Abstract
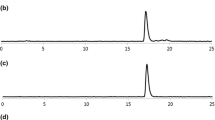
The purpose of this study is to synthesize 123I-labeled hesperetin and to investigate its in vivo behavior. The optimized labeling condition provided two isomers of 123I-labeled hesperetin with high radiochemical yields and radiochemical purities. Both 123I-labeled products were orally administered to normal ICR mice, and the initial result showed that most of 123I activity was detected in the stomach and the intestines. A part of 123I-labeled hesperetin was absorbed from the small intestine to bloodstream and then it was distributed in normal organs. The results in the present study provided an efficient radiolabeling method of flavonoid and quantitative organ distribution of orally administered hesperetin.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tomás-Barberán FA, Clifford MN (2000) Flavanones, chalcones and dihydrochalcones—nature, occurrence and dietary burden. J Sci Food Agric 80(7):1073–1080
Manthey JA, Grohmann K (1996) Concentrations of hesperidin and other orange peel flavonoids in citrus processing byproducts. J Agric Food Chem 44(3):811–814
Shin KC, Nam HK, Oh DK (2013) Hydrolysis of flavanone glycosides by β-glucosidase from Pyrococcus furiosus and its application to the production of flavanone aglycones from citrus extracts. J Agric Food Chem 61(47):11532–11540
Yang HL, Chen SC, Kumar KJS, Yu KN, Chao PDL, Tsai SY, Hou YC, Hseu YC (2012) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential of hesperetin metabolites obtained from hesperetin-administered rat serum: an ex vivo approach. J Agric Food Chem 60(1):522–532
Iio A, Ohguchi K, Iinuma M, Nozawa Y, Ito M (2012) Hesperetin upregulates ABCA1 expression and promotes cholesterol efflux from THP-1 macrophages. J Nat Prod 75(4):563–566
Ruen-ngam D, Quitain AT, Sasaki M, Goto M (2012) Hydrothermal hydrolysis of hesperidin into more valuable compounds under supercritical carbon dioxide condition. Ind Eng Chem Res 51(42):13545–13551
Kanaza FI, Bounartzi MI, Georgarakis M, Niopas I (2007) Pharmacokinetics of the citrus flavanone aglycones hesperetin and naringenin after single oral administration in human subjects. Eur J Clin Nutr 61(4):472–477
Yáñez JA, Remsberg CM, Miranda ND, Vega-Villa KR, Andrew PK, Davies NM (2008) Pharmacokinetics of selected chiral flavonoids: hesperetin, naringenin and eriodictyol in rats and their content in fruit juices. Biopharm Drug Dispos 29(2):63–82
Maiti K, Mukherjee K, Murugan V, Saha BP, Mukherjee PK (2009) Exploring the effect of hesperetin-HSPC complex—a novel drug delivery system on the in vivo release, therapeutic efficacy and pharmacokinetics. AAPS PharmSciTech 10(3):943–950
Srirangam R, Hippalgaonkar K, Avula B, Khan IA, Majumdar S (2012) Evaluation of the intravenous and topical routes for ocular delivery of hesperidin and hesperetin. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther 28(6):618–627
Sun H, Dong T, Zhang A, Yang J, Yan G, Sakurai T, Wu X, Han Y, Wang X (2013) Pharmacokinetics of hesperetin and naringenin in the Zhi Zhu Wan, a traditional Chinese medicinal formulae, and its pharmacodynamics study. Phytother Res 27(9):1345–1351
Barolli MG, Pomilio AB (1997) Synthesis of [131-I]-iodinated quercetin. J Label Compd Radiopharm 39(11):927–933
Kim SK, Ham I, Bu Y, Kim H, Cho JH, Choi H (2008) Study on the attributive channel theory of herbal medicine by the pharmacodynamics research of I-131 labelled hesperetin. Korea J Herbol 23(1):117–125
Seyitoglu B, Lambrecht FY, Durkan K (2009) Labeling of apigenin with 131I and bioactivity of 131I-apigenin in male and female rats. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 279(3):867–873
Lambrecht FY, Yilmaz O, Bayrak E, Kocagozoglu G, Durkan K (2010) Could be radiolabeled flavonoid used to evaluate infection? J Radioanal Nucl Chem 283(2):503–506
Diao Y, Zhao W, Li Y, Liao L, Wang O, Liu J, Zhao X, Yu C, Cui Z (2014) Radiolabeling of EGCG with 125I and its biodistribution in mice. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 301(1):167–173
Masumoto H, Ikoma Y, Sugiura M, Yano M, Hasegawa Y (2004) Identification and quantification of the conjugated metabolites derived from orally administered hesperidin in rat plasma. J Agric Food Chem 52(21):6653–6659
Mullen W, Archeveque MA, Edwards CA, Matsumoto H, Crozier A (2008) Bioavailability and metabolism of orange juice flavanones in humans: impact of a full-fat yogurt. J Agric Food Chem 56(23):11157–11164
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea grant funded by the Korea government (Grant Nos. 2012M2B2B1055245 and 2012M2A2A6011335) and Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeon, J., Ma, SY., Choi, D.S. et al. Radiosynthesis of 123I-labeled hesperetin for biodistribution study of orally administered hesperetin. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 306, 437–443 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4093-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4093-6