Abstract
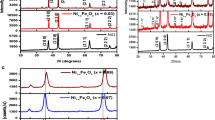
Nanocrystalline ε-Fe3N and γ′-Ni x Fe4−xN (0.2 ≤ x ≤ 0.8) nitride materials are synthesized in pure phase via sol-gel-mediated oxide precursors. The materials are characterized using XRD, SEM (EDX), and magnetic measurements. ε-Fe3N and γ′-Ni x Fe4−x N (0.2 ≤ x ≤ 0.8) materials crystallize in hexagonal and cubic structures, respectively. The lattice parameters are estimated to be a = 4.7812(36) Å and c = 4.4232(31) Å for ε-Fe3N and in the range of 3.7922(10)–3.7957(3) Å for various γ′-Ni x Fe4 −xN (0.2 ≤ x ≤ 0.8) materials. The values of the lattice parameters show increasing trend up to x = 0.6, showing a peak, and thereafter decreases with the increase in Ni weight percent in γ′-Ni x Fe4−xN (0.2 ≤ x ≤ 0.8) materials. The average crystallite sizes are in the range of 31–54 nm and confirm the nanocrystalline nature of the materials. The SEM particle sizes are in the range of 153(7)–250(14) nm. For pure ε-Fe3N, the values of saturation magnetization (M s) and coercivity (H c) are 12 emu/g and 225 Oe, respectively. With the progressive substitution of Ni atoms, hexagonal (ε-phase) changes to cubic (γ′-phase) at the same reaction temperature, which is evident from the increase in M s and H c values, i.e., in the range of 144–181 emu/g and 76–109 Oe, respectively, for γ′-Ni x Fe4 −xN (0.2 ≤ x ≤ 0.8) compounds. The values of the saturation magnetization for γ′-Ni x Fe4 −xN (0.2 ≤ x ≤ 0.8) are found to increase with the increase in Ni content in the materials up to the value of x = 0.6 and decrease thereafter. These results have been interpreted in terms of size and shape effects in nanomaterials including lattice strain and surface effects.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Theerthagiri, J., Dalavi, S. B., Manivel Raja, M., Panda, R. N.: Magnetic properties of nanocrystalline ε-Fe3N and Co 4N phases synthesized by newer precursor route. Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 4444–4448 (2013)
Panda, R.N., Gajbhiye, N. S.: Mossbauer and magnetic studies of nanocrystalline γ′-Fe4−xNi x N (0.2 ≤ x ≤0.8) compounds. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 195, 396–495 (1999)
Tasaki, A., Tagawa, K., Kita, E., Harada, S., Kusunose, T.: Recording tapes using iron nitride fine powder. IEEE Trans. Magn. 17, 3026–3028 (1981)
Andrimandroso, D., Fefilatiev, L., Demazeau, G., Fournes, L., Pouchard, M.: Mössbauer resonance studies on Sn substituted Fe4N. Mater. Res. Bull. 19, 1187–1194 (1984)
Loloee, R.: Epitaxial Ni3FeN thin films: a candidate for spintronic devices and magnetic sensors. J. appl. Phys. 112, 023902(1–6) (2012)
Zhang, P., Wang, X., Wang, W., Lei, X., Yin, W., Yang, H.: The structure and magnetic properties of Fe3N as photo-catalyst applied in hydrogen generation induced by visible light. RSC Adv. (2015). doi:. to be published
Shoji, H., Nashi, H., Eguchi, K., Takahashi, M.: An experimental trial for the synthesis of α ″-(Fe100−x Co x) 16 N 2(x =0-30) martensite films by reactive sputtering. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 162, 202–210 (1996)
Panda, R.N., Gajbhiye, N. S.: Magnetic properties of nanocrystalline γ′–Fe4 N and ε–Fe3N synthesized by citrate route. IEEE Trans. Magn. 30, 542–548 (1998)
Suzuki, K., Morita, H., Kaneko, T., Yoshida, H., Fujimori, H.: Crystal structure and magnetic properties of the compound FeN. J. Alloys Compd. 201, 11–16 (1993)
Panda, R.N., Gajbhiye, N. S.: Magnetic properties of nanocrystalline γ-Fe-Ni-N nitride systems. J. appl. Phys. 86, 3295–3302 (1999)
Xue, D., Li, F., Yang, J., Kong, Y., Gao, M.: Effects of substitutional atoms on the properties of γ′-(Fe1−x-TM x)4N (TM = Co, Ni) compounds. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 172, 165–172 (1997)
Siberchicot, B., Matar, S.F., Fournes, L., Demazeau, G., Hagenmuller, P.: Influence of the substitution of manganese for iron in the Fe4N lattice on particle formation and magnetic properties. J. Solid State Chem. 84, 10–15 (1990)
Diao, X.G., Scorzelli, R. B., Rechenberg, H.: R.: 57Fe Mossbauer study of perovskite-type Fe-Ni nitrides γ′-(Fe1−xNi x )4N (0 ≤x≤ 0.8). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 218, 81–90 (2000)
Mi, W.B., Guo, Z.B., Feng, X.P., Bai, H.L.: Reactively sputtered epitaxial γ′-Fe4N films: surface morphology, microstructure, magnetic and electrical transport properties. Acta Mater. 61, 6387–6395 (2013)
Kurian, S., Bhattacharya, S., Desimoni, J., Peltzer, E.L., Blanca, Y., Rebaza, A. V. G, Gajbhiye, N.S.: Investigation of γ′-Fe4N-GaN nanocomposites: structural and magnetic characterization, Mossbauer spectroscopy and ab initio calculations. J. Phys. Chem. C. 114, 17542–17549 (2010)
Wang, L.L., Zheng, W.T., Ana, T., Mab, N., Gong, J.: Effect of Ni concentration on the structure and magnetic properties for nanocrystalline Fe–Ni–N thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 495, 265–267 (2010)
Panda, R. N., Kaskel, S.: Synthesis and characterization of high surface area molybdenum nitride. J. mater. Sci. 41, 2465–2470 (2006)
Bem, D.S., Zur Loye, H.-C.: Synthesis of the new ternary transition metal nitride FeWN 2 via ammonolysis of a solid state oxide precursor. J. Solid State Chem. 104, 467–469 (1993)
Feng, Y.B.: Magnetic properties of nanometer-sized Fe4N compound. J. appl. Phys. 76, 6594 (1994)
Jack, K.H.: The occurrence and the crystal structure of α ″ – iron nitride, a new type of interstitial alloy formed during the tempering of nitrogen-martensite. Proc. Roy. Soc. (London) A. 208, 216–224 (1951)
Culity, B. D.: Elements of X-ray diffraction. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley (1956)
Gajbhiye, N. S., Bhattacharya, S.: Mossbauer and magnetic studies for the coexistence of ε–Fe3−xNixN and γ′-Fe4−yNiyN phases in Fe-Ni-N nano particles. Indian. J. Pure Appl. Phys. 45, 834–838 (2007)
Gajbhiye, N.S., Panda, R. N., Ningthoujam, R. S., Bhattacharya, S.: Magnetism of nanostructured iron nitride (Fe–N) systems. Phys.stat.sol.(c). 12, 3252–3259 (2004)
Wei, Z., Xia, T., Ma, J., Feng, W., Dai, J., Wang, Q., Yan, P.: Investigation of the lattice expansion for Ni nanoparticles. Mater. Charact. 58, 1019–1024 (2007)
Diehm, P. M., Agoston, P., Albe, K.: Size-dependent lattice expansion in nanoparticles: reality or anomaly? ChemPhysChem 13, 2443–2454 (2012)
Pak, J., Lin, W., Wang, K., Chinchore, A., Shi, M., Ingram, D.C., Smith, A. R.: Growth of epitaxial iron nitride ultrathin film on zinc-blende gallium nitride. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 28, 536–540 (2010)
Mammeri, F.Z., Chekour, L., Rouag, N.: Characterization of nitride thin films using SEM and EDX. Acta. Phys. Pol. A 123, 294–295 (2013)
Liu, J., Meng, X.M., Jiang, Y., Lee, C.S., Bello, I., Lee, S.T.: Gallium nitride nanowires doped with silicon. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 4241–4243 (2003)
Bean, C. P., Jacobs, I. S.: Magnetization of a dilute suspension of a multidomain ferromagnetic. J. Appl. Phys. 31, 1228–1230 (1960)
Morup, S., Brok, E., Frandsen, C.: Spin structures in magnetic nanoparticles. J Nanomaterials. 2013(2013)1–8, Article ID 720629
Hwang, J.H., Dravid, V. P., Teng, M. H., Host, J. J., Elliott, B. R., Johnson, D. L., Mason, T. O.: Magnetic properties of graphitically encapsulated nickel nanocrystals. J. Mater. Res. 12, 1076–1082 (1997)
Li, F., Yang, J., Xue, D., Zhou, R.: Mössbauer study of the (Fe1−xNi x )4N compounds (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.6). Appl. Phys. Lett. 66, 2343–2345 (1995)
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Department of Science and Technology (DST), New Delhi, India. We also express our thanks to Mr. A. Raja, Karunya University, India, for SEM measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, P.P., Raja, M.M. & Panda, R.N. Novel Synthesis and Nanostructure Controlled Magnetic Characteristics of ε-Fe3N and γ′-Ni x Fe4−x N (0.2 ≤ x ≤ 0.8) Nitrides. J Supercond Nov Magn 29, 1347–1356 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-016-3406-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-016-3406-5