Abstract
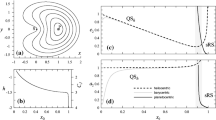
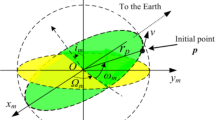
The problem of identifying orbits that enclose both the Earth and the Moon in a predictable way has theoretical relevance as well as practical implications. In the context of the restricted three-body problem with primaries in circular orbits, periodic trajectories exist and have the property that a third body (e.g. a spacecraft) can describe them indefinitely. Several approaches have been employed in the past for the purpose of identifying similar orbits. In this work the theorem of image trajectories, proven five decades ago, is employed for determining periodic image trajectories in Earth–Moon space. These trajectories exhibit two fundamental features: (i) counterclockwise departure from a perigee on the far side of the Earth, and (ii) counterclockwise arrival to a periselenum on the far side of the Moon. An extensive, systematic numerical search is performed, with the use of a modified Poincaré map, in conjunction with a numerical refinement process, and leads to a variety of periodic orbits, with various interesting features for possible future lunar missions.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Broucke, R.A.: Periodic orbits in the restricted three-body problem with Earth–Moon masses. NASA TR 32-1168 (1968)
Farquhar, R.W., Kamel, A.A.: Quasi-periodic orbits about the translunar libration point. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 7(4), 458–473 (1973)
Richardson, D.L.: Analytic construction of periodic orbits about the collinear points. Celest. Mech. 22, 241–253 (1980)
Gomez, G., Marcote, M.: High-order analytical solutions of Hill’s equations. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 94(2), 197–211 (2006)
Howell, K.C., Pernicka, H.J.: Numerical determination of Lissajous trajectories in the restricted three-body problem. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 41(1–4), 107–124 (1987)
Gomez, G., Masdemont, J., Simo, C.: Quasihalo orbits associated with libration points. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 46(2), 135–176 (1998)
Guibout, V., Scheeres, D.: Periodic orbits from generating functions. Adv. Astronaut. Sci. 116(2), 1029–1048 (2004)
Martin, C., Conway, B.A., Ibanez, P.: Optimal low-thrust trajectories to the interior Earth–Moon Lagrange point. In: Perozzi, E., Ferraz-Mello, S. (eds.) Space Manifold Dynamics, pp. 161–184. Springer, New York (2010)
Pontani, M., Martin, C., Conway, B.A.: New numerical methods for determining periodic orbits in the circular restricted three-body problem. In: Proceedings of the 61st International Astronautical Congress, Prague (2010)
Miele, A.: Theorem of image trajectories in Earth–Moon space. Acta Astron. 6(5), 225–232 (1960)
Miele, A., Mancuso, S.: Optimal trajectories for Earth–Moon–Earth flight. Acta Astron. 49(2), 59–71 (2001)
Roy, A.E.: Orbital Motion. IOP Publishing Ltd., London (2005)
Szebehely, V.: Theory of Orbits. The Restricted Problem of Three Bodies. Academic Press, New York (1967)
Miele, A.: Revisit of the theorem of image trajectories in Earth–Moon space. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 147(3), 483–490 (2010)
Schwaniger, A.J.: Trajectories in the Earth–Moon space with symmetric free-return properties. NASA Technical Note D-1833 (1963)
Pontani, M., Conway, B.A.: Swarming theory applied to space trajectory optimization. In: Conway, B.A. (ed.) Spacecraft Trajectory Optimization, pp. 263–293. Cambridge University Press, New York (2010)
Pontani, M., Conway, B.A.: Optimal space trajectories via particle swarm technique. Adv. Astronaut. Sci. 136, 53–72 (2010)
Pontani, M., Miele, A.: Periodic image trajectories in Earth–Moon space. Aero-astronautics report no. 369, Rice University (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pontani, M., Miele, A. Periodic Image Trajectories in Earth–Moon Space. J Optim Theory Appl 157, 866–887 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10957-012-0220-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10957-012-0220-5