and National Key Technology R&D Program of China (2013BAJ01B01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, W., Du, A., Zhou, B. et al. Ultra-low-density GNS/CA composite aerogels with ultra-high specific surface for dye removal. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 80, 68–76 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-4047-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-4047-7