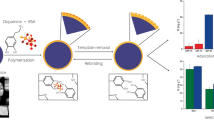
Abstract
Bovine serum albumin imprinted polyethylene glycol 600 (PEG600) grafted Calcium alginate (CaA) hydrogel microspheres were prepared and characterized. The adsorption and recognition properties of PEG600 grafted calcium alginate (CaA-g-PEG600) microspheres were evaluated and the results showed that the crosslinking structure of CaA-g-PEG600 microspheres exerted an obvious effect on the adsorption capacity and imprinting properties for bovine serum albumin. The adsorption isotherms and recognition properties indicated that the imprinted modified microspheres had excellent rebinding affinity toward target proteins and the imprinting efficiency varied according to PEG600 grafting degree. The adsorption capacity and the imprinting factor were 5.5 mg g−1 and 3.6, respectively. Adsorption kinetics of CaA-g-PEG600 microspheres in accordance with the molecular weight between crosslinks (Mc) was investigated and the structural influence on protein selective rebinding was discussed. Furthermore, the binary solution separation performance of CaA-g-PEG600 microspheres with different Mc was investigated by selective binding bovine serum albumin from protein mixture solution.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li X, Zhou J, Tian L, Li W, Zafar A, Nisar A, Zhang B, Zhang H, Zhang Q (2016) Effect of crosslinking degree and thickness of thermosensitive imprinted layers on recognition and elution efficiency of protein imprinted magnetic microspheres. Sensors Actuators B 225:436–445
Sunayama H, Ooya T, Takeuchi T (2014) Fluorescent protein-imprinted polymers capable of signal transduction of specific binding events prepared by a site-directed two-step post-imprinting modification. Chem Commun 50:1347–1349
Haupt K, Linares AV, Bompart M, Bui BT (2012) Molecularly imprinted polymers. Top Curr Chem 325:1–28
Moreira FTC, Sharma S, Dutra RAF, Noronha JPC, Cass AEG, Sales MGF (2014) Protein-responsive polymers for point-of-care detection of cardiac biomarker. Sensors Actuators B Chem 196:123–132
Mahon CS, Fulton DA (2014) Mimicking nature with synthetic macromolecules capable of recognition. J Nat Chem 6:665–672
Schirhagl R (2014) Bioapplications for molecularly imprinted polymers. J Anal Chem 86:250–261
Li D, He X, Chen Y, Li W, Zhang Y (2013) Novel hybrid structure silica/cdte/molecularly imprinted polymer: synthesis, specific recognition, and quantitative fluorescence detection of bovine hemoglobin. J ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:12609–12616
Yang C, Yan X, Guo H, Fu G (2016) Synthesis of surface protein-imprinted nanoparticles endowed with reversible physical cross-links. Biosens Bioelectron 75:129–135
Li L, Lu Y, Bie Z, Chen H, Liu Z (2013) Photolithographic boronate affinity molecular imprinting: a general and facile approach for glycoprotein imprinting. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:7451–7454
Kryscio DR, Peppas NA (2012) Critical review and perspective of macromolecularly imprinted polymers. Acta Biomater 8:461–473
Verheyen E, Schillemans JP, van Wijk M, Demeniex MA, Hennink WE, van Nostrum CF (2011) Challenges for the effective molecular imprinting of proteins. Biomaterials 32:3008–3020
Whitcombe MJ, Chianella I, Larcombe L, Piletsky SA, Noble J, Porter R, Horgan A (2011) The rational development of molecularly imprinted polymer-based sensors for protein detection. Chem Soc Rev 40:1547–1571
Zayats M, Kanwar M, Ostermeier M, Searson PC (2011) Tuning protein recognition at the molecular level. Macromolecules 44:3966–3972
Zdyrko B, Hoy O, Luzinov I (2009) Toward protein imprinting with polymer brushes. Biointerphases 4:FA17–FA21
Asliyuce S, Uzun L, Rad AY, Unal S, Say R, Denizli AJ (2012) Molecular imprinting based composite cryogel membranes for purification of anti-hepatitis B surface antibody by fast protein liquid chromatography. Chromatogr B 889:95–102
Feng H, Mao X, Chu B, Xie C (2014) Influence of gelling properties on protein imprinted agarose gel membrane. J Appl Polym Sci 131:40323
Reddy SM, Hawkins DM, Phan QT, Stevenson D, Warriner K (2013) Protein detection using hydrogel-based molecularly imprinted polymers integrated with dual polarisation interferometry. Sensors Actuators B Chem 176:190–197
Abdulla R, Ravindra PJ (2013) Characterization of cross linked Burkholderia cepacia lipase in alginate and κ-carrageenan hybrid matrix. Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 44:545–551
Zhang F, Cheng G, Ying X (2006) Emulsion and macromolecules templated alginate based polymer microspheres. React Funct Polym 66:712–719
Zeeb B, Saberi AH, Weiss J, McClements DJ (2015) Retention and release of oil-in-water emulsions from filled hydrogel beads composed of calcium alginate: impact of emulsifier type and pH. Soft Matter 11:2228–2236
Popeski-Dimovski R (2015) Work of adhesion between mucin macromolecule and calcium-alginate gels on molecular level. Carbohydr Polym 123:146–149
Lee KY, Mooney DJ (2012) Alginate: properties and biomedical applications. Prog Polym Sci 37:106–126
Herrero EP, Marin Del Valle EM, Peppas NA (2010) Protein imprinting by means of alginate-based polymer microcapsules. Ind Eng Chem Res 49:9811–9814
Kan B, Lin B, Zhao K, Zhang X, Feng L, Wei J, Fan Y (2014) Imprinting of bovine serum albumin in a nonwoven polypropylene membrane supported polyacrylamide/calcium alginate interpenetrating polymer network hydrogel. RSC Adv 4:55846–55852
Ying X, Qi L, Li X, Zhang W, Cheng G (2013) Stimuli-responsive recognition of BSA-imprinted poly vinyl acetate grafted calcium alginate Core-Shell hydrogel microspheres. J Appl Polym Sci 127:3898–3909
Zhao K, Cheng G, Huang J, Ying X (2008) Rebinding and recognition properties of protein-macromolecularly imprinted calcium phosphate/alginate hybrid polymer microspheres. React Funct Polym 68:732–741
Zhu D, Chen Z, Zhao K, Kan B, Liu L, Dong X, Wang H, Zhang C, Leng X, Zhang L (2015) Polypropylene non-woven supported fibronectin molecular imprinted calcium alginate/polyacrylamide hydrogel film for cell adhesion. Chin Chem Lett 26:807–810
Li L, Ying X, Liu J, Li X, Zhang W (2015) Protein imprinted polyurethane-grafted calcium alginate hydrogel microspheres. J Appl Polym Sci 132:42140
Zhao K, Lin B, Cui W, Feng L, Chen T, Wei J (2014) Preparation and adsorption of bovine serum albumin-imprinted polyacrylamide hydrogel membrane grafted on non-woven polypropylene. Talanta 121:256–262
Liu J, Ying X, Wang H, Li X, Zhang W (2016) BSA imprinted polyethylene glycol grafted calcium alginate hydrogel microspheres. J Appl Polym Sci 133:43617
Brandrup J, Immergut EH (1975) Polymer handbook, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Fu J, Chen Z, Wang M, Liu S, Zhang J, Zhang J, Han R, Xu Q (2015) Adsorption of methylene blue by a high-efficiency adsorbent (polydopamine microspheres): kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamics and mechanism analysis. Chem Eng J 259:53–61
Guo T, Xia Y, Hao G, Song M, Zhang B (2004) Adsorptive separation of hemoglobin bymolecularly imprinted chitosan beads. Biomaterials 25:5905–5912
Pang X, Cheng G, Lu S, Tang J (2006) Synthesis of polyacrylamide gel beads with electrostatic functional groups for the molecular imprinting of bovine serum albumin. Anal Bioanal Chem 384:225–230
Pang X, Cheng G, Li R, Lu S, Zhang Y (2005) Bovine serum albumin–imprinted polyacrylamide gel beads prepared via inverse-phase seed suspension polymerization. Anal Chim Acta 550:13–17
Abd El-Ghaffar MA, Hashem MS (2013) Calcium alginate beads encapsulated PMMA-g-CS nano-particles for α-chymotrypsin immobilization. Carbohydr Polym 92:2095–2102
Wang J, Ying X, Li X, Zhang W (2014) Preparation, characterization and swelling behaviors of polyurethane-grafted calcium alginate hydrogels. Mater Lett 126:263–266
Samiullah MH, Reichert D, Zinkevich T, Kressler J (2013) NMR characterization of PEG networks synthesized by CuAAC using reactive oligomers. Macromolecules 46:6922–6930
Li L, Ying X, Liu J, Li X, Zhang W (2015) Molecularly imprinted polyurethane grafted calcium alginate hydrogel with specific recognition for proteins. Mater Lett 143:248–251
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the support of 2017 College Joint Funded Project of Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province, the China Scholarship Council, Fuzhou University Science Technology Development Fund (2014-XQ-23) and Fuzhou University Postdoctoral Station Fund (XDJ201206).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Ying, X., Liu, J. et al. Specific rebinding of protein imprinted polyethylene glycol grafted calcium alginate hydrogel with different crosslinking degree. J Polym Res 24, 93 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-017-1256-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-017-1256-x